TKMybatis的使用方法是什么
本篇内容介绍了“TKMybatis的使用方法是什么”的有关知识,在实际案例的操作过程中,不少人都会遇到这样的困境,接下来就让小编带领大家学习一下如何处理这些情况吧!希望大家仔细阅读,能够学有所成!
一、什么是 TKMybatis
TKMybatis 是基于 Mybatis 框架开发的一个工具,内部实现了对单表的基本数据操作,只需要简单继承 TKMybatis 提供的接口,就能够实现无需编写任何 sql 即能完成单表操作。
二、TKMybatis 使用
2.1 Springboot 项目中加入依赖
<!--通用mapper起步依赖--><dependency> <groupId>tk.mybatis</groupId> <artifactId>mapper-spring-boot-starter</artifactId> <version>2.0.4</version></dependency>在 POJO 类中加入依赖
<!--每个工程都有Pojo,都需要用到该包对应的注解--><dependency> <groupId>javax.persistence</groupId> <artifactId>persistence-api</artifactId> <version>1.0</version> <scope>compile</scope></dependency>在启动类中配置 @MapperScan 扫描
@SpringBootApplication@MapperScan(basePackages = {"com.tom.order.mapper"})public class OrderApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(OrderApplication.class, args); }}2.2 使用讲解
2.1 实体类中使用
在实体类中,常用的注解和意义为:
@Table:描述数据库表信息,主要属性有name(表名)、schema、catalog、uniqueConstraints等。
@Id:指定表主键字段,无属性值。
@Column:描述数据库字段信息,主要属性有name(字段名)、columnDefinition、insertable、length、nullable(是否可为空)、precision、scale、table、unique、updatable等。
@ColumnType:描述数据库字段类型,可对一些特殊类型作配置,进行特殊处理,主要属性有jdbcType、column、typeHandler等。
其他注解如:@Transient、@ColumnResult、@JoinColumn、@OrderBy、@Embeddable等暂不描述
2.2 dao中使用
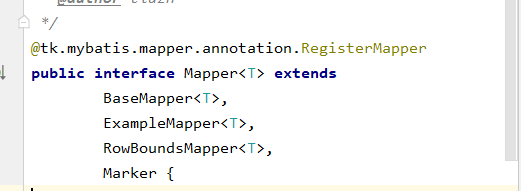
单表操作,只需要继承 tk.mybatis 下的 Mapper 接口即可使用
import tk.mybatis.mapper.common.Mapper; @Repositorypublic interface BrandMapper extends Mapper<Brand> {}查看具体使用:内部都已经封装了基本的单表操作

2.2.3 Service 层中使用
| 操作 | 类型 | 介绍 |
| 增加 | Mapper.insert(record); | 保存一个实体,null的属性也会保存,不会使用数据库默认值 |
| Mapper.insertSelective(record); | 保存一个实体,忽略空值,即没提交的值会使用使用数据库默认值 | |
| 删除 | Mapper.delete(record); | 根据实体属性作为条件进行删除,查询条件使用等号 |
| Mapper.deleteByExample(example) | 根据Example条件删除数据 | |
| Mapper.deleteByPrimaryKey(key) | 根据主键字段进行删除,方法参数必须包含完整的主键属性 | |
| 修改 | Mapper.updateByExample(record,example) | 根据Example条件更新实体`record`包含的全部属性,null值会被更新 |
| Mapper.updateByExampleSelective(record, example) | 根据Example条件更新实体`record`包含的不是null的属性值 | |
| Mapper.updateByPrimaryKey(record) | 根据主键更新实体全部字段,null值会被更新 | |
| Mapper.updateByPrimaryKeySelective(record) | 根据主键更新属性不为null的值 | |
| 查询 | Mapper.select(record) | 根据实体中的属性值进行查询,查询条件使用等号 |
| Mapper.selectAll() | 查询全部结果 | |
| Mapper.selectByExample(example) | 根据Example条件进行查询 | |
| Mapper.selectByPrimaryKey(key) | 根据主键字段进行查询,方法参数必须包含完整的主键属性,查询条件使用等号 | |
| Mapper.selectCount(record) | 根据实体中的属性查询总数,查询条件使用等号 | |
| Mapper.selectCountByExample(example) | 根据Example条件进行查询总数 | |
| Mapper.selectOne(record) | 根据实体中的属性进行查询,只能有一个返回值,有多个结果是抛出异常,查询条件使用等号。 但是如果存在某个属性为int,则会初始化为0。可能影响到实际使用 | |
2.3 实际案例
1 dao 层使用
import tk.mybatis.mapper.common.Mapper; @Repositorypublic interface BrandMapper extends Mapper<Brand> { }2 service 层使用
import com.github.pagehelper.PageHelper;import com.github.pagehelper.PageInfo;import org.apache.commons.lang.StringUtils;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;import tk.mybatis.mapper.entity.Example; import java.util.List; @Servicepublic class BrandServiceImpl implements BrandService { @Autowired private BrandMapper brandMapper; public Example createExample(Brand brand) { // 自定义条件搜索对象 Example Example example = new Example(Brand.class); Example.Criteria criteria = example.createCriteria(); //条件构造器 if (brand != null) { if (!StringUtils.isEmpty(brand.getName())) { criteria.andLike("name", '%' + brand.getName() + '%'); } if (!StringUtils.isEmpty(brand.getLetter())) { criteria.andEqualTo("letter", brand.getLetter()); } } return example; } @Override public List<Brand> findAll() { return brandMapper.selectAll(); } @Override public List<Brand> findList(Brand