改进YOLO系列:改进YOLOv8,教你YOLOv8如何添加20多种注意力机制,并实验不同位置。
改进YOLOv8,YOLOv8添加20多种注意力机制
一、注意力机制介绍
注意力机制(Attention Mechanism)是深度学习中一种重要的技术,它可以帮助模型更好地关注输入数据中的关键信息,从而提高模型的性能。注意力机制最早在自然语言处理领域的序列到序列(seq2seq)模型中得到广泛应用,后来逐渐扩展到了计算机视觉、语音识别等多个领域。
注意力机制的基本思想是为输入数据的每个部分分配一个权重,这个权重表示该部分对于当前任务的重要程度。在自然语言处理任务中,这通常意味着对输入句子中的每个单词分配一个权重,而在计算机视觉任务中,这可能意味着为输入图像的每个像素或区域分配一个权重。
二.添加方法
1.GAM注意力
论文原文:https://arxiv.org/pdf/2112.05561v1.pdf
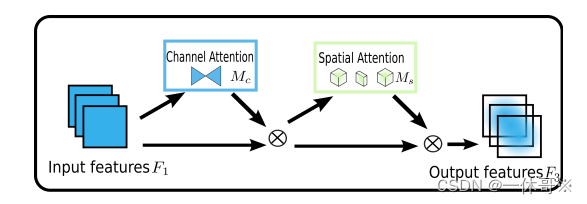
该论文提出了一种全局注意力机制(GAM),可以通过保留空间和通道信息之间的关联来提高模型的性能。GAM能够有效地捕捉不同通道之间的相关性,进而更好地区分不同的目标。
网络结构图:
import torch.nn as nnimport torch class GAM_Attention(nn.Module): def __init__(self, in_channels,c2, rate=4): super(GAM_Attention, self).__init__() self.channel_attention = nn.Sequential( nn.Linear(in_channels, int(in_channels / rate)), nn.ReLU(inplace=True), nn.Linear(int(in_channels / rate), in_channels) ) self.spatial_attention = nn.Sequential( nn.Conv2d(in_channels, int(in_channels / rate), kernel_size=7, padding=3), nn.BatchNorm2d(int(in_channels / rate)), nn.ReLU(inplace=True), nn.Conv2d(int(in_channels / rate), in_channels, kernel_size=7, padding=3), nn.BatchNorm2d(in_channels) ) def forward(self, x): b, c, h, w = x.shape x_permute = x.permute(0, 2, 3, 1).view(b, -1, c) x_att_permute = self.channel_attention(x_permute).view(b, h, w, c) x_channel_att = x_att_permute.permute(0, 3, 1, 2).sigmoid() x = x * x_channel_att x_spatial_att = self.spatial_attention(x).sigmoid() out = x * x_spatial_att return out if __name__ == '__main__': x = torch.randn(1, 64, 20, 20) b, c, h, w = x.shape net = GAM_Attention(in_channels=c) y = net(x) print(y.size())添加方法1
此方法适用于较早版本的yolov8代码,最新的yolov8代码加入方式看方法2
##将以上代码放到ultralytics/nn/modules.py里
在tasks.py里要加入from yltralytics.nn.modules import *
在ultralytics/nn/tasks.py处引用
注册以下代码:
# """**************add Attention***************""" elif m in {GAM_Attention}: c1, c2 = ch[f], args[0] if c2 != nc: # if not output c2 = make_divisible(min(c2, max_channels) * width, 8) args = [c1, c2, *args[1:]]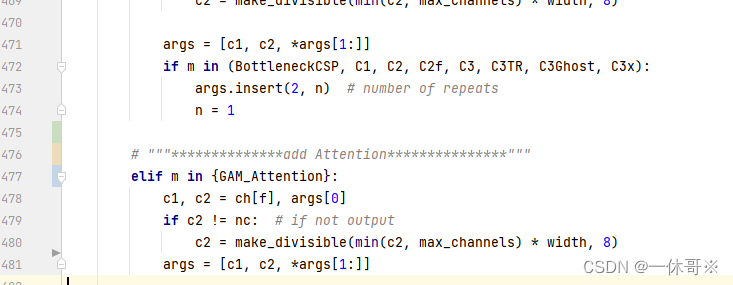
2.骨干中添加
