Android 系统属性(SystemProperties)介绍
我们在开发过程中有时需要使用系统属性,例如获取系统软件版本,获取设备名名称等,有时也需要设置自定义属性。本文将基于Android 10(Q)介绍Android系统属性(以下简称prop)使用,下文围绕以下几点展开介绍:
- prop的作用,如何调试和使用?
- prop实现原理,代码流程,prop存储在哪里,何时init?
- 如何添加自定义prop?
- 使用注意事项。
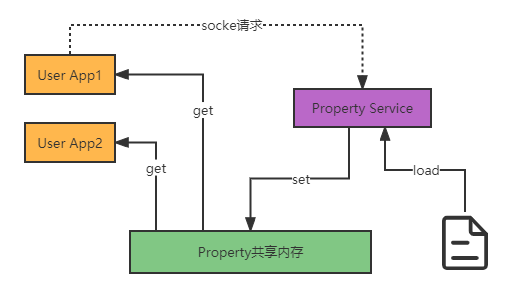
系统属性简单来说是用来存储系统中某些键值对数据,具有全局性、存取灵活方便的特点,因此广泛用于android系统的各个层级。
一、终端prop命令
在终端设备中,可以通过以下命令进行prop调试。
1.1、查看prop
#查看系统所有props$getprop...[persist.sys.timezone]: [Asia/Shanghai] //时区[ro.system.build.type]: [userdebug] //系统编译类型[vendor.display.lcd_density]: [320] //屏幕密度...#获取时区属性persist.sys.timezone的值$getprop persist.sys.timezoneAsia/Shanghai#过滤属性名或属性值含有关键字"timezone"的属性$getprop | grep timezone[persist.sys.timezone]: [Asia/Shanghai]#获取不存在的属性时结果为空$getprop hello1.2、设置prop
$getprop my.prop.test //属性my.prop.test为空$setprop my.prop.test 123 //设置属性my.prop.test为123$getprop my.prop.test //获取属性my.prop.test为1231231.3、监听prop
显示属性值发生变化的值
$watchprops[my.prop.test]: [123456]1.4 常用prop
| Prop | Value | Feature |
|---|---|---|
| persist.sys.boot.reason | “shutdown”:关机 “reboot”: 重启 “shutdown,userrequested”: 用户触发关机 “shutdown,thermal”:过热关机 “shutdown,battery”:低电量关机 “shutdown,themal,battery” “reboot,adb”:adb 触发重启 “reboot,shell”: shell 触发重启 “reboot,bootloader”:bootloader模式触发重启 "reboot,recovery"recovery模式触发重启等 | 记录上一次关机/启动原因 |
| persist.sys.boot.reason.history | [shutdown,userrequested,946684808 reboot,shell,946684808 reboot,ota,1680834107] | 记录多条关机/启动原因(detail为时间戳) |
| persist.sys.timezone | Asia/Shanghai | 系统时区 |
| ro.boot.serialno | 9212f447 | 设备序列号 |
| ro.product.build.* | date:Fri Apr 7 10:21:42 CST 2023 固件编译时间为2023-4-7 10:21:42 type:userdebug等 | 设备编译相关信息 |
| ro.product.name | xxx | 设备名称 |
| ro.sf.lcd_density | 240 | 设备显示密度 |
| sys.usb.config | mtp,adb | usb连接模式 |
注意:部分系统属性为厂商定制,且不同Android版本属性名称会所有差异,因此不同平台系统属性略有差异
1.5、init.rc 监听prop
system/core/rootdir/init.rc
...on property:sys.init_log_level=*#sys.init_log_level属性有值时,启动设置log级别进程 loglevel ${sys.init_log_level}...on property:sys.boot_completed=1#开机完成时擦除/data/per_boot文件夹数据 bootchart stop#BootChart是用于linux启动过程性能分析的开源软件工具, #它可以在内核装载后就开始运行,记录各个程序启动占用的时间、CPU #以及硬盘读写,直到系统启动完成为止。 # Setup per_boot directory so other .rc could start to use it on boot_completed exec - system system -- /bin/rm -rf /data/per_boot mkdir /data/per_boot 0700 system system...二、get和set prop代码流程
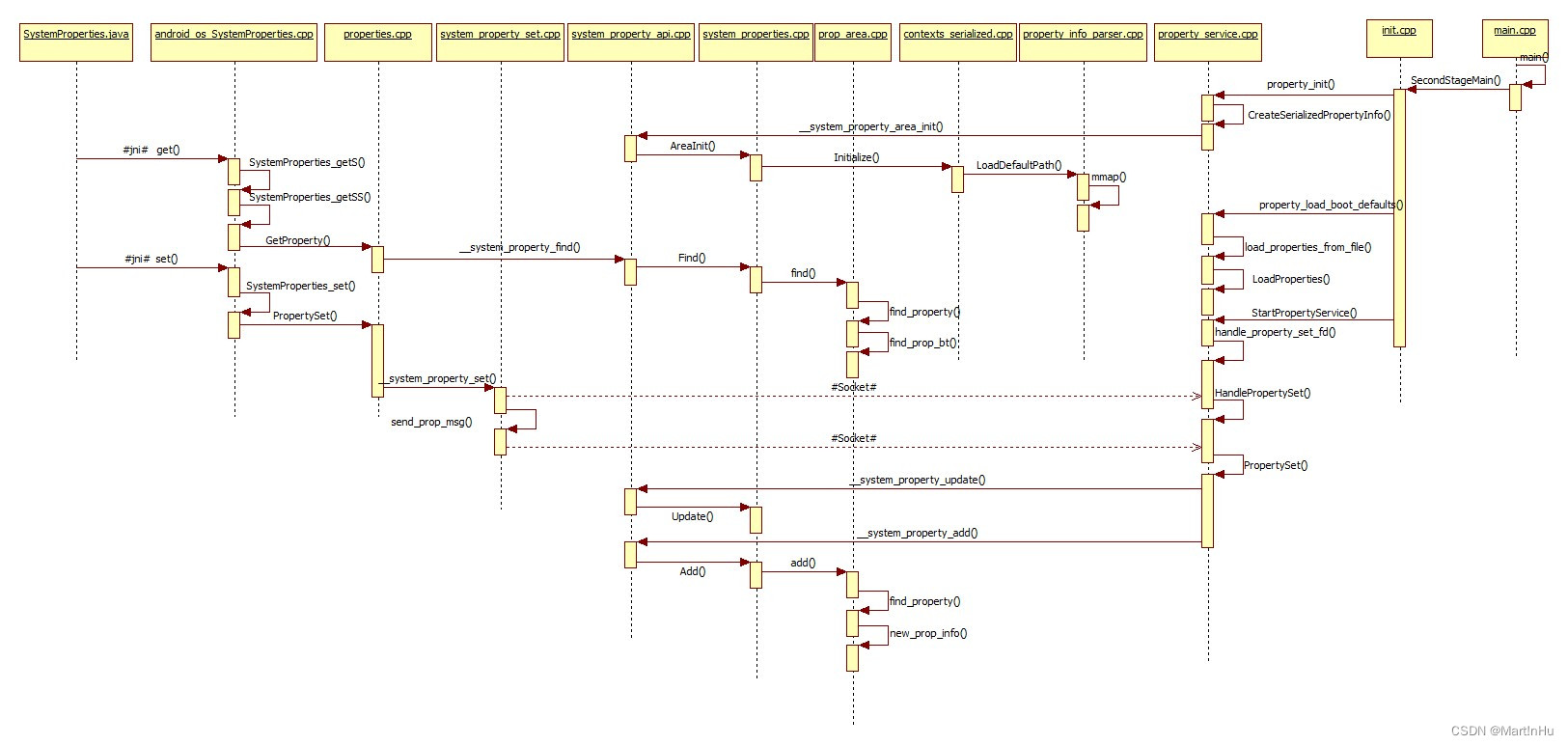
2.1、get和set prop代码流程图
涉及的代码路径汇总如下:
frameworks\base\core\java\android\os\SystemProperties.javaframeworks\base\core\jni\android_os_SystemProperties.cppsystem\core\base\properties.cppsystem\core\init\main.cppsystem\core\init\init.cppsystem\core\init\property_service.cppsystem\core\property_service\libpropertyinfoparser\property_info_parser.cppbionic\libc\include\sys\_system_properties.hbionic\libc\include\sys\system_properties.hbionic\libc\bionic\system_property_set.cppbionic\libc\bionic\system_property_api.cppbionic\libc\system_properties\contexts_serialized.cppbionic\libc\system_properties\system_properties.cppbionic\libc\system_properties\prop_area.cpp代码流程整体时序图如下:
(注:流程图android_os_SystemProperties.cpp->properties.cpp PropertySet()笔误,应为SetProperty())
系统属性架构设计如下:
2.2、代码流程介绍
frameworks\base\core\java\android\os\SystemProperties.java
SystemProperties提供了setprop和多种返回数据类型的getprop,采用键值对(key-value)的数据格式进行操作,具体如下:
public class SystemProperties { ... @UnsupportedAppUsage public static final int PROP_NAME_MAX = Integer.MAX_VALUE;//自android 8开始,取消对属性名长度限制 public static final int PROP_VALUE_MAX = 91; ... public static String get(@NonNull String key) public static String get(@NonNull String key, @Nullable String def) public static int getInt(@NonNull String key, int def) public static long getLong(@NonNull String key, long def) public static boolean getBoolean(@NonNull String key, boolean def) public static void set(@NonNull String key, @Nullable String val) public static void addChangeCallback(@NonNull Runnable callback) ... //获取属性key的值,如果没有该属性则返回默认值def public static String get(@NonNull String key, @Nullable String def) { if (TRACK_KEY_ACCESS) onKeyAccess(key); return native_get(key, def); }... //设置属性key的值为val,其不可为空、不能是"ro."