brand) { Example example = createExample(brand); return brandMapper.selectByExample(example); } @Override public Brand findById(Integer id) { return brandMapper.selectByPrimaryKey(id); } @Override public PageInfo<Brand> pageSearch(Integer page, Integer size) { // 分页实现 // 后面的查询必须是紧跟集合查询 PageHelper.startPage(page, size); // 查询集合 List<Brand> brands = brandMapper.selectAll(); return new PageInfo<Brand>(brands); } @Override public PageInfo<Brand> pageSearchAndCondition(Brand brand, Integer page, Integer size) { // 开始分页 PageHelper.startPage(page, size); // 搜索数据 Example example = createExample(brand); List<Brand> list = brandMapper.selectByExample(example); return new PageInfo<Brand>(list); } @Override public void add(Brand brand) { // 使用通用 Mapper.insertSelective // 方法中但凡带有selective就会忽略空值 int i = brandMapper.insertSelective(brand); } @Override public void update(Brand brand) { // 使用通用mapper.update(); brandMapper.updateByPrimaryKeySelective(brand); } @Override public void del(Integer id) { brandMapper.deleteByPrimaryKey(id); }}三、扩展介绍
使用
public interface BaseMapper<T> extends tk.mybatis.mapper.common.BaseMapper<T>, IdsMapper<T>, MySqlMapper<T>, OracleMapper<T> {}pom.xml引入<dependency> <groupId>tk.mybatis</groupId> <artifactId>mapper-spring-boot-starter</artifactId> <version>2.1.5</version></dependency>注:为了演示所以同时引用了MySqlMapper和OracleMapper 正常情况是只能引用一种因为他们有一个相同的方法insertList(List list)
泛型(实体类)的类型必须符合要求
实体类按照如下规则和数据库表进行转换,注解全部是JPA中的注解:
表名默认使用类名,驼峰转下划线(只对大写字母进行处理),如UserInfo默认对应的表名为user_info。
表名可以使用@Table(name = “tableName”)进行指定,对不符合第一条默认规则的可以通过这种方式指定表名。
字段默认和@Column一样,都会作为表字段,表字段默认为Java对象的Field名字驼峰转下划线形式。
可以使用@Column(name = “fieldName”)指定不符合第3条规则的字段名。
使用@Transient注解可以忽略字段,添加该注解的字段不会作为表字段使用。
建议一定是有一个@Id注解作为主键的字段,可以有多个@Id注解的字段作为联合主键。
所有的mapper继承此类将具有以下通用方法
查询方法
BaseSelectMapper下的通用方法
| 方法名称 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| List selectAll(); | 查询全部数据 |
| T selectByPrimaryKey(Object key); | 通过主键查询 |
| T selectOne(T record); | 通过实体查询单个数据 |
| List select(T record); | 通过实体查询多个数据 |
| int selectCount(T record); | 通过实体查询实体数量 |
| boolean existsWithPrimaryKey(Object key); | 通过主键查询此主键是否存在 |
SelectByIdsMapper下的通用方法
| 方法名称 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| List selectByIds(String var1); | 通过多个主键查询数据 |
添加方法
BaseInsertMapper下的通用方法
| 方法名称 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| int insert(T record); | 全部添加 |
| int insertSelective(T record); | 选择性(不为null)的添加 |
MySqlMapper下的通用方法
| 方法名称 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| int insertList(List list); | 批量插入 |
| int insertUseGeneratedKeys(T record); | 如果主键为自增可使用此方法获取添加成功的主键 |
OracleMapper下的通用方法
| 方法名称 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| int insertList(List list); | 批量插入 |
修改方法
BaseUpdateMapper下的通用方法
| 方法名称 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| int updateByPrimaryKey(T record); | 按照实体进行修改 |
| int updateByPrimaryKeySelective(T record); | 按照实体进行有选择的修改 |
删除方法
BaseDeleteMapper下的通用方法
| 方法名称 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| int delete(T record); | 按照实体进行删除 |
| int deleteByPrimaryKey(Object o); | 按照主键进行删除 |
IdsMapper下的通用方法
| 方法名称 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| int deleteByIds(String var1); | 按照主键批量删除 |
“TKMybatis的使用方法是什么”的内容就介绍到这里了,感谢大家的阅读。如果想了解更多行业相关的知识可以关注编程网网站,小编将为大家输出更多高质量的实用文章!
免责声明:
① 本站未注明“稿件来源”的信息均来自网络整理。其文字、图片和音视频稿件的所属权归原作者所有。本站收集整理出于非商业性的教育和科研之目的,并不意味着本站赞同其观点或证实其内容的真实性。仅作为临时的测试数据,供内部测试之用。本站并未授权任何人以任何方式主动获取本站任何信息。
② 本站未注明“稿件来源”的临时测试数据将在测试完成后最终做删除处理。有问题或投稿请发送至: 邮箱/279061341@qq.com QQ/279061341




