新建yaml文件
添加方法2
1.block代码中加入注意力代码

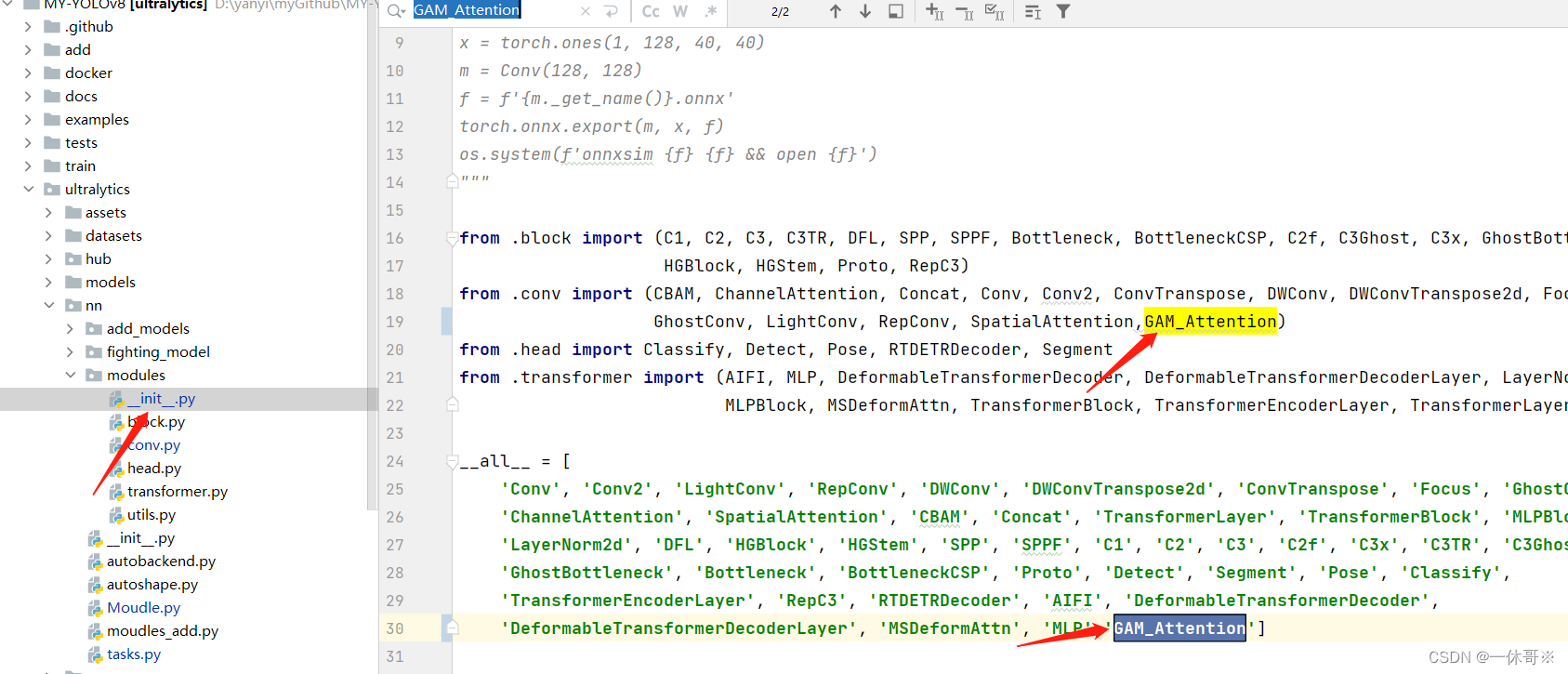
2.注册及引用GAM注意力代码
ultralytics/nn/modules/init.py文件中
ultralytics/nn/tasks.py文件中
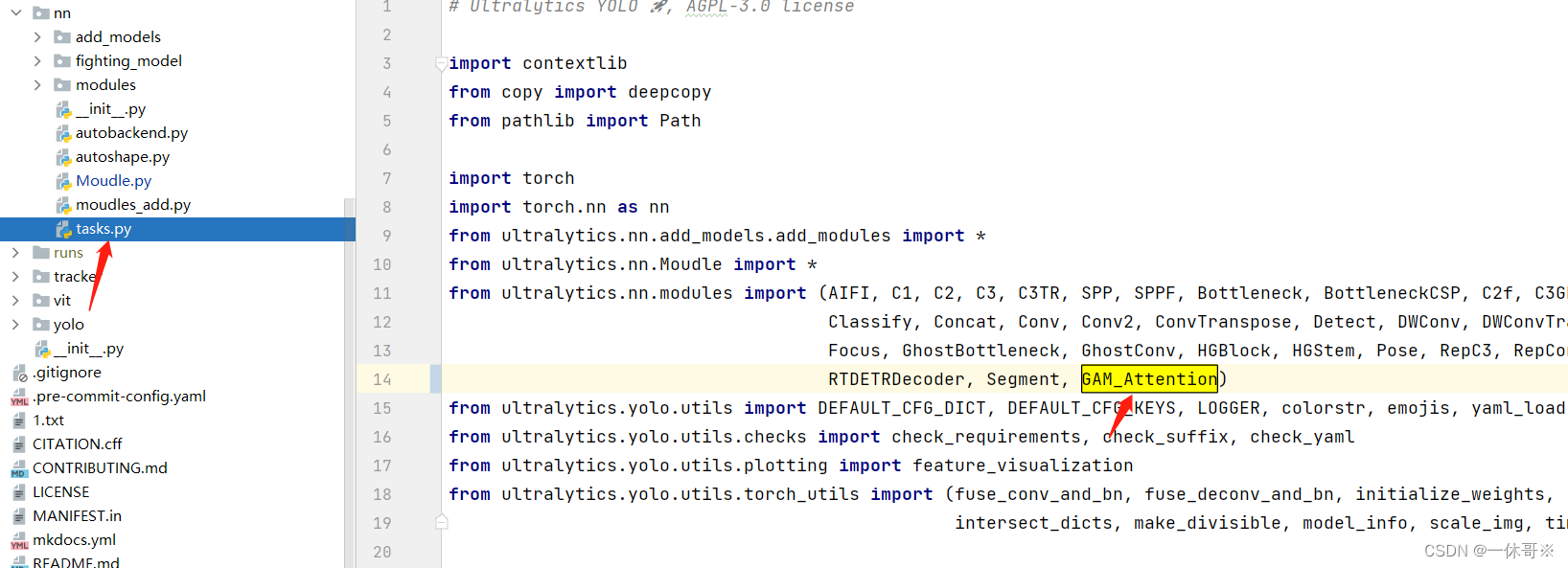
tasks里写入调用方式
# """**************add Attention***************""" elif m in {GAM_Attention}: c1, c2 = ch[f], args[0] if c2 != nc: # if not output c2 = make_divisible(min(c2, max_channels) * width, 8) args = [c1, c2, *args[1:]]示例
yaml文件
# Ultralytics YOLO 🚀, GPL-3.0 license# YOLOv8 object detection model with P3-P5 outputs. For Usage examples see https://docs.ultralytics.com/tasks/detect# Parametersnc: 80 # number of classesscales: # model compound scaling constants, i.e. 'model=yolov8n.yaml' will call yolov8-SPPCSPC.yaml with scale 'n' # [depth, width, max_channels] n: [0.33, 0.25, 1024] # YOLOv8n summary: 225 layers, 3157200 parameters, 3157184 gradients, 8.9 GFLOPs s: [0.33, 0.50, 1024] # YOLOv8s summary: 225 layers, 11166560 parameters, 11166544 gradients, 28.8 GFLOPs m: [0.67, 0.75, 768] # YOLOv8m summary: 295 layers, 25902640 parameters, 25902624 gradients, 79.3 GFLOPs l: [1.00, 1.00, 512] # YOLOv8l summary: 365 layers, 43691520 parameters, 43691504 gradients, 165.7 GFLOPs x: [1.00, 1.25, 512] # YOLOv8x summary: 365 layers, 68229648 parameters, 68229632 gradients, 258.5 GFLOPs# YOLOv8.0n backbonebackbone: # [from, repeats, module, args] - [-1, 1, Conv, [64, 3, 2]] # 0-P1/2 - [-1, 1, Conv, [128, 3, 2]] # 1-P2/4 - [-1, 3, C2f, [128, True]] - [-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]] # 3-P3/8 - [-1, 6, C2f, [256, True]] - [-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]] # 5-P4/16 - [-1, 6, C2f, [512, True]] - [-1, 1, Conv, [1024, 3, 2]] # 7-P5/32 - [-1, 3, C2f, [1024, True]] - [-1, 3, GAM_Attention, [1024]] - [-1, 1, SPPF, [1024, 5]] # 10# YOLOv8.0n headhead: - [-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']] - [[-1, 6], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat backbone P4 - [-1, 3, C2f, [512]] # 13 - [-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']] - [[-1, 4], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat backbone P3 - [-1, 3, C2f, [256]] # 16 (P3/8-small) - [-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]] - [[-1, 13], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat head P4 - [-1, 3, C2f, [512]] # 19 (P4/16-medium) - [-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]] - [[-1, 10], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat head P5 - [-1, 3, C2f, [1024]] # 22 (P5/32-large) - [[16, 19, 22], 1, Detect, [nc]] # Detect(P3, P4, P5)源目录下新建py文件,运行即可
from ultralytics import YOLOif __name__ == '__main__': # 加载模型 model = YOLO("yolov8s-Backbone-ATT.yaml") # 从头开始构建新模型 # model = YOLO("yolov8s.pt") # 加载预训练模型(推荐用于训练) # Use the model results = model.train(data="VOC_five.yaml", epochs=150, batch=16, workers=8, close_mosaic=0, name='cfg') # 训练模型 # results = model.val() # 在验证集上评估模型性能 # results = model("https://ultralytics.com/images/bus.jpg") # 预测图像 # success = model.export(format="onnx") # 将模型导出为 ONNX 格式注意:yolov8s表示为调用s模型结构
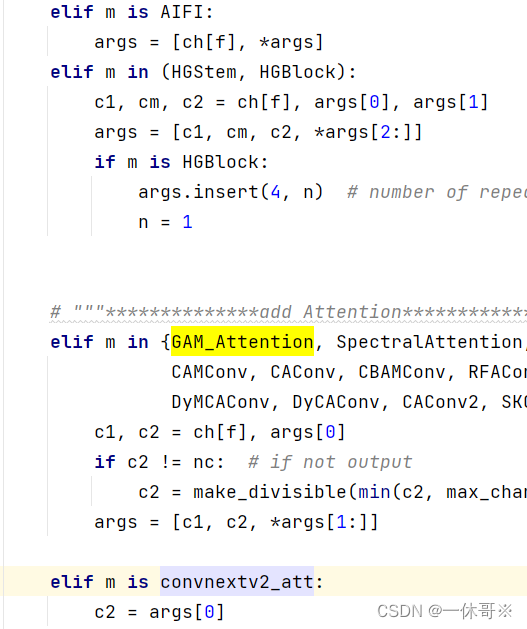
3. 瓶颈模块中添加
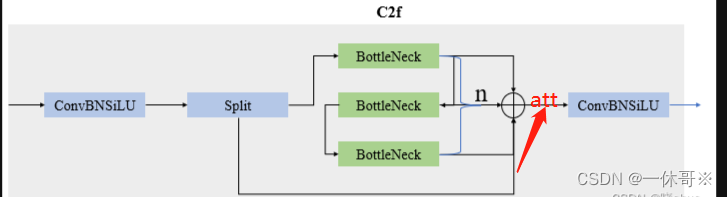
代码:此代码实现了可以选择在一层中加入注意力机制,将0改为1即可
# Ultralytics YOLO 🚀, GPL-3.0 license# YOLOv8 object detection model with P3-P5 outputs. For Usage examples see https://docs.ultralytics.com/tasks/detect# Parametersnc: 80 # number of classesscales: # model compound scaling constants, i.e. 'model=yolov8n.yaml' will call yolov8-SPPCSPC.yaml with scale 'n' # [depth, width, max_channels] n: [0.33, 0.25, 1024] # YOLOv8n summary: 225 layers, 3157200 parameters, 3157184 gradients, 8.9 GFLOPs s: [0.33, 0.50, 1024] # YOLOv8s summary: 225 layers, 11166560 parameters, 11166544 gradients, 28.8 GFLOPs m: [0.67, 0.75, 768] # YOLOv8m summary: 295 layers, 25902640 parameters, 25902624 gradients, 79.3 GFLOPs l: [1.00, 1.00, 