【一起学数据结构与算法】Java实现双链表
目录
一、双链表的概念
双向链表也叫双链表,是链表的一种,它的每个数据结点中都有两个指针,分别指向直接后继和直接前驱。所以,从双向链表中的任意一个结点开始,都可以很方便地访问它的前驱结点和后继结点。一般我们都构造双向循环链表。
二、双链表一些方法的实现
2.1 双链表的属性
class ListNode { public int val; public ListNode prev; public ListNode next; public ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }}public class MyLinkedList { public ListNode head;//指向双向链表的头节点 public ListNode last;//指向的是尾巴结点 }2.2 打印双链表
打印双链表非常简单,只需要单独创一个结点cur来遍历链表并打印
//打印双向链表public void display() { //和单链表的打印方式是一样的 ListNode cur = this.head; while (cur != null) { System.out.print(cur.val + " "); cur = cur.next; } System.out.println(); }2.3 得到双链表的长度
单独创一个结点cur来遍历链表同时创一个count计数器来计算长度即可
//得到双链表的长度 public int size() { ListNode cur = this.head; int count = 0; while (cur != null) { count++; cur = cur.next; } return count; }2.4 查找是否包含关键字key是否在双链表中
单独创一个结点cur来遍历链表并且判断是否包含key
//查找是否包含关键字key是否在双链表中 public boolean contains(int key) { ListNode cur = this.head; while (cur != null) { if (cur.val == key) { return true; } cur = cur.next; } return false; }2.5 头插法
当我们想把新的结点插入到第一个结点位置处,可以先建立一个结点,然后把头结点的prev变为我们新建立结点的next值,然后将我们新建立的结点值变为null,最后将头结点指向新的插入的结点。
注意我们需要首先判断这个链表是否为空,假如为空就直接构建链表即可
//头插法 public void addFirst(int data) { ListNode node = new ListNode(data); if (this.head == null) { this.head = node; this.last = node; } else { node.next = this.head; head.prev = node; this.head = node; } }2.6 尾插法
尾插法顾名思义就是从结尾插入新的结点,这个和头插法过程差不多,只不过一个是改变head的位置,一个是改变last的位置。
和头插法一样,这个同样需要判断链表是否初始为空
//尾插法 public void addLast(int data) { ListNode node = new ListNode(data); if (this.head == null) { this.head = node; this.last = node; } else { this.last.next = node; node.prev = this.last; this.last = node; } }2.7 任意位置插入,第一个数据结点为0号下标
首先要考虑,插入的位置是头部或尾部或中间。根据具体的位置实现具体的操作。
如果是头部,直接调用头插,如果是尾部,就直接调用尾插即可。
如果是中间插的的话:
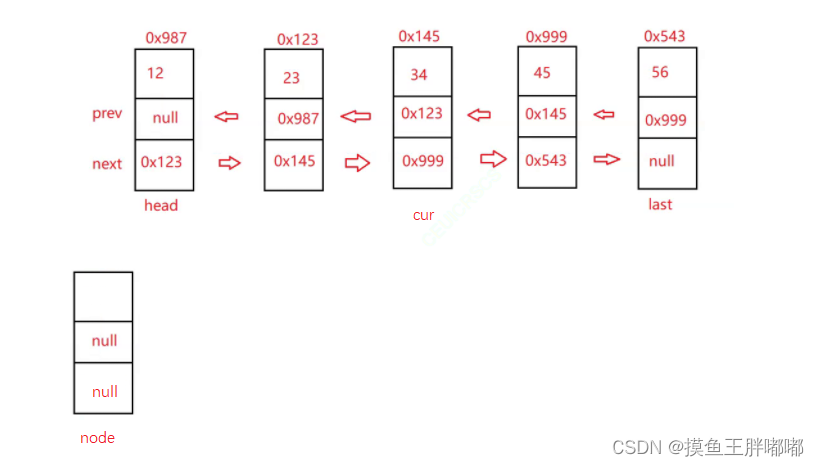
1.node.next = cur.prev.next;
2.cur.prev.next = node;
3.node.prev = cur.prev;
4.cur.prev = node;

public ListNode searchIndex(int index) { ListNode cur = this.head; while (index != 0) { cur = cur.next; index--; } return cur; } //任意位置插入,第一个数据结点为0号下标 public void addIndex(int index, int data) { ListNode node = new ListNode(data); if (index < 0 || index >size()) { System.out.println("index位置不合法!"); return; } if (index == 0) { addFirst(data); return; } if (index == size()) { addLast(data); return; } ListNode cur = searchIndex(index); node.next = cur.prev.next; cur.prev.next = node; node.prev = cur.prev; cur.prev = node; }2.8 删除第一次出现为key的结点
假如是头结点的话我们还需要判断这个链表是否只有一个结点,如果是那么last指针也会为空,head指针也会为空,否则,我们只移动头指针结点就可以
当删除中间结点的时候我们可以先找到对于位置的结点cur,利用对应位置的cur.prev和cur.next确定附近两个结点,然后进行删除即可,这个删除与链表相似,只是多了一个删除头结点而已。
//删除第一次出现为key的结点 public void remove(int key) { ListNode cur = this.head; while (cur != null) { if (cur.val == key) { if (cur == head) { this.head = this.head.next; if (this.head != null) { this.head.prev = null; } else { this.last = null; } } else { cur.prev.next = cur.next; if (cur.next != null) { cur.next.prev = cur.prev; } else { this.last = this.last.prev; } } return; } cur = cur.next; } }2.9 删除所有key的值
//删除所有key的值 public void removeAllKey(int key) { ListNode cur = this.head; while (cur != null) { if (cur.val == key) { if (cur == head) { this.head = this.head.next; if (this.head != null) { this.head.prev = null; } else { this.last = null; } } else { cur.prev.next = cur.next; if (cur.next != null) { cur.next.prev = cur.prev; } else { this.last = this.last.prev; } } } cur = cur.next; } }2.10 清空双链表
//清空双链表 public void clear() { while (this.head != null) { ListNode curNext = head.next; this.head.next = null; this.head.prev = null; this.head = curNext; } last = null; }三、MyLinkedList.java