开头的只读属性 //长度不能超过PROP_VALUE_MAX(91) public static void set(@NonNull String key, @Nullable String val) { if (val != null && !val.startsWith("ro.") && val.length() > PROP_VALUE_MAX) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("value of system property '" + key + "' is longer than " + PROP_VALUE_MAX + " characters: " + val); } if (TRACK_KEY_ACCESS) onKeyAccess(key); native_set(key, val); }}通过JNI上述 native_set()和native_get()走到
frameworks\base\core\jni\android_os_SystemProperties.cpp
//获取属性的方法最终调用GetProperty()jstring SystemProperties_getSS(JNIEnv *env, jclass clazz, jstring keyJ, jstring defJ){ auto handler = [&](const std::string& key, jstring defJ) { std::string prop_val = android::base::GetProperty(key, ""); ... }; return ConvertKeyAndForward(env, keyJ, defJ, handler);}jstring SystemProperties_getS(JNIEnv *env, jclass clazz, jstring keyJ){ return SystemProperties_getSS(env, clazz, keyJ, nullptr);}//设置属性的接口最终调用SetProperty()void SystemProperties_set(JNIEnv *env, jobject clazz, jstring keyJ, jstring valJ){ auto handler = [&](const std::string& key, bool) { ... return android::base::SetProperty(key, val); }; ...}...跟着调用关系,接着进入:
system\core\base\properties.cpp
//调用__system_property_find()查找属性值std::string GetProperty(const std::string& key, const std::string& default_value) { ... const prop_info* pi = __system_property_find(key.c_str()); ...}//调用__system_property_set()设置属性值bool SetProperty(const std::string& key, const std::string& value) { return (__system_property_set(key.c_str(), value.c_str()) == 0);}2.2.1、set prop流程
_system_properties.h头文件定义PROP_SERVICE_NAME
bionic\libc\include\sys_system_properties.h
#define PROP_SERVICE_NAME "property_service"bionic\libc\bionic\system_property_set.cpp
static const char property_service_socket[] = "/dev/socket/" PROP_SERVICE_NAME;static const char* kServiceVersionPropertyName = "ro.property_service.version";...int __system_property_set(const char* key, const char* value) { if (g_propservice_protocol_version == 0) { detect_protocol_version();//获取属性服务协议版本 } //旧协议版本限定prop name最大长度为PROP_NAME_MAX,prop val最大长度为PROP_VALUE_MAX if (g_propservice_protocol_version == kProtocolVersion1) { //在bionic\libc\include\sys\system_properties.h中定义 //#define PROP_NAME_MAX 32 //#define PROP_VALUE_MAX 92 if (strlen(key) >= PROP_NAME_MAX) return -1; if (strlen(value) >= PROP_VALUE_MAX) return -1; ... return send_prop_msg(&msg);//send_prop_msg()也通过Socket与property_service进行通信 } else {//进入新版本协议,仅对prop val长度有要求,不超过92,且属性不为只读属性 // New protocol only allows long values for ro. properties only. if (strlen(value) >= PROP_VALUE_MAX && strncmp(key, "ro.", 3) != 0) return -1; ... SocketWriter writer(&connection);//通过Socket与property_service进行通信 ... }...static const char* kServiceVersionPropertyName = "ro.property_service.version";static constexpr uint32_t kProtocolVersion1 = 1;static constexpr uint32_t kProtocolVersion2 = 2; // currentstatic atomic_uint_least32_t g_propservice_protocol_version = 0;static void detect_protocol_version() { //从ro.property_service.version中获取协议版本,可在平台终端getprop ro.property_service.version //在后续2.2.5小节中可找到设置该属性的位置 if (__system_property_get(kServiceVersionPropertyName, value) == 0) { g_propservice_protocol_version = kProtocolVersion1; } else { uint32_t version = static_cast(atoll(value)); if (version >= kProtocolVersion2) { g_propservice_protocol_version = kProtocolVersion2; } else { g_propservice_protocol_version = kProtocolVersion1; } ...} 2.2.2、属性服务(property_service)
流程到了这里会发现,最终需要通过Socket与property_service来通信进行设置属性值,那么问题来了:
- property_service是谁创建的?
- property_service是怎么启动的?
- property_service是如何setprop的?
熟悉Android开机流程的同学会马上联想到init进程,property_service正是init进程来初始化和启动的。
system\core\init\init.cpp