512] # YOLOv8l summary: 365 layers, 43691520 parameters, 43691504 gradients, 165.7 GFLOPs x: [1.00, 1.25, 512] # YOLOv8x summary: 365 layers, 68229648 parameters, 68229632 gradients, 258.5 GFLOPs# YOLOv8.0n backbonebackbone: # [from, repeats, module, args] - [-1, 1, Conv, [64, 3, 2]] # 0-P1/2 - [-1, 1, Conv, [128, 3, 2]] # 1-P2/4 - [-1, 3, C2f_Bottleneck_ATT, [128, True, 0]] - [-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]] # 3-P3/8 - [-1, 6, C2f_Bottleneck_ATT, [256, True, 0]] - [-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]] # 5-P4/16 - [-1, 6, C2f_Bottleneck_ATT, [512, True, 0]] - [-1, 1, Conv, [1024, 3, 2]] # 7-P5/32 - [-1, 3, C2f_Bottleneck_ATT, [1024, True, 0]] - [-1, 1, SPPF, [1024, 5]] # 9# YOLOv8.0n headhead: - [-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']] - [[-1, 6], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat backbone P4 - [-1, 3, C2f_Bottleneck_ATT, [512]] # 12 - [-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']] - [[-1, 4], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat backbone P3 - [-1, 3, C2f_Bottleneck_ATT, [256]] # 15 (P3/8-small) - [-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]] - [[-1, 12], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat head P4 - [-1, 3, C2f_Bottleneck_ATT, [512]] # 18 (P4/16-medium) - [-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]] - [[-1, 9], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat head P5 - [-1, 3, C2f_Bottleneck_ATT, [1024]] # 21 (P5/32-large) - [[15, 18, 21], 1, Detect, [nc]] # Detect(P3, P4, P5)C2f_Bottleneck_ATT代码,添加到common里:
class C2f_Bottleneck_ATT(nn.Module): # CSP Bottleneck with 2 convolutions def __init__(self, c1, c2, n=1, shortcut=False, use_ATT=0., g=1, e=0.5): # ch_in, ch_out, number, shortcut, groups, expa super().