MySQL— 基础语法大全及操作演示!!!(下)
MySQL—— 基础语法大全及操作演示(下)
MySQL— 基础语法大全及操作演示!!!(上)
MySQL— 基础语法大全及操作演示!!!(中)
MySQL— 基础语法大全及操作演示!!!(下)
五、多表查询
在讲解 SQL语句 的时候,讲解了DQL语句,也就是数据查询语句,但是之前讲解的查询都是单表查询,而本章节我们要学习的则是多表查询操作,主要从以下几个方面进行讲解。
5.1 多表关系
项目开发中,在进行数据库表结构设计时,会根据业务需求及业务模块之间的关系,分析并设计表结
构,由于业务之间相互关联,所以各个表结构之间也存在着各种联系,基本上分为三种:
- 一对多(多对一)
- 多对多
- 一对一
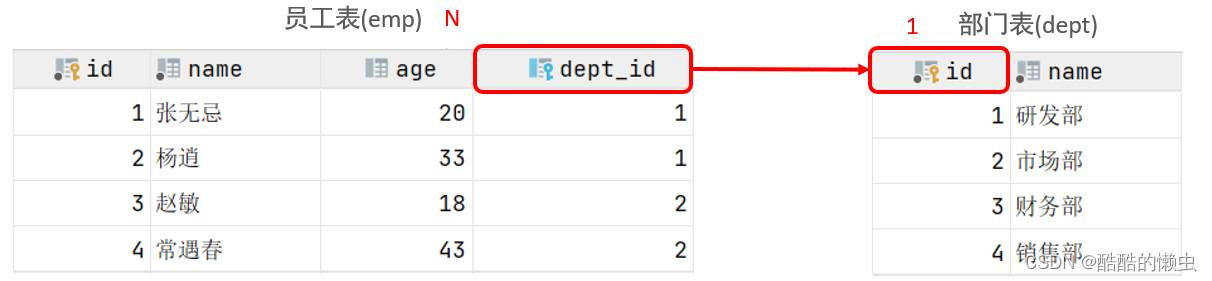
5.1.1 一对多
- 案例: 部门 与 员工的关系
- 关系: 一个部门对应多个员工,一个员工对应一个部门
- 实现: 在多的一方建立外键,指向一的一方的主键
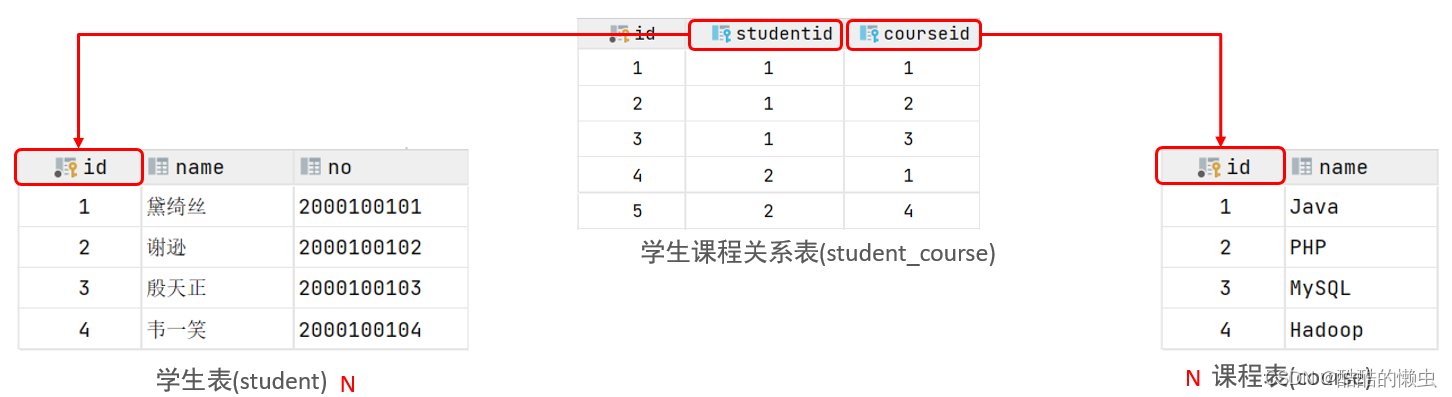
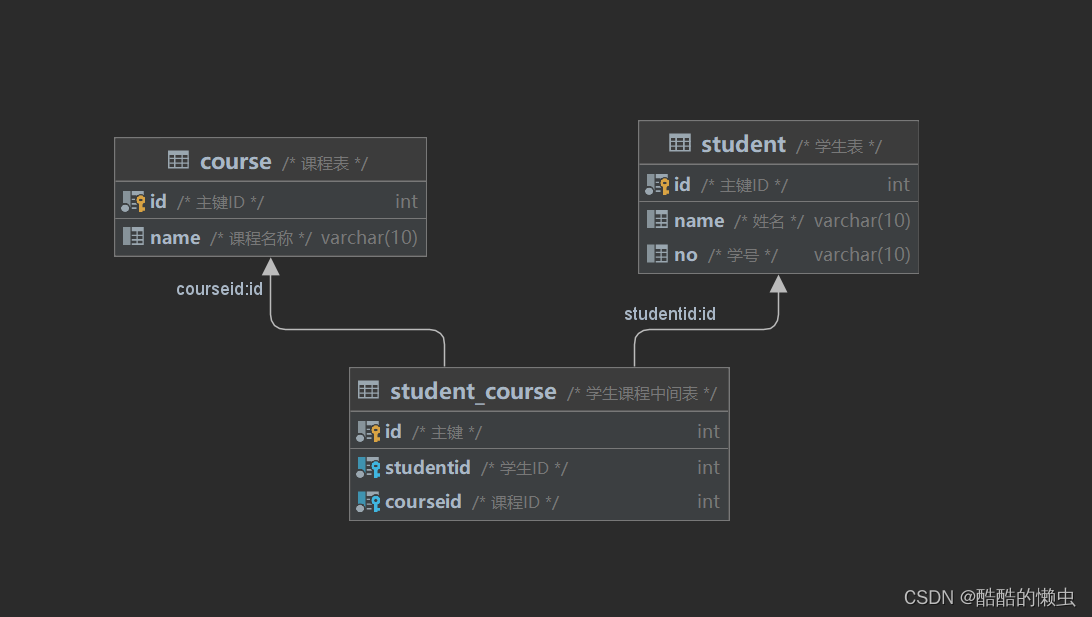
5.1.2 多对多
- 案例: 学生 与 课程的关系