int SecondStageMain(int argc, char** argv) { ... property_init();//属性初始化 ... property_load_boot_defaults(load_debug_prop);//加载开机默认属性配置 StartPropertyService(&epoll);//启动属性服务 ...}2.2.3、属性初始化
system\core\init\property_service.cpp
void property_init() { mkdir("/dev/__properties__", S_IRWXU | S_IXGRP | S_IXOTH); CreateSerializedPropertyInfo();//创建属性信息property_info if (__system_property_area_init()) {//创建共享内存 LOG(FATAL) << "Failed to initialize property area"; } if (!property_info_area.LoadDefaultPath()) { LOG(FATAL) << "Failed to load serialized property info file"; }}......//读取selinux模块中的property相关文件,解析并加载到property_info中void CreateSerializedPropertyInfo() { auto property_infos = std::vector(); if (access("/system/etc/selinux/plat_property_contexts", R_OK) != -1) { if (!LoadPropertyInfoFromFile("/system/etc/selinux/plat_property_contexts", &property_infos)) { return; } // Don't check for failure here, so we always have a sane list of properties. // E.g. In case of recovery, the vendor partition will not have mounted and we // still need the system / platform properties to function. if (!LoadPropertyInfoFromFile("/vendor/etc/selinux/vendor_property_contexts", &property_infos)) { // Fallback to nonplat_* if vendor_* doesn't exist. LoadPropertyInfoFromFile("/vendor/etc/selinux/nonplat_property_contexts", &property_infos); } if (access("/product/etc/selinux/product_property_contexts", R_OK) != -1) { LoadPropertyInfoFromFile("/product/etc/selinux/product_property_contexts", &property_infos); } if (access("/odm/etc/selinux/odm_property_contexts", R_OK) != -1) { LoadPropertyInfoFromFile("/odm/etc/selinux/odm_property_contexts", &property_infos); } } else { if (!LoadPropertyInfoFromFile("/plat_property_contexts", &property_infos)) { return; } if (!LoadPropertyInfoFromFile("/vendor_property_contexts", &property_infos)) { // Fallback to nonplat_* if vendor_* doesn't exist. LoadPropertyInfoFromFile("/nonplat_property_contexts", &property_infos); } LoadPropertyInfoFromFile("/product_property_contexts", &property_infos); LoadPropertyInfoFromFile("/odm_property_contexts", &property_infos); } auto serialized_contexts = std::string(); auto error = std::string(); if (!BuildTrie(property_infos, "u:object_r:default_prop:s0", "string", &serialized_contexts, &error)) { LOG(ERROR) << "Unable to serialize property contexts: " << error; return; } //将序列化属性写入/dev/__properties__/property_info constexpr static const char kPropertyInfosPath[] = "/dev/__properties__/property_info"; if (!WriteStringToFile(serialized_contexts, kPropertyInfosPath, 0444, 0, 0, false)) { PLOG(ERROR) << "Unable to write serialized property infos to file"; } selinux_android_restorecon(kPropertyInfosPath, 0);} bionic\libc\bionic\system_property_api.cpp
int __system_property_area_init() { bool fsetxattr_failed = false; return system_properties.AreaInit(PROP_FILENAME, &fsetxattr_failed) && !fsetxattr_failed ? 0 : -1;}初始化属性内存共享区域
bionic\libc\system_properties\system_properties.cpp
bool SystemProperties::AreaInit(const char* filename, bool* fsetxattr_failed) { if (strlen(filename) >= PROP_FILENAME_MAX) { return false; } strcpy(property_filename_, filename); contexts_ = new (contexts_data_) ContextsSerialized(); if (!contexts_->Initialize(true, property_filename_, fsetxattr_failed)) { return false; } initialized_ = true; return true;}bionic\libc\system_properties\contexts_serialized.cpp
bool ContextsSerialized::Initialize(bool writable, const char* filename, bool* fsetxattr_failed) { filename_ = filename; if (!InitializeProperties()) { return false; } ...}bool ContextsSerialized::InitializeProperties() { if (!property_info_area_file_.LoadDefaultPath()) { return false; } ...}__system_property_area_init()经过一系列的方法调用,最终通过mmap()将/dev/__property __/property_info加载到共享内存。
system\core\property_service\libpropertyinfoparser\property_info_parser.cpp