__init__() self.c = int(c2 * e) # hidden channels self.cv1 = Conv(c1, 2 * self.c, 1, 1) self.cv2 = Conv((2 + n) * self.c, c2, 1) # optional act=FReLU(c2) self.m = nn.ModuleList( Bottleneck_ATT(self.c, self.c, shortcut, g, k=((3, 3), (3, 3)), e=1.0, use_ATT=use_ATT) for _ in range(n)) def forward(self, x): y = list(self.cv1(x).chunk(2, 1)) y.extend(m(y[-1]) for m in self.m) return self.cv2(torch.cat(y, 1)) def forward_split(self, x): y = list(self.cv1(x).split((self.c, self.c), 1)) y.extend(m(y[-1]) for m in self.m) return self.cv2(torch.cat(y, 1))class Bottleneck_ATT(nn.Module): # Standard bottleneck def __init__(self, c1, c2, shortcut=True, g=1, k=(3, 3), e=0.5, use_ATT=0.): # ch_in, ch_out, shortcut, groups, kernels, expand super().__init__() c_ = int(c2 * e) # hidden channels self.cv1 = Conv(c1, c_, k[0], 1) self.cv2 = Conv(c_, c2, k[1], 1, g=g) self.add = shortcut and c1 == c2 # self.ATT = GAM_Attention(c_) #这里可以随意更换注意力机制,使用use_ATT控制 has_ATT = use_ATT is not None and use_ATT > 0. # Squeeze-and-excitation if has_ATT: # self.ATT = GAM_Attention(c2,c2) self.ATT = BiLevelRoutingAttention(c2,c2) else: self.ATT = None def forward(self, x): if self.ATT is not None: out = x + self.ATT(self.cv2(self.cv1(x))) if self.add else self.ATT(self.cv2(self.cv1(x))) else: out = x + self.cv2(self.cv1(x)) if self.add else self.cv2(self.cv1(x)) return out添加到tasks里:首先引用

其次注册:
# """**************add Attention***************""" elif m in {GAM_Attention, SpectralAttention, SoftThresholdAttentionResidual, MultiSpectralAttentionLayer, CAMConv, CAConv, CBAMConv}: c1, c2 = ch[f], args[0] if c2 != nc: # if not output c2 = make_divisible(min(c2, max_channels) * width, 8) args = [c1, c2, *args[1:]]
三、所有的注意力机制代码:
部分注意力需要安装timm. 如运行提示缺少timm安装即可. 安装命令:pip install timm,点击下面链接即可使用!
注意力网络链接地址
来源地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_44224801/article/details/130059070
免责声明:
① 本站未注明“稿件来源”的信息均来自网络整理。其文字、图片和音视频稿件的所属权归原作者所有。本站收集整理出于非商业性的教育和科研之目的,并不意味着本站赞同其观点或证实其内容的真实性。仅作为临时的测试数据,供内部测试之用。本站并未授权任何人以任何方式主动获取本站任何信息。
② 本站未注明“稿件来源”的临时测试数据将在测试完成后最终做删除处理。有问题或投稿请发送至: 邮箱/279061341@qq.com QQ/279061341