- 关系: 一个学生可以选修多门课程,一门课程也可以供多个学生选择
- 实现: 建立第三张中间表,中间表至少包含两个外键,分别关联两方主键
对应的SQL脚本:
create table student(id int auto_increment primary key comment '主键ID',name varchar(10) comment '姓名',no varchar(10) comment '学号') comment '学生表';insert into student values (null, '黛绮丝', '2000100101'), (null, '谢逊', '2000100102'), (null, '殷天正', '2000100103'),(null, '韦一笑', '2000100104');create table course(id int auto_increment primary key comment '主键ID',name varchar(10) comment '课程名称') comment '课程表';insert into course values (null, 'Java'), (null, 'PHP'), (null , 'MySQL'), (null, 'Hadoop');create table student_course(id int auto_increment comment '主键' primary key,studentid int not null comment '学生ID',courseid int not null comment '课程ID',constraint fk_courseid foreign key (courseid) references course (id),constraint fk_studentid foreign key (studentid) references student (id))comment '学生课程中间表';insert into student_course values (null,1,1), (null,1,2), (null,1,3), (null,2,2), (null,2,3), (null,3,4);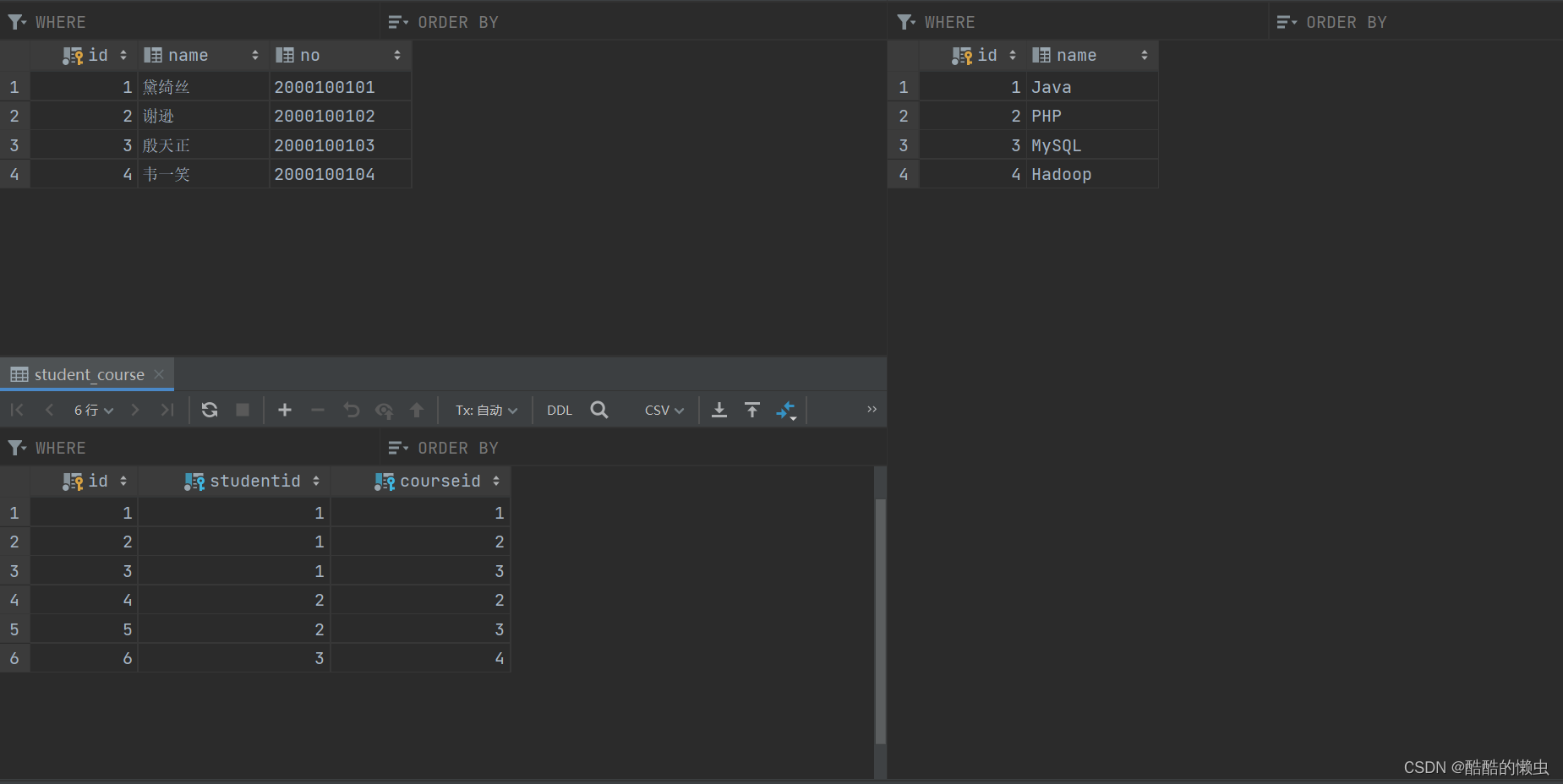
5.1.3 一对一
- 案例: 用户 与 用户详情的关系
- 关系: 一对一关系,多用于单表拆分,将一张表的基础字段放在一张表中,其他详情字段放在另一张表中,以提升操作效率
- 实现: 在任意一方加入外键,关联另外一方的主键,并且设置外键为唯一的(
unique)
