java重试机制使用RPC要考虑什么
这篇文章主要介绍“java重试机制使用RPC要考虑什么”的相关知识,小编通过实际案例向大家展示操作过程,操作方法简单快捷,实用性强,希望这篇“java重试机制使用RPC要考虑什么”文章能帮助大家解决问题。
1 为什么重试
如果简单对一个RPC交互过程进行分类,我们可以分为三类:响应成功、响应失败、没有响应。
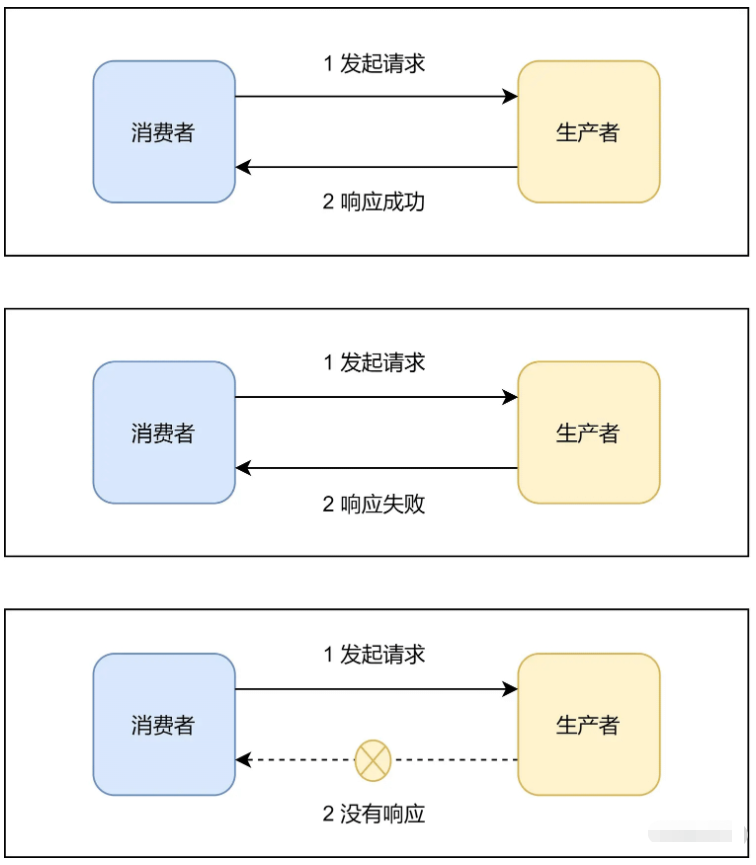
对于响应成功和响应失败这两种情况,消费者很好处理。因为响应信息明确,所以只要根据响应信息,继续处理成功或者失败逻辑即可。但是没有响应这种场景比较难处理,这是因为没有响应可能包含以下情况:
(1) 生产者根本没有接收到请求
(2) 生产者接收到请求并且已处理成功,但是消费者没有接收到响应
(3) 生产者接收到请求并且已处理失败,但是消费者没有接收到响应
假设你是一名RPC框架设计者,究竟是选择重试还是放弃调用呢?其实最终如何选择取决于业务特性,有的业务本身就具有幂等性,但是有的业务不能允许重试否则会造成重复数据。
那么谁对业务特性最熟悉呢?答案是消费者,因为消费者作为调用方肯定最熟悉自身业务,所以RPC框架只要提供一些策略供消费者选择即可。
2 怎么做重试
2.1 集群容错策略
DUBBO作为一款优秀RPC框架,提供了如下集群容错策略供消费者选择:
Failover: 故障转移
Failfast: 快速失败
Failsafe: 安全失败
Failback: 异步重试
Forking: 并行调用
Broadcast:广播调用
(1) Failover
故障转移策略。作为默认策略当消费发生异常时通过负载均衡策略再选择一个生产者节点进行调用,直到达到重试次数
(2) Failfast
快速失败策略。消费者只消费一次服务,当发生异常时则直接抛出
(3) Failsafe
安全失败策略。消费者只消费一次服务,如果消费失败则包装一个空结果,不抛出异常
(4) Failback
异步重试策略。当消费发生异常时返回一个空结果,失败请求将会进行异步重试。如果重试超过最大重试次数还不成功,放弃重试并不抛出异常
(5) Forking
并行调用策略。消费者通过线程池并发调用多个生产者,只要有一个成功就算成功
(6) Broadcast
广播调用策略。消费者遍历调用所有生产者节点,任何一个出现异常则抛出异常
2.2 源码分析
2.2.1 Failover
Failover故障转移策略作为默认策略,当消费发生异常时通过负载均衡策略再选择一个生产者节点进行调用,直到达到重试次数。即使业务代码没有显示重试,也有可能多次执行消费逻辑从而造成重复数据:
public class FailoverClusterInvoker<T> extends AbstractClusterInvoker<T> { public FailoverClusterInvoker(Directory<T> directory) { super(directory); } @Override public Result doInvoke(Invocation invocation, final List<Invoker<T>> invokers, LoadBalance loadbalance) throws RpcException { // 所有生产者Invokers List<Invoker<T>> copyInvokers = invokers; checkInvokers(copyInvokers, invocation); String methodName = RpcUtils.getMethodName(invocation); // 获取重试次数 int len = getUrl().getMethodParameter(methodName, Constants.RETRIES_KEY, Constants.DEFAULT_RETRIES) + 1; if (len <= 0) { len = 1; } RpcException le = null; // 已经调用过的生产者 List<Invoker<T>> invoked = new ArrayList<Invoker<T>>(copyInvokers.size()); Set<String> providers = new HashSet<String>(len); // 重试直到达到最大次数 for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) { if (i > 0) { // 如果当前实例被销毁则抛出异常 checkWhetherDestroyed(); // 根据路由策略选出可用生产者Invokers copyInvokers = list(invocation); // 重新检查 checkInvokers(copyInvokers, invocation); } // 负载均衡选择一个生产者Invoker Invoker<T> invoker = select(loadbalance, invocation, copyInvokers, invoked); invoked.add(invoker); RpcContext.getContext().setInvokers((List) invoked); try { // 服务消费发起远程调用 Result result = invoker.invoke(invocation); if (le != null && logger.isWarnEnabled()) { logger.warn("Although retry the method " + methodName + " in the service " + getInterface().getName() + " was successful by the provider " + invoker.getUrl().getAddress() + ", but there have been failed providers " + providers + " (" + providers.size() + "/" + copyInvokers.size() + ") from the registry " + directory.getUrl().getAddress() + " on the consumer " + NetUtils.getLocalHost() + " using the dubbo version " + Version.getVersion() + ". Last error is: " + le.getMessage(), le); } // 