bool PropertyInfoAreaFile::LoadDefaultPath() { return LoadPath("/dev/__properties__/property_info");}bool PropertyInfoAreaFile::LoadPath(const char* filename) { int fd = open(filename, O_CLOEXEC | O_NOFOLLOW | O_RDONLY); ... void* map_result = mmap(nullptr, mmap_size, PROT_READ, MAP_SHARED, fd, 0); ...}2.2.4、加载开机默认属性配置
接着init进程中property_load_boot_defaults(load_debug_prop)函数分析
system\core\init\property_service.cpp
void property_load_boot_defaults(bool load_debug_prop) { std::map properties; //加载属性build.prop、default.prop至properties if (!load_properties_from_file("/system/etc/prop.default", nullptr, &properties)) { // Try recovery path if (!load_properties_from_file("/prop.default", nullptr, &properties)) { // Try legacy path load_properties_from_file("/default.prop", nullptr, &properties); } } load_properties_from_file("/system/build.prop", nullptr, &properties); load_properties_from_file("/vendor/default.prop", nullptr, &properties); load_properties_from_file("/vendor/build.prop", nullptr, &properties); if (SelinuxGetVendorAndroidVersion() >= __ANDROID_API_Q__) { load_properties_from_file("/odm/etc/build.prop", nullptr, &properties); } else { load_properties_from_file("/odm/default.prop", nullptr, &properties); load_properties_from_file("/odm/build.prop", nullptr, &properties); } load_properties_from_file("/product/build.prop", nullptr, &properties); load_properties_from_file("/product_services/build.prop", nullptr, &properties); load_properties_from_file("/factory/factory.prop", "ro.*", &properties); ... //将properties中属性通过PropertySet存入属性属性 for (const auto& [name, value] : properties) { std::string error; if (PropertySet(name, value, &error) != PROP_SUCCESS) { LOG(ERROR) << "Could not set '" << name << "' to '" << value << "' while loading .prop files" << error; } } property_initialize_ro_product_props();//初始化ro_product前缀的只读属性 property_derive_build_props();//初始化编译相关属性 update_sys_usb_config();//设置persist.sys.usb.config属性,用于控制USB调试和文件传输功能} 从上面代码可以看出从多个属性文件.prop中系统属性加载至properties变量,再通过PropertySet()将properties添加到系统中,并初始化只读、编译、usb相关属性值。
PropertySet()流程在2.2.1小节中有介绍,通过Socket与属性服务进行通信,将props存储共享内存。
2.2.5、启动属性服务
2.2小节中提到init进程StartPropertyService(&epoll)启动了属性服务。
system\core\init\property_service.cpp
void StartPropertyService(Epoll* epoll) { selinux_callback cb; cb.func_audit = SelinuxAuditCallback; selinux_set_callback(SELINUX_CB_AUDIT, cb); //这里设置了2.2.1小节提到的属性ro.property_service.version property_set("ro.property_service.version", "2"); property_set_fd = CreateSocket(PROP_SERVICE_NAME, SOCK_STREAM | SOCK_CLOEXEC | SOCK_NONBLOCK, false, 0666, 0, 0, nullptr); if (property_set_fd == -1) { PLOG(FATAL) << "start_property_service socket creation failed"; } listen(property_set_fd, 8);//设置Socket连接数为8 //注册epoll,监听property_set_fd改变时调用handle_property_set_fd if (auto result = epoll->RegisterHandler(property_set_fd, handle_property_set_fd); !result) { PLOG(FATAL) << result.error(); }}static void handle_property_set_fd() { ... switch (cmd) { case PROP_MSG_SETPROP: {//设置属性 ... uint32_t result = HandlePropertySet(prop_name, prop_value, socket.source_context(), cr, &error); ... } case PROP_MSG_SETPROP2: { ... uint32_t result = HandlePropertySet(name, value, socket.source_context(), cr, &error); ... } ...}uint32_t HandlePropertySet(const std::string& name, const std::string& value, const std::string& source_context, const ucred& cr, std::string* error) { //检查prop 权限 if (auto ret = CheckPermissions(name, value, source_context, cr, error); ret != PROP_SUCCESS) { return ret; } if (StartsWith(name, "ctl.")) {//ctl属性:ctl.start启动服务,ctl.stop关闭服务 HandleControlMessage(name.c_str() + 4, value, cr.pid); return PROP_SUCCESS; } // sys.powerctl is a special property that is used to make the device reboot. We want to log // any process that sets this property to be able to accurately blame the cause of a shutdown. if (name == "sys.powerctl") {//sys.powerctl属性可控制设备重启 std::string cmdline_path = StringPrintf("proc/%d/cmdline", cr.pid); std::string process_cmdline; std::string process_log_string; if (ReadFileToString(cmdline_path, &process_cmdline)) { // Since cmdline is null deliminated, .c_str() conveniently gives us just the process // path. process_log_string = StringPrintf(" (%s)", process_cmdline.c_str()); } LOG(INFO) << "Received sys.powerctl='" << value << "' from pid: " << cr.pid << process_log_string; } if (name == "selinux.restorecon_recursive") { return PropertySetAsync(name, value, RestoreconRecursiveAsync, error); } return PropertySet(name, value, error);//设置属性}//检查prop 权限uint32_t CheckPermissions(const std::string& name, const std::string& value, const std::string& source_context, const ucred& cr, std::string* error) { //检查属性名称是否正确:1、属性名长度需不小于1;2、开头与结尾不能为.;3、字符:0~9+a~z+A~Z+'.'+'@'+'-'+'_'+':' if (!IsLegalPropertyName(name)) { *error = "Illegal property name"; return PROP_ERROR_INVALID_NAME; } if (StartsWith(name, "ctl.")) { //检查ctl控制属性selinux权限 if (!CheckControlPropertyPerms(name, value, source_context, cr)) { *error = StringPrintf("Invalid permissions to perform '%s' on '%s'", name.c_str() + 4, value.c_str()); return PROP_ERROR_HANDLE_CONTROL_MESSAGE; } return PROP_SUCCESS; } ... if (!CheckMacPerms(name, target_context, source_context.c_str(), cr)) { *error = "SELinux permission check failed"; return PROP_ERROR_PERMISSION_DENIED; }... return PROP_SUCCESS;}static bool CheckMacPerms(const std::string& name, const char* target_context, const char* source_context, const ucred& cr) {...//检查selinux权限,property_service对该属性是否有set权限 bool has_access = (selinux_check_access(source_context, target_context, "property_service", "set", &audit_data) == 0); ...}...static uint32_t PropertySet(const std::string& name, const std::string& value, std::string* error) { size_t valuelen = value.size(); if (!IsLegalPropertyName(name)) {//检测属性合法性 *error = "Illegal property name"; return PROP_ERROR_INVALID_NAME; } if (valuelen >= PROP_VALUE_MAX && !StartsWith(name, "ro.")) { *error = "Property value too long"; return PROP_ERROR_INVALID_VALUE; } if (mbstowcs(nullptr, value.data(), 0) == static_cast(-1)) { *error = "Value is not a UTF8 encoded string"; return PROP_ERROR_INVALID_VALUE; } //检测属性是否已存在 prop_info* pi = (prop_info*) __system_property_find(name.c_str()); if (pi != nullptr) { // ro.* properties are actually "write-once". if (StartsWith(name, "ro.")) { *error = "Read-only property was already set"; return PROP_ERROR_READ_ONLY_PROPERTY; } //属性已存在,并且非ro只读属性,更新属性值 __system_property_update(pi, value.c_str(), valuelen); } else { //属性不存在,添加属性值 int rc = __system_property_add(name.c_str(), name.size(), value.c_str(), valuelen); if (rc < 0) { *error = "__system_property_add failed"; return PROP_ERROR_SET_FAILED; } } // Don't write properties to disk until after we have read all default // properties to prevent them from being overwritten by default values. //避免在load所有属性之前将属性写入disk,防止属性值被覆盖。 if (persistent_properties_loaded && StartsWith(name, "persist.")) { WritePersistentProperty(name, value);//将persist属性持久化disk和/data/property/persistent_properties } property_changed(name, value);//特殊属性值(如sys.powerctl)改变后系统需要立即处理。 return PROP_SUCCESS;} 2.2.6、更新和添加属性
bionic\libc\bionic\system_property_api.cpp
int __system_property_update(prop_info* pi, const char* value, unsigned int len) { return system_properties.Update(pi, value, len);//更新属性值}int __system_property_add(const char* name, unsigned int namelen, const char* value, unsigned int valuelen) { return system_properties.Add(name, namelen, value, valuelen);//添加属性值}bionic\libc\system_properties\system_properties.cpp
int SystemProperties::Update(prop_info* pi, const char* value, unsigned int len) { ... prop_area* pa = contexts_->GetSerialPropArea(); uint32_t serial = atomic_load_explicit(&pi->serial, memory_order_relaxed); serial |= 1; atomic_store_explicit(&pi->serial, serial, memory_order_relaxed); atomic_thread_fence(memory_order_release); strlcpy(pi->value, value, len + 1);//属性值更新 ... return 0;}int SystemProperties::Add(const char* name, unsigned int namelen, const char* value, unsigned int valuelen) { ... prop_area* serial_pa = contexts_->GetSerialPropArea(); prop_area* pa = contexts_->GetPropAreaForName(name); bool ret = pa->add(name, namelen, value, valuelen);//向共享内存添加新属性 ... return 0;}bionic\libc\system_properties\prop_area.cpp