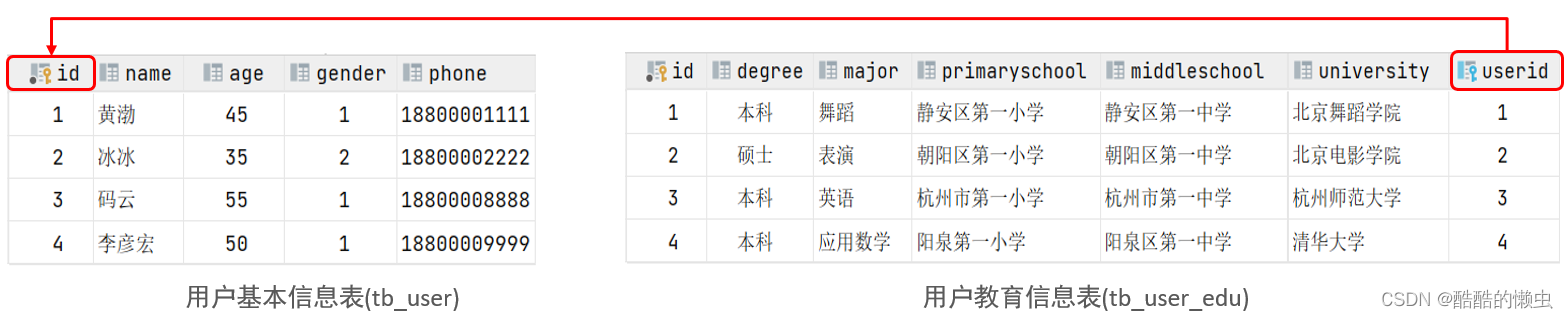
对应的SQL脚本:
create table tb_user(id int auto_increment primary key comment '主键ID',name varchar(10) comment '姓名',age int comment '年龄',gender char(1) comment '1: 男 , 2: 女',phone char(11) comment '手机号') comment '用户基本信息表';create table tb_user_edu(id int auto_increment primary key comment '主键ID',degree varchar(20) comment '学历',major varchar(50) comment '专业',primaryschool varchar(50) comment '小学',middleschool varchar(50) comment '中学',university varchar(50) comment '大学',userid int unique comment '用户ID',constraint fk_userid foreign key (userid) references