有结果则返回 return result; } catch (RpcException e) { // 业务异常直接抛出 if (e.isBiz()) { throw e; } le = e; } catch (Throwable e) { // RpcException不抛出继续重试 le = new RpcException(e.getMessage(), e); } finally { // 保存已经访问过的生产者 providers.add(invoker.getUrl().getAddress()); } } throw new RpcException(le.getCode(), "Failed to invoke the method " + methodName + " in the service " + getInterface().getName() + ". Tried " + len + " times of the providers " + providers + " (" + providers.size() + "/" + copyInvokers.size() + ") from the registry " + directory.getUrl().getAddress() + " on the consumer " + NetUtils.getLocalHost() + " using the dubbo version " + Version.getVersion() + ". Last error is: " + le.getMessage(), le.getCause() != null ? le.getCause() : le); }}消费者调用生产者节点A发生RpcException异常时(例如超时异常),在未达到最大重试次数之前,消费者会通过负载均衡策略再次选择其它生产者节点消费。试想如果生产者节点A其实已经处理成功了,但是没有及时将成功结果返回给消费者,那么再次重试可能就会造成重复数据问题。
2.2.2 Failfast
快速失败策略。消费者只消费一次服务,当发生异常时则直接抛出,不会进行重试:
public class FailfastClusterInvoker<T> extends AbstractClusterInvoker<T> { public FailfastClusterInvoker(Directory<T> directory) { super(directory); } @Override public Result doInvoke(Invocation invocation, List<Invoker<T>> invokers, LoadBalance loadbalance) throws RpcException { // 检查生产者Invokers是否合法 checkInvokers(invokers, invocation); // 负载均衡选择一个生产者Invoker Invoker<T> invoker = select(loadbalance, invocation, invokers, null); try { // 服务消费发起远程调用 return invoker.invoke(invocation); } catch (Throwable e) { // 服务消费失败不重试直接抛出异常 if (e instanceof RpcException && ((RpcException) e).isBiz()) { throw (RpcException) e; } throw new RpcException(e instanceof RpcException ? ((RpcException) e).getCode() : 0, "Failfast invoke providers " + invoker.getUrl() + " " + loadbalance.getClass().getSimpleName() + " select from all providers " + invokers + " for service " + getInterface().getName() + " method " + invocation.getMethodName() + " on consumer " + NetUtils.getLocalHost() + " use dubbo version " + Version.getVersion() + ", but no luck to perform the invocation. Last error is: " + e.getMessage(), e.getCause() != null ? e.getCause() : e); } }}2.2.3 Failsafe
安全失败策略。消费者只消费一次服务,如果消费失败则包装一个空结果,不抛出异常,不会进行重试:
public class FailsafeClusterInvoker<T> extends AbstractClusterInvoker<T> { private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(FailsafeClusterInvoker.class); public FailsafeClusterInvoker(Directory<T> directory) { super(directory); } @Override public Result doInvoke(Invocation invocation, List<Invoker<T>> invokers, LoadBalance loadbalance) throws RpcException { try { // 检查生产者Invokers是否合法 checkInvokers(invokers, invocation); // 负载均衡选择一个生产者Invoker Invoker<T> invoker = select(loadbalance, invocation, invokers, null); // 服务消费发起远程调用 return invoker.invoke(invocation); } catch (Throwable e) { // 消费失败包装为一个空结果对象 logger.error("Failsafe ignore exception: " + e.getMessage(), e); return new RpcResult(); } }}2.2.4 Failback
