NewGL Basic Overview
Objective of New GL
SAP has the following objectives behind the introduction of the New General Ledger:
- Efficiently handle Financial Reporting, according to both local and international accounting principles
- Facilitate increased convergence between financial and management accounting
- Considerably accelerate your period-end closings
- Flexibly perform reporting tasks based on data reconciled in real time
- Anunified accounting structure that combines individual ledgers,cost-of-sales, profit-center-accounting & Consolidation-stagingledgers.
Advantages of New GL
- Introduction and portrayalof new business models within a single solution, thus avoiding separateledgers like Cost of Sales Ledger, Profit Center Ledger, specialpurpose ledger etc.
- Data is stored in a single totals table eliminating data redundancy.
- No need for additional reconciliation activities during closing
- Easyto make adjustments to business specific requirements, such as theintroduction of customer fields as part of flexible reporting.
Why use the NEW GL?
The following table gives the business requirements at the backendwhich prompts the finance department of the comapny to go for NEW GLimplementation.
| S.N | Business Requirements | New GL Functionality |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Reporting as per different GAAP | Concept of multile ledgers- leading and non leading ledgers |
| 2 | Unified Mangement & legal reporting | Profit Centre integrated with the New ledger |
| 3 | Requirement of segmental reporting(in line with US GAAP) | Segment can be defined as an enterprise element |
| 4 | Financial statement below company code level | Document spilt functionality |
| 5 | Reporting as per cost of sales accounting | Functional area included |
Each one of these functionality is unique and elaborate and has thefeatures ingrained to meet the different requirements emerging for theexternal reporting purpose.
Concept of Ledger
A leading ledger is defined and additional ledgers are defined forparallel accounting or management reporting by assigning differentcharacteristic values and fiscal-year definitions
Additional ledgers can be defined - Leading Ledger & Non-leadingledgers are created and maintained, with only one accounting entry.
The new general ledger uses the special-purpose ledger techniques to save total values.
All Company Codes are assigned to a Leading ledger for each client,which contains the group-valuation view. Additional ledgers can bedefined for each company code.
Additional ledgers can be used for parallel accounting or managementreporting by assigning different characteristic values and fiscal-yeardefinitions.
For general-ledger account postings that have a specified costcenter, the system always reconciles the profit center andgeneral-ledger account simultaneously, since the data is stored in thesame table.
Two views of the new General Ledger:
Ø Regular entry view &
Ø General-Ledger view
Real time integration
- Integration with Controlling
- Transfer of cross-entity controlling postings to the new GL in real time.
- Integration with Asset Accounting
- Depreciation postings are done to all the ledgers, with the concept of delta depreciation.
- Integration with Consolidation
- Transferof financial data to EC-CS, real time, as Business partners,Transaction types are defined at the time of GL Posting itself.
- Extract / Transfer of data from GL to BI / CS.
Fast period end closing
Elimination of following activities
- Maintenance & use of Reconciliation Ledger
- Balance Sheet adjustment / P & L Adjustment
- Maintenance & use of Special Purpose ledger
- Segmental reporting is also available.
- Different ledgers are available to freely define management reporting too
Segment Reporting
- IAS/IFRS/US GAAP requires Segmental reporting.
- Segment is provided in addition to Business area / Profit center.
- It is one of the standard account assignment object available for running analyses of objects below the company code level.
- The objective is to give a detailed look at the various business activities (markets / products) at a broad based enterprise.
Parallel Accounting
- Parallel accounting can be done using the ledger approach instead as an alternative to the account approach.
- No additional account assignments are required as all account assignment components are defined as Scenarios for each ledger.
Document Splitting
Document splitting means the document is split according to theproportions of the account assignments in the expense or revenue linesof the original document. Examples: Cash discounts and realizedexchange rate differences are split according to the source document.
- Document-splitting is built at 2 technical points:
- Documentcreation - The controlling functions in the SAP are updated accordinglyand reconciled with the general-ledger accounting information
- Accounting interface -
- Account assignment projection - Account assignment are copied from base rows to target rows.
- Inheritance - Subsequent process of business transaction such as clearing.
- Itis a tool for determining missing account assignments according tocause in common accounting processes in SAP software (invoices,payments or clearing)
- It applies account-assignment information to non-assigned accounts according to assignment rules set in the customizing area.
- The functionality can help one to create balance sheets for entities that exist beyond the scope of the company code.
Example: Creation of balance sheets at the segment orprofit-center level or balance sheets based on company-specific orindustry-specific entities
New Tables
Three new tables in the new general ledger handle totals, storegeneral-ledger and specific line items, and calculate valuations foryear-end closings in parallel ledgers
Two new tables (FAGLFLEXA & FAGLFLEXP) store the ledger-specificline items (Actual & Planned) & contain additional informationfor use in the entry view. The tables help in updating differentcharacteristics and document splitting information, different periodshifts, and different currencies in specific ledgers for individualdocuments. Helps in preparing reports for specific dimensions at itemlevel.
The third table (BSEG_ADD) contains documents that are posted inconnection with valuations for year-end closing in selected parallelledgers. However, these documents are inapplicable if one do not useparallel accounting or use the accounting approach to portray parallelaccounting.
In addition to the three tables, own table can be defined using FAGLFLEXT as template
The new totals table contains additional standard fields for storingtotals. This standard table can activate support for many scenarios bycustomizing the software. It supports Segment Reporting, Profit-Centerupdating, Cost-of-Sales accounting, Cost-center updating, Preparationfor consolidation and Business-area updating
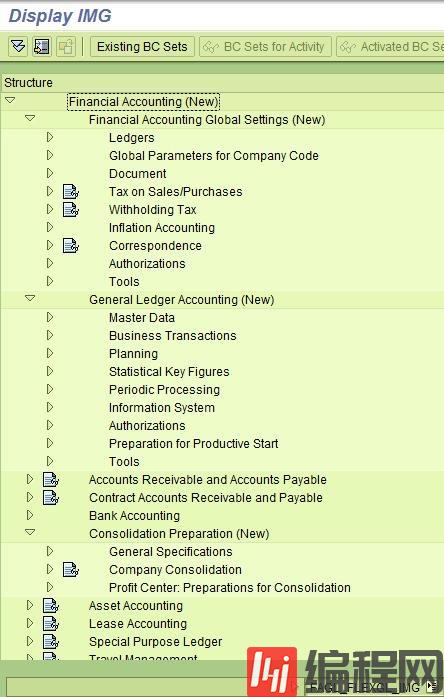
Customization
Customization of the NewGL is reusing the nodes of the original GL,but now has additional branches. e.g. Ledgers. The shell transaction isFAGL_FLEXGL_IMG.
免责声明:
① 本站未注明“稿件来源”的信息均来自网络整理。其文字、图片和音视频稿件的所属权归原作者所有。本站收集整理出于非商业性的教育和科研之目的,并不意味着本站赞同其观点或证实其内容的真实性。仅作为临时的测试数据,供内部测试之用。本站并未授权任何人以任何方式主动获取本站任何信息。
② 本站未注明“稿件来源”的临时测试数据将在测试完成后最终做删除处理。有问题或投稿请发送至: 邮箱/279061341@qq.com QQ/279061341
