tb_user(id)) comment '用户教育信息表';insert into tb_user(id, name, age, gender, phone) values(null,'黄渤',45,'1','18800001111'),(null,'冰冰',35,'2','18800002222'),(null,'码云',55,'1','18800008888'),(null,'李彦宏',50,'1','18800009999');insert into tb_user_edu(id, degree, major, primaryschool, middleschool, university, userid) values(null,'本科','舞蹈','静安区第一小学','静安区第一中学','北京舞蹈学院',1),(null,'硕士','表演','朝阳区第一小学','朝阳区第一中学','北京电影学院',2),(null,'本科','英语','杭州市第一小学','杭州市第一中学','杭州师范大学',3),(null,'本科','应用数学','阳泉第一小学','阳泉区第一中学','清华大学',4);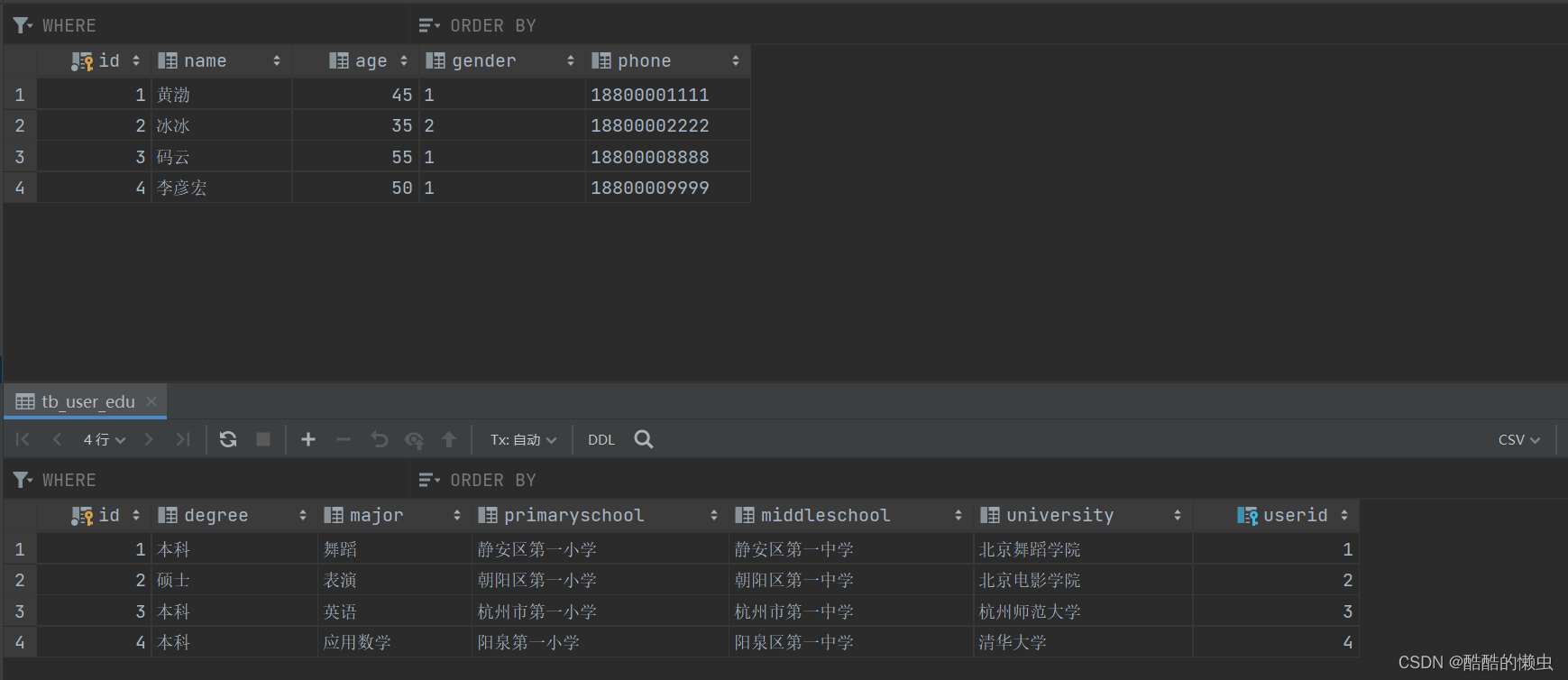
一对一经常用作单表的拆分,当然也可以合并成一张表!