异步重试策略。当消费发生异常时返回一个空结果,失败请求将会进行异步重试。如果重试超过最大重试次数还不成功,放弃重试并不抛出异常:
public class FailbackClusterInvoker<T> extends AbstractClusterInvoker<T> { private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(FailbackClusterInvoker.class); private static final long RETRY_FAILED_PERIOD = 5; private final int retries; private final int failbackTasks; private volatile Timer failTimer; public FailbackClusterInvoker(Directory<T> directory) { super(directory); int retriesConfig = getUrl().getParameter(Constants.RETRIES_KEY, Constants.DEFAULT_FAILBACK_TIMES); if (retriesConfig <= 0) { retriesConfig = Constants.DEFAULT_FAILBACK_TIMES; } int failbackTasksConfig = getUrl().getParameter(Constants.FAIL_BACK_TASKS_KEY, Constants.DEFAULT_FAILBACK_TASKS); if (failbackTasksConfig <= 0) { failbackTasksConfig = Constants.DEFAULT_FAILBACK_TASKS; } retries = retriesConfig; failbackTasks = failbackTasksConfig; } private void addFailed(LoadBalance loadbalance, Invocation invocation, List<Invoker<T>> invokers, Invoker<T> lastInvoker) { if (failTimer == null) { synchronized (this) { if (failTimer == null) { // 创建定时器 failTimer = new HashedWheelTimer(new NamedThreadFactory("failback-cluster-timer", true), 1, TimeUnit.SECONDS, 32, failbackTasks); } } } // 构造定时任务 RetryTimerTask retryTimerTask = new RetryTimerTask(loadbalance, invocation, invokers, lastInvoker, retries, RETRY_FAILED_PERIOD); try { // 定时任务放入定时器等待执行 failTimer.newTimeout(retryTimerTask, RETRY_FAILED_PERIOD, TimeUnit.SECONDS); } catch (Throwable e) { logger.error("Failback background works error,invocation->" + invocation + ", exception: " + e.getMessage()); } } @Override protected Result doInvoke(Invocation invocation, List<Invoker<T>> invokers, LoadBalance loadbalance) throws RpcException { Invoker<T> invoker = null; try { // 检查生产者Invokers是否合法 checkInvokers(invokers, invocation); // 负责均衡选择一个生产者Invoker invoker = select(loadbalance, invocation, invokers, null); // 消费服务发起远程调用 return invoker.invoke(invocation); } catch (Throwable e) { logger.error("Failback to invoke method " + invocation.getMethodName() + ", wait for retry in background. Ignored exception: " + e.getMessage() + ", ", e); // 如果服务消费失败则记录失败请求 addFailed(loadbalance, invocation, invokers, invoker); // 返回空结果 return new RpcResult(); } } @Override public void destroy() { super.destroy(); if (failTimer != null) { failTimer.stop(); } } private class RetryTimerTask implements TimerTask { private final Invocation invocation; private final LoadBalance loadbalance; private final List<Invoker<T>> invokers; private final int retries; private final long tick; private Invoker<T> lastInvoker; private int retryTimes = 0; RetryTimerTask(LoadBalance loadbalance, Invocation invocation, List<Invoker<T>> invokers, Invoker<T> lastInvoker, int retries, long tick) { this.loadbalance = loadbalance; this.invocation = invocation; this.invokers = invokers; this.retries = retries; this.tick = tick; this.lastInvoker = lastInvoker; } @Override public void run(Timeout timeout) { try { // 负载均衡选择一个生产者Invoker Invoker<T> retryInvoker = select(loadbalance, invocation, invokers, Collections.singletonList(lastInvoker)); lastInvoker = retryInvoker; // 服务消费发起远程调用 retryInvoker.invoke(invocation); } catch (Throwable e) { logger.error("Failed retry to invoke method " + invocation.getMethodName() + ", waiting again.", e); // 超出最大重试次数记录日志不抛出异常 if ((++retryTimes) >= retries) { logger.error("Failed retry times exceed threshold (" + retries + "), We have to abandon, invocation->" + invocation); } else { // 未超出最大重试次数重新放入定时器 rePut(timeout); } } } private void rePut(Timeout timeout) { if (timeout == null) { return; } Timer timer = timeout.timer(); if (timer.isStop() || timeout.isCancelled()) { return; } timer.newTimeout(timeout.task(), tick, TimeUnit.SECONDS); } }}2.2.5 Forking
并行调用策略。消费者通过线程池并发调用多个生产者,只要有一个成功就算成功:
public class ForkingClusterInvoker<T> extends AbstractClusterInvoker<T> { private final ExecutorService executor = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(new NamedInternalThreadFactory("forking-cluster-timer", true)); public ForkingClusterInvoker(Directory<T> directory) { super(directory); } @Override public Result doInvoke(final Invocation invocation, List<Invoker<T>> invokers, LoadBalance loadbalance) throws RpcException { try { checkInvokers(invokers, invocation); final List<Invoker<T>> selected; // 获取配置参数 final int forks = getUrl().getParameter(Constants.FORKS_KEY, Constants.DEFAULT_FORKS); final int timeout = getUrl().getParameter(Constants.TIMEOUT_KEY, Constants.DEFAULT_TIMEOUT); // 获取并行执行的Invoker列表 if (forks <= 0 || forks >= invokers.size()) { selected = invokers; } else { selected = new ArrayList<>(); for (int i = 0; i < forks; i++) { // 选择生产者 Invoker<T> invoker = select(loadbalance, invocation, invokers, selected); // 防止重复增加Invoker if (!selected.contains(invoker)) { selected.add(invoker); } } } RpcContext.getContext().setInvokers((List) selected); final AtomicInteger count = new AtomicInteger(); final BlockingQueue<Object> ref = new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(); for (final Invoker<T> invoker : selected) { // 在线程池中并发执行 executor.execute(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { try { // 执行消费逻辑 Result result = invoker.invoke(invocation); // 存储消费结果 ref.offer(result); } catch (Throwable e) { // 如果异常次数大于等于forks参数值说明全部调用失败,则把异常放入队列 int value = count.incrementAndGet(); if (value >= selected.size()) { ref.offer(e); } } } }); } try { // 从队列获取结果 Object ret = ref.poll(timeout, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS); // 如果异常类型表示全部调用失败则抛出异常 if (ret instanceof Throwable) { Throwable e = (Throwable) ret; throw new RpcException(e instanceof RpcException ? ((RpcException) e).getCode() : 0, "Failed to forking invoke provider " + selected + ", but no luck to perform the invocation. Last error is: " + e.getMessage(), e.getCause() != null ? e.getCause() : e); } return (Result) ret; } catch (InterruptedException e) { throw new RpcException("Failed to forking invoke provider " + selected + ", but no luck to perform the invocation. Last error is: " + e.getMessage(), e); } } finally { RpcContext.getContext().clearAttachments(); } }}2.2.6 Broadcast