bool prop_area::add(const char* name, unsigned int namelen, const char* value, unsigned int valuelen) { return find_property(root_node(), name, namelen, value, valuelen, true);}...const prop_info* prop_area::find_property(prop_bt* const trie, const char* name, uint32_t namelen, const char* value, uint32_t valuelen, bool alloc_if_needed) { ... prop_bt* root = nullptr; uint_least32_t children_offset = atomic_load_explicit(¤t->children, memory_order_relaxed); if (children_offset != 0) {//找到属性节点 root = to_prop_bt(¤t->children); } else if (alloc_if_needed) {//未找到时新建节点 uint_least32_t new_offset; root = new_prop_bt(remaining_name, substr_size, &new_offset); if (root) { atomic_store_explicit(¤t->children, new_offset, memory_order_release); } } ... current = find_prop_bt(root, remaining_name, substr_size, alloc_if_needed); remaining_name = sep + 1; } uint_least32_t prop_offset = atomic_load_explicit(¤t->prop, memory_order_relaxed); if (prop_offset != 0) { return to_prop_info(¤t->prop);//返回已存在的prop_info } else if (alloc_if_needed) { uint_least32_t new_offset; //添加新属性 prop_info* new_info = new_prop_info(name, namelen, value, valuelen, &new_offset); ... }}prop_info* prop_area::new_prop_info(const char* name, uint32_t namelen, const char* value, uint32_t valuelen, uint_least32_t* const off) { ... prop_info* info; if (valuelen >= PROP_VALUE_MAX) { uint32_t long_value_offset = 0; char* long_location = reinterpret_cast(allocate_obj(valuelen + 1, &long_value_offset)); if (!long_location) return nullptr; memcpy(long_location, value, valuelen); long_location[valuelen] = '\0'; long_value_offset -= new_offset; info = new (p) prop_info(name, namelen, long_value_offset); } else { info = new (p) prop_info(name, namelen, value, valuelen); } *off = new_offset; return info;} 从上述code可分析出设置属性流程中根据所设置的属性值是否存在分别走update()和add()流程,而add 最后调用查找属性方法,如果不存在则新建共享内存节点,将prop_info存入。自此,set prop流程结束。
2.2.7、get prop流程
承接2.2节system\core\base\properties.cpp中__system_property_find(key.c_str())
bionic\libc\bionic\system_property_api.cpp
const prop_info* __system_property_find(const char* name) { return system_properties.Find(name);}bionic\libc\system_properties\system_properties.cpp
const prop_info* SystemProperties::Find(const char* name) { ... prop_area* pa = contexts_->GetPropAreaForName(name); ... return pa->find(name);}bionic\libc\system_properties\prop_area.cpp
const prop_info* prop_area::find(const char* name) { return find_property(root_node(), name, strlen(name), nullptr, 0, false);}find_property后续流程同2.2.6小节。
三、代码中使用属性
在上一章节中详细介绍了获取和设置属性的代码流程,但仍有部分问题仍待解决:
- 2.2.4小节中build.prop、default.prop在哪里生成的,如何打包进系统
- 如何添加自定义hello.prop
- 如何添加系统级默认属性
- prop有哪些类型,不同前缀有什么区别
上述疑问先保留一点神秘感,稍后介绍,先介绍在java、C++代码中如何使用属性
3.1、java代码中使用prop
Systemproperties部分源码如下:
frameworks\base\core\java\android\os\SystemProperties.java
...public class SystemProperties {... //获取属性key的值,如果没有该属性则返回默认值def @SystemApi public static String get(@NonNull String key, @Nullable String def) { if (TRACK_KEY_ACCESS) onKeyAccess(key); return native_get(key, def); }... //设置属性key的值为val @SystemApi public static void set(@NonNull String key, @Nullable String val) { if (val != null && !val.startsWith("ro.") && val.length() > PROP_VALUE_MAX) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("value of system property '" + key + "' is longer than " + PROP_VALUE_MAX + " characters: " + val); } if (TRACK_KEY_ACCESS) onKeyAccess(key); native_set(key, val); }....}由于SystemProperties.java的API为系统API,普通应用无法直接使用,可以通过反射来get和set prop。