🚀🚀🚀 多表关系 快速食用:---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------->
# 1、一对多在多的一方建立外键,指向一的一方的主键。# 2、多对多建立第三张中间表,中间表至少包含两个外键,分别关联两方主键。# 3、一对一在任意一方加入外键,关联另外一方的主键,并且设置外键为唯一的(unique)。5.2 多表查询概述
5.2.1 数据准备
1). 删除之前 emp, dept表的测试数据
2). 执行如下脚本,创建 emp 表与 dept 表并插入测试数据
-- 创建dept表,并插入数据create table dept(id int auto_increment comment 'ID' primary key,name varchar(50) not null comment '部门名称')comment '部门表';INSERT INTO dept (id, name) VALUES (1, '研发部'), (2, '市场部'),(3, '财务部'), (4, '销售部'), (5, '总经办'), (6, '人事部');-- 创建emp表,并插入数据create table emp(id int auto_increment comment 'ID' primary key,name varchar(50) not null comment '姓名',age int comment '年龄',job varchar(20) comment '职位',salary int comment '薪资',entrydate date comment '入职时间',managerid int comment '直属领导ID',dept_id int comment '部门ID')comment '员工表';-- 添加外键alter table emp add constraint fk_emp_dept_id foreign key (dept_id) references dept(id);INSERT INTO emp (id, name, age, job,salary, entrydate, managerid, dept_id) VALUES(1, '金庸', 66, '总裁',20000, '2010-01-01', null,5),(2, '张无忌', 20, '项目经理',12500, '2015-12-05', 1,1),(3, '杨逍', 33, '开发', 8400,'2010-11-03', 2,1),(4, '韦一笑', 48, '开发',11000, '2012-02-05', 2,1),(5, '常遇春', 43, '开发',10500, '2014-09-07', 3,1),(6, '小昭', 19, '程序员鼓励师',6600, '2014-10-12', 2,1),(7, '灭绝', 60, '财务总监',8500, '2012-09-12', 1,3),(8, '周芷若', 19, '会计',48000, '2016-06-02', 7,3),(9, '丁敏君', 23, '出纳',5250, '2019-05-13', 7,3),(10, '赵敏', 20, '市场部总监',12500, '2014-10-12', 1,2),(11, '鹿杖客', 56, '职员',3750, '2016-10-03', 10,2),(12, '鹤笔翁', 19, '职员',3750, '2017-05-09', 10,2),(13, '方东白', 19, '职员',5500, '2019-02-12', 