class ListNode { public int val; public ListNode prev; public ListNode next; public ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }}public class MyLinkedList { public ListNode head;//指向双向链表的头节点 public ListNode last;//指向的是尾巴结点 //打印双向链表 public void display() { //和单链表的打印方式是一样的 ListNode cur = this.head; while (cur != null) { System.out.print(cur.val + " "); cur = cur.next; } System.out.println(); } //得到双链表的长度 public int size() { ListNode cur = this.head; int count = 0; while (cur != null) { count++; cur = cur.next; } return count; } //查找是否包含关键字key是否在双链表中 public boolean contains(int key) { ListNode cur = this.head; while (cur != null) { if (cur.val == key) { return true; } cur = cur.next; } return false; } //头插法 public void addFirst(int data) { ListNode node = new ListNode(data); if (this.head == null) { this.head = node; this.last = node; } else { node.next = this.head; head.prev = node; this.head = node; } } //尾插法 public void addLast(int data) { ListNode node = new ListNode(data); if (this.head == null) { this.head = node; this.last = node; } else { this.last.next = node; node.prev = this.last; this.last = node; } } public ListNode searchIndex(int index) { ListNode cur = this.head; while (index != 0) { cur = cur.next; index--; } return cur; } //任意位置插入,第一个数据结点为0号下标 public void addIndex(int index, int data) { ListNode node = new ListNode(data); if (index < 0 || index >size()) { System.out.println("index位置不合法!"); return; } if (index == 0) { addFirst(data); return; } if (index == size()) { addLast(data); return; } ListNode cur = searchIndex(index); node.next = cur.prev.next; cur.prev.next = node; node.prev = cur.prev; cur.prev = node; } //删除第一次出现为key的结点 public void remove(int key) { ListNode cur = this.head; while (cur != null) { if (cur.val == key) { if (cur == head) { this.head = this.head.next; if (this.head != null) { this.head.prev = null; } else { this.last = null; } } else { cur.prev.next = cur.next; if (cur.next != null) { cur.next.prev = cur.prev; } else { this.last = this.last.prev; } } return; } cur = cur.next; } } //删除所有key的值 public void removeAllKey(int key) { ListNode cur = this.head; while (cur != null) { if (cur.val == key) { if (cur == head) { this.head = this.head.next; if (this.head != null) { this.head.prev = null; } else { this.last = null; } } else { cur.prev.next = cur.next; if (cur.next != null) { cur.next.prev = cur.prev; } else { this.last = this.last.prev; } } } cur = cur.next; } } //清空双链表 public void clear() { while (this.head != null) { ListNode curNext = head.next; this.head.next = null; this.head.prev = null; this.head = curNext; } last = null; }}四、Test.java
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { MyLinkedList myLinkedList = new MyLinkedList(); myLinkedList.addFirst(1); myLinkedList.addFirst(2); myLinkedList.addFirst(3); myLinkedList.addFirst(4); System.out.println(myLinkedList.size()); myLinkedList.display(); System.out.println(myLinkedList.contains(1)); myLinkedList.addLast(1); myLinkedList.addLast(2); myLinkedList.addLast(3); myLinkedList.addLast(4); myLinkedList.display(); myLinkedList.remove(1); myLinkedList.display(); myLinkedList.removeAllKey(4); myLinkedList.display(); myLinkedList.addIndex(0,99); myLinkedList.display(); myLinkedList.clear(); myLinkedList.display(); }}五、效果展示

来源地址:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_61341342/article/details/127136237
免责声明:
① 本站未注明“稿件来源”的信息均来自网络整理。其文字、图片和音视频稿件的所属权归原作者所有。本站收集整理出于非商业性的教育和科研之目的,并不意味着本站赞同其观点或证实其内容的真实性。仅作为临时的测试数据,供内部测试之用。本站并未授权任何人以任何方式主动获取本站任何信息。
② 本站未注明“稿件来源”的临时测试数据将在测试完成后最终做删除处理。有问题或投稿请发送至: 邮箱/279061341@qq.com QQ/279061341