广播调用策略。消费者遍历调用所有生产者节点,任何一个出现异常则抛出异常:
public class BroadcastClusterInvoker<T> extends AbstractClusterInvoker<T> { private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(BroadcastClusterInvoker.class); public BroadcastClusterInvoker(Directory<T> directory) { super(directory); } @Override public Result doInvoke(final Invocation invocation, List<Invoker<T>> invokers, LoadBalance loadbalance) throws RpcException { checkInvokers(invokers, invocation); RpcContext.getContext().setInvokers((List) invokers); RpcException exception = null; Result result = null; // 遍历调用所有生产者节点 for (Invoker<T> invoker : invokers) { try { // 执行消费逻辑 result = invoker.invoke(invocation); } catch (RpcException e) { exception = e; logger.warn(e.getMessage(), e); } catch (Throwable e) { exception = new RpcException(e.getMessage(), e); logger.warn(e.getMessage(), e); } } // 任何一个出现异常则抛出异常 if (exception != null) { throw exception; } return result; }}3 怎么做幂等
经过上述分析我们知道,RPC框架自带的重试机制可能会造成数据重复问题,那么在使用中必须考虑幂等性。幂等性是指一次操作与多次操作产生结果相同,并不会因为多次操作而产生不一致性。常见幂等方案有取消重试、幂等表、数据库锁、状态机。
3.1 取消重试
取消重试有两种方法,第一是设置重试次数为零,第二是选择不重试的集群容错策略。
<!-- 设置重试次数为零 --><dubbo:reference id="helloService" interface="com.java.front.dubbo.demo.provider.HelloService" retries="0" /><!-- 选择集群容错方案 --><dubbo:reference id="helloService" interface="com.java.front.dubbo.demo.provider.HelloService" cluster="failfast" />3.2 幂等表
假设用户支付成功后,支付系统将支付成功消息,发送至消息队列。物流系统订阅到这个消息,准备为这笔订单创建物流单。
但是消息队列可能会重复推送,物流系统有可能接收到多次这条消息。我们希望达到效果是:无论接收到多少条重复消息,只能创建一笔物流单。
解决方案是幂等表方案。新建一张幂等表,该表就是用来做幂等,无其它业务意义,有一个字段名为key建有唯一索引,这个字段是幂等标准。
物流系统订阅到消息后,首先尝试插入幂等表,订单编号作为key字段。如果成功则继续创建物流单,如果订单编号已经存在则违反唯一性原则,无法插入成功,说明已经进行过业务处理,丢弃消息。
这张表数据量会比较大,我们可以通过定时任务对数据进行归档,例如只保留7天数据,其它数据存入归档表。
还有一种广义幂等表就是我们可以用Redis替代数据库,在创建物流单之前,我们可以检查Redis是否存在该订单编号数据,同时可以为这类数据设置7天过期时间。
3.3 状态机
物流单创建成功后会发送消息,订单系统订阅到消息后更新状态为完成,假设变更是将订单状态0更新至状态1。订单系统也可能收到多条消息,可能在状态已经被更新至状态1之后,依然收到物流单创建成功消息。
解决方案是状态机方案。首先绘制状态机图,分析状态流转形态。例如经过分析状态1已经是最终态,那么即使接收到物流单创建成功消息也不再处理,丢弃消息。
3.4 数据库锁
数据库锁又可以分为悲观锁和乐观锁两种类型,悲观锁是在获取数据时加锁:
select * from table where col='xxx' for update乐观锁是在更新时加锁,第一步首先查出数据,数据包含version字段。第二步进行更新操作,如果此时记录已经被修改则version字段已经发生变化,无法更新成功:
update table set xxx,version = #{version} + 1 where id = #{id} and version = #{version}关于“java重试机制使用RPC要考虑什么”的内容就介绍到这里了,感谢大家的阅读。如果想了解更多行业相关的知识,可以关注编程网行业资讯频道,小编每天都会为大家更新不同的知识点。
免责声明:
① 本站未注明“稿件来源”的信息均来自网络整理。其文字、图片和音视频稿件的所属权归原作者所有。本站收集整理出于非商业性的教育和科研之目的,并不意味着本站赞同其观点或证实其内容的真实性。仅作为临时的测试数据,供内部测试之用。本站并未授权任何人以任何方式主动获取本站任何信息。
② 本站未注明“稿件来源”的临时测试数据将在测试完成后最终做删除处理。有问题或投稿请发送至: 邮箱/279061341@qq.com QQ/279061341




