10,2),(14, '张三丰', 88, '销售总监',14000, '2014-10-12', 1,4),(15, '俞莲舟', 38, '销售',4600, '2014-10-12', 14,4),(16, '宋远桥', 40, '销售',4600, '2014-10-12', 14,4),(17, '陈友谅', 42, null,2000, '2021-10-12', 1,null);dept 表共6条记录,emp 表共17条记录。
5.2.2 概述
多表查询就是指从多张表中查询数据。
- 原来查询单表数据,执行的SQL形式为:
select * from emp; - 那么我们要执行多表查询,就只需要使用逗号分隔多张表即可,如:
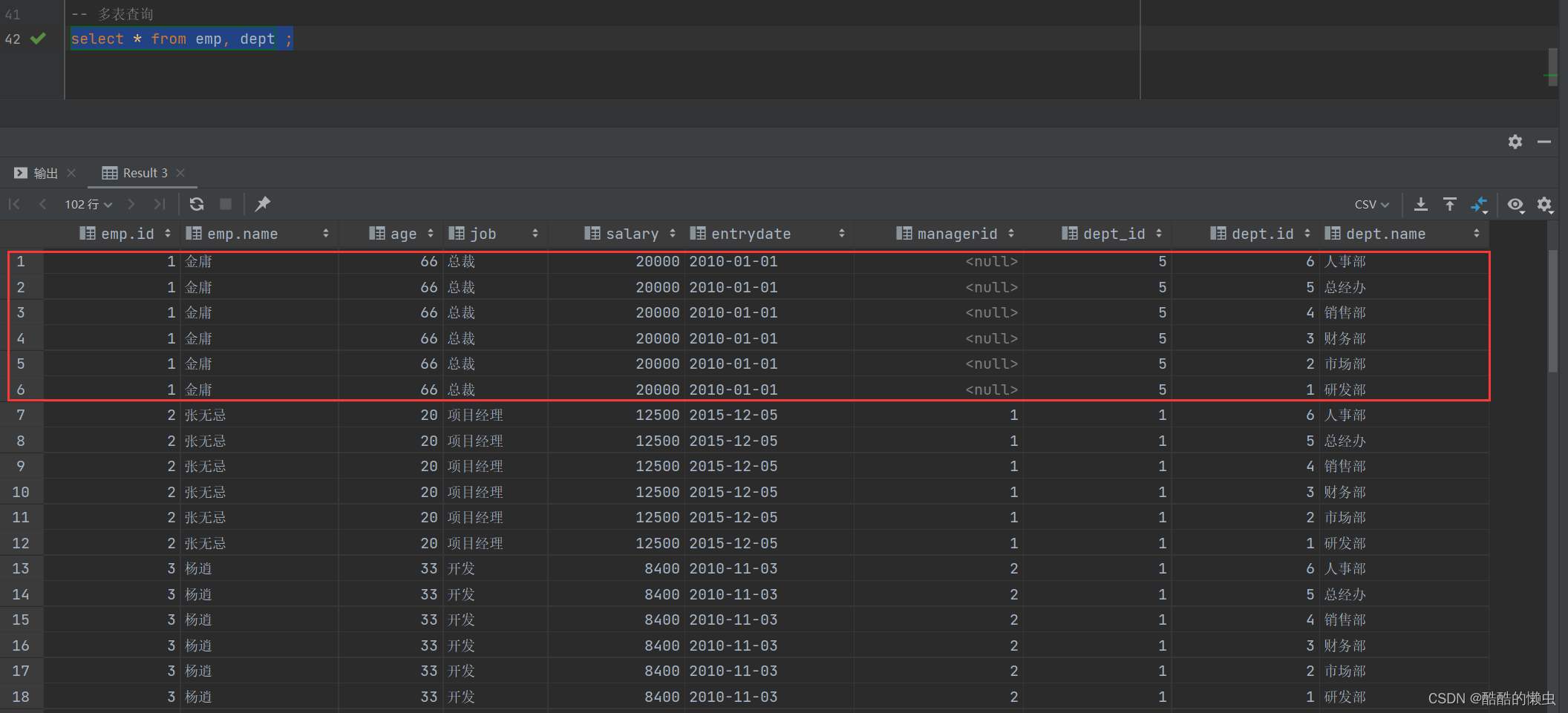
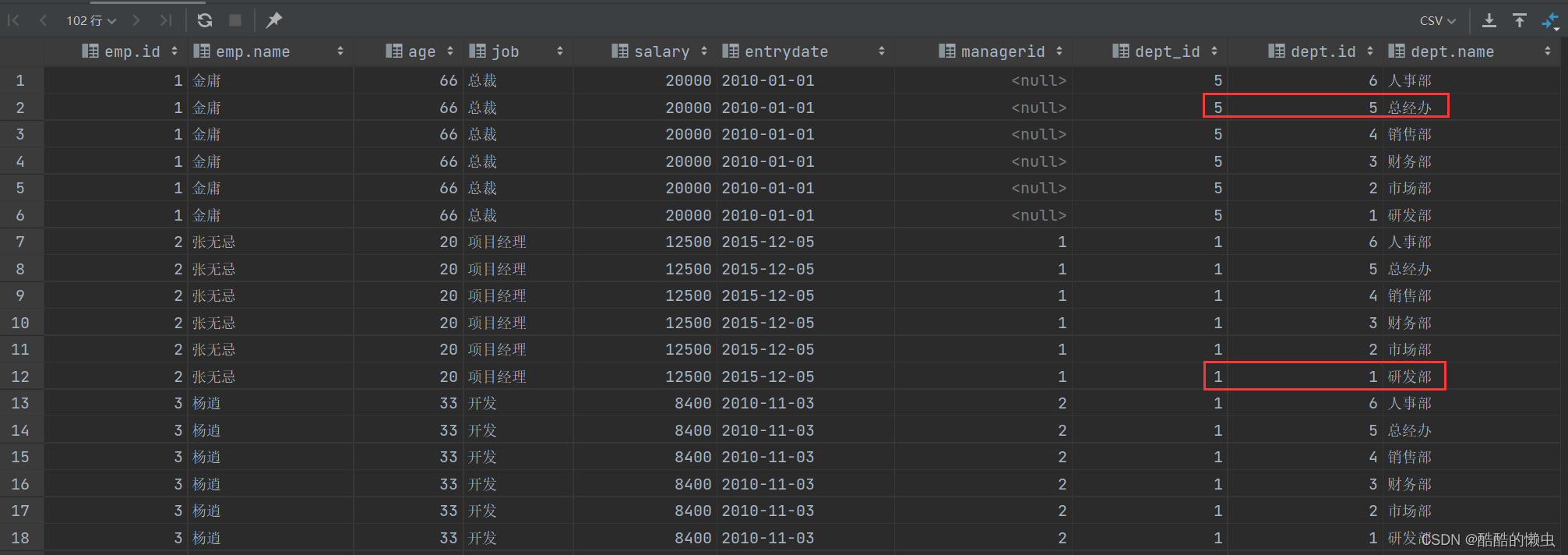
select * from emp, dept ;
具体的执行结果如下:
-
此时,我们看到查询结果中包含了大量的结果集,总共102条记录,而这其实就是员工表
emp所有的记录(17) 与 部门表dept所有记录(6) 的所有组合情况,这种现象称之为 笛卡尔积。接下来,就来简单介绍下笛卡尔积。 -
笛卡尔积: 笛卡尔乘积是指在数学中,两个集合A集合 和 B集合的所有组合情况。(在多表查询时,需要消除无效的笛卡尔积)
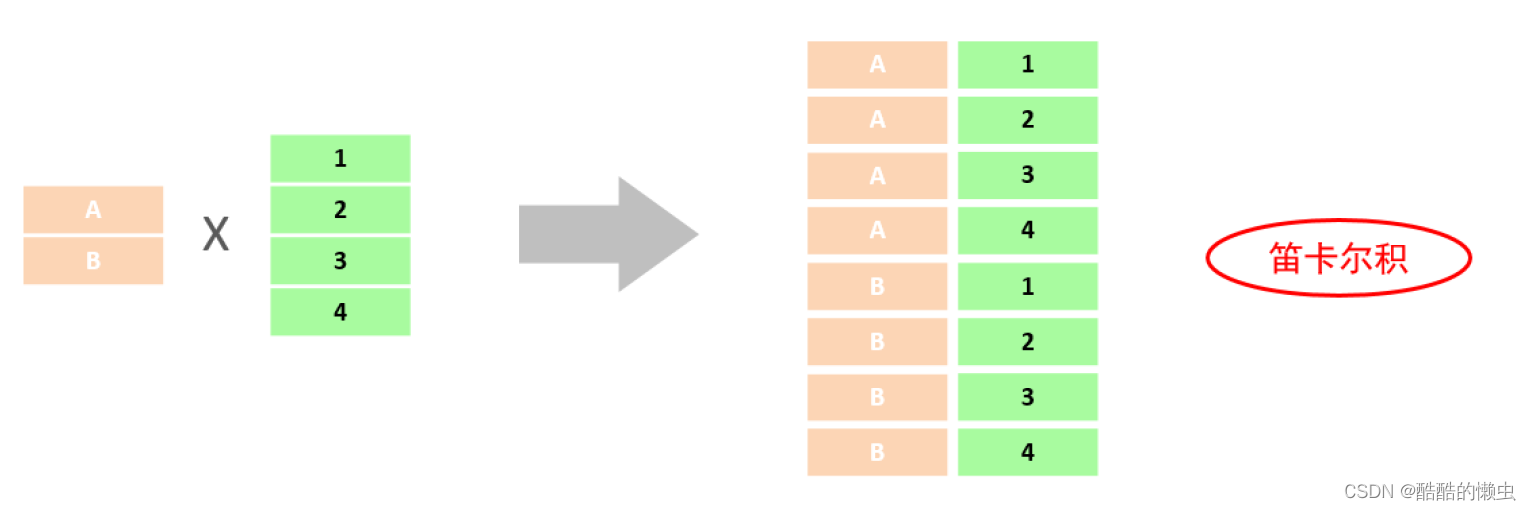
- 而在多表查询中,我们是需要消除无效的笛卡尔积的,只保留两张表关联部分的数据。
在SQL语句中,如何来去除无效的笛卡尔积呢? 我们可以给多表查询加上连接查询的条件即可。
select * from emp, dept where emp.dept_id = dept.id ;