package com.giada.reflectiondemo;import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;import android.os.Bundle;import android.util.Log;import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;import java.lang.reflect.Method;public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity { @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); Log.d(TAG, "ro.vendor.build.version.incremental:"+getString("ro.vendor.build.version.incremental", "fuckyou")); Log.d(TAG, "sys.isolated_storage_snapshot:"+getBoolean("sys.isolated_storage_snapshot", false)); } public static boolean getBoolean(String key, boolean def) throws IllegalArgumentException { try { Class SystemPropertiesClass = Class.forName("android.os.SystemProperties"); Method getBooleanMethod = SystemPropertiesClass.getDeclaredMethod("getBoolean", String.class, boolean.class); getBooleanMethod.setAccessible(true); return (boolean) getBooleanMethod.invoke(SystemPropertiesClass, key, def); } catch (InvocationTargetException | IllegalAccessException | NoSuchMethodException | ClassNotFoundException e) { Log.e(TAG, "Failed to invoke SystemProperties.getBoolean()", e); } return def;在framework中, get和set prop以ActivityManagerService.java代码为例:
frameworks\base\services\core\java\com\android\server\am\ActivityManagerService.java
final void finishBooting() { ... //设置开机完成标志属性sys.boot_completed SystemProperties.set("sys.boot_completed", "1");}...private static void maybePruneOldTraces(File tracesDir) { ... //获取tombstoned.max_anr_count属性值 final int max = SystemProperties.getInt("tombstoned.max_anr_count", 64);}获取属性值可以根据值的类型使用合适返回值类型的方法如getInt()、getBoolean()、getLong(),SystemProperties.get()获取的值为String。
3.2、C++代码中使用prop
这里以MPEG4Writer.cpp为例
frameworks\av\media\libstagefright\MPEG4Writer.cpp
#include ...void MPEG4Writer::addDeviceMeta() { ... if (property_get("ro.build.version.release", val, NULL) ... if (property_get("ro.product.model", val, NULL) ...} 在C++代码中使用prop需要:
- include
- Android.mk或Android.bp或Makefile中需要链接libcutils库
frameworks\av\media\libstagefright\Android.bp
shared_libs: [ ... "libcutils", ...properties.h源码在:
system/core/libcutils/include/cutils/properties.h
int property_get(const char* key, char* value, const char* default_value);int property_set(const char *key, const char *value);int property_list(void (*propfn)(const char *key, const char *value, void *cookie), void *cookie);3.3、特殊属性
从2.2.5小节中可以看到有些属性比较特殊,特总结如下:
3.3.1、 ro只读属性
ro即read only这类属性通常是系统默认属性,在系统编译或初始化时设置的。
$ getprop ro.vendor.build.version.release10$ setprop ro.vendor.build.version.release 9setprop: failed to set property 'ro.vendor.build.version.release' to '9'3.3.2、persist持久属性
设置persist开头的属性,断电后仍能保存,值写入data/property/persistent_properties。
$ getprop persist.hello.test //属性为空$ setprop persist.hello.test abc //设置属性persist.hello.test值为abc$ getprop persist.hello.test abc //属性get正常abc$reboot //重启设备$ getprop persist.hello.test //属性为abcabc3.3.3、ctl 控制属性
setprop ctl.start xxx //启动某服务setprop ctl.stop xxx //关闭某服务setprop ctl.restart xxx //重启某服务3.3.4、sys.powerctl属性
sys.powerctl属性可控制设备重启关机
setprop sys.powerctl shutdown //设备关机setprop sys.powerctl reboot //设备重启3.3.5、普通属性
设置其他格式开头的属性,断电后不能保存
$ getprop hello.test //属性为空$ setprop hello.test 123//设置属性persist.hello.test值为abc$ getprop hello.test 123//属性get正常123$reboot //重启设备$ getprop hello.test //属性为空注意:属性命名需符合2.2.5小节中属性命名规范,否则报错,例如
$ setprop good.good.study. day.day.upsetprop: property names must not start or end with '.'3.4、添加系统默认属性
从前面的介绍中我们知道系统开机时会load *.prop属性配置文件中的属性,因此开机后就有了默认属性。这里我们可以在device/xxx/xxx/system.prop 中添加
device/google/marlin/system.prop
# 添加自己的系统默认属性persist.hello.world=hello注意:这里添加的属性前缀必须是在system/sepolicy/private/property_contexts中被定义过的,否则无效;定制化前缀属性在后面定制prop属性配置中会介绍。
make android后在out/target/product/xxx/system/build.prop 或out/target/product/xxx/vendor/build.prop可找到添加的属性persist.hello.world,则说明基本添加成功,烧录img验证即可。
四、prop打包
我们已经知道如何添加系统默认属性,但项目中有许多*.prop配置文件,
- 这些文件是如何最终打包至out/tartget/product/…/build.prop的呢?
- 为了便于客制化属性管控,如何添加自己的prop配置文件呢?
本章将围绕上面两个问题进行介绍
4.1、prop打包流程
build.prop是在代码编译时,build/core/Makefile完成打包的
//指定编译信息及设备基本信息脚本BUILDINFO_SH := build/make/tools/buildinfo.shBUILDINFO_COMMON_SH := build/make/tools/buildinfo_common.sh//指定build.prop生成路径INSTALLED_BUILD_PROP_TARGET := $(TARGET_OUT)/build.propINSTALLED_PRODUCT_BUILD_PROP_TARGET := $(TARGET_OUT_PRODUCT)/build.propINSTALLED_VENDOR_BUILD_PROP_TARGET := $(TARGET_OUT_VENDOR)/build.prop...//生成build.prop$(intermediate_system_build_prop): $(BUILDINFO_SH) $(BUILDINFO_COMMON_SH) $(INTERNAL_BUILD_ID_MAKEFILE) $(BUILD_SYSTEM)/version_defaults.mk $(system_prop_file) $(INSTALLED_ANDROID_INFO_TXT_TARGET) $(API_FINGERPRINT) @echo Target buildinfo: $@ @mkdir -p $(dir $@) $(hide) echo > $@ifneq ($(PRODUCT_OEM_PROPERTIES),) $(hide) echo "#" >> $@; \ echo "# PRODUCT_OEM_PROPERTIES" >> $@; \ echo "#" >> $@; $(hide) $(foreach prop,$(PRODUCT_OEM_PROPERTIES), \ echo "import /oem/oem.prop $(prop)" >> $@;)endif $(hide) PRODUCT_BRAND="$(PRODUCT_SYSTEM_BRAND)" \ ... TARGET_CPU_ABI2="$(TARGET_CPU_ABI2)" \ bash $(BUILDINFO_SH) >> $@//将许多属性追加至out/.../build.propbuild/make/tools/buildinfo.sh中配置了系统编译常见信息,具体如下
...echo "ro.build.version.incremental=$BUILD_NUMBER"//软件增量版本echo "ro.build.version.sdk=$PLATFORM_SDK_VERSION"//软件使用的sdk版本echo "ro.build.version.release=$PLATFORM_VERSION"//系统版本号echo "ro.build.date=`$DATE`"//软件编译日期...经过Makefile,将系统中各种prop配置文件合并生成在out指定路径下。
也是在Makefile中将各路径下build.prop随系统分区一同打包进img,out\target\product\xxx\system\build.prop打包进system.img
out\target\product\xxx\vendor\build.prop打包进vendor.img
五、添加定制hello.prop
涉及的代码路径汇总如下:
device/qcom/qssi/hello.propdevice/qcom/qssi/qssi.mkdevice/qcom/sepolicy/generic/private/property_contextssystem/core/rootdir/init.rcsystem/core/init/property_service.cpp为了方便统一管理定制化属性,有时会将定制化属性都写在定制的.prop文件中,下面以添加hello.prop为例说明添加过程。
5.1、device下添加hello.prop
device/qcom/qssi/hello.prop
## system.prop for qssi#ro.hello.year=2022 //添加ro属性persist.hello.month=07 //添加persist属性hello.day=25 //添加hello属性ro.product.model=HelloWorld //定制系统已有ro.product.model属性5.2 配置预置路径
修改device下的device.mk来指定hello.prop的预置路径
device/qcom/qssi/qssi.mk
#将hello.prop预置到system/hello.propPRODUCT_COPY_FILES += \ device/qcom/qssi/hello.prop:system/hello.prop5.3、SELinux权限配置
hello.开头的属性是新添加的配置,需要在配置对应的SELinux规则,否则无效,配置方法如下:
device/qcom/sepolicy/generic/private/property_contexts
hello. u:object_r:system_prop:s0详细SELinux介绍和配置可参考Android SELinux权限概念和配置说明
5.4、配置hello.prop权限
此步骤可省略,若未配置读写权限,默认system/prop为644
这里配置与system/build.prop相同的600权限
system/core/rootdir/init.rc
on fs chmod 0600 /system/hello.prop5.5、load hello.prop
2、小节中仅仅将hello.prop预置到system/hello.prop还不够,系统启动时需要load hello.prop才能使其生效
system/core/init/property_service.cpp
load_properties_from_file("/system/build.prop", nullptr, &properties); load_properties_from_file("/vendor/default.prop", nullptr, &properties); load_properties_from_file("/vendor/build.prop", nullptr, &properties); if (SelinuxGetVendorAndroidVersion() >= __ANDROID_API_Q__) { load_properties_from_file("/odm/etc/build.prop", nullptr, &properties); } else { load_properties_from_file("/odm/default.prop", nullptr, &properties); load_properties_from_file("/odm/build.prop", nullptr, &properties); } load_properties_from_file("/product/build.prop", nullptr, &properties); load_properties_from_file("/product_services/build.prop", nullptr, &properties); load_properties_from_file("/factory/factory.prop", "ro.*", &properties); //load 预置的hello.prop ,最后load保证其配置属性优先级更高 load_properties_from_file("/system/hello.prop", nullptr, &properties);5.6、验证hello.prop
Android全编译后正常情况可找到生成的
out/target/product/qssi/system/hello.prop
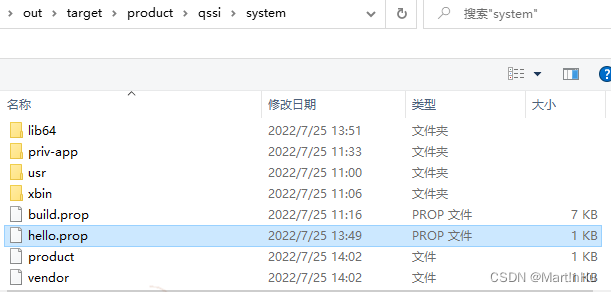
检查其内容应与device/qcom/qssi/hello.prop内容保持一致。
将打包好的img烧录到设备中进行确认
//hello.prop预置成功$ ls -al system/-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 117 2009-01-01 08:00 hello.prop//新增属性设置成功$ getprop | grep hello[hello.day]: [25][persist.hello.month]: [07][ro.hello.year]: [2022]//ro.product.model覆盖了默认值$ getprop ro.product.modelHelloWorld来源地址:https://blog.csdn.net/supernova_TOP/article/details/125971945
免责声明:
① 本站未注明“稿件来源”的信息均来自网络整理。其文字、图片和音视频稿件的所属权归原作者所有。本站收集整理出于非商业性的教育和科研之目的,并不意味着本站赞同其观点或证实其内容的真实性。仅作为临时的测试数据,供内部测试之用。本站并未授权任何人以任何方式主动获取本站任何信息。
② 本站未注明“稿件来源”的临时测试数据将在测试完成后最终做删除处理。有问题或投稿请发送至: 邮箱/279061341@qq.com QQ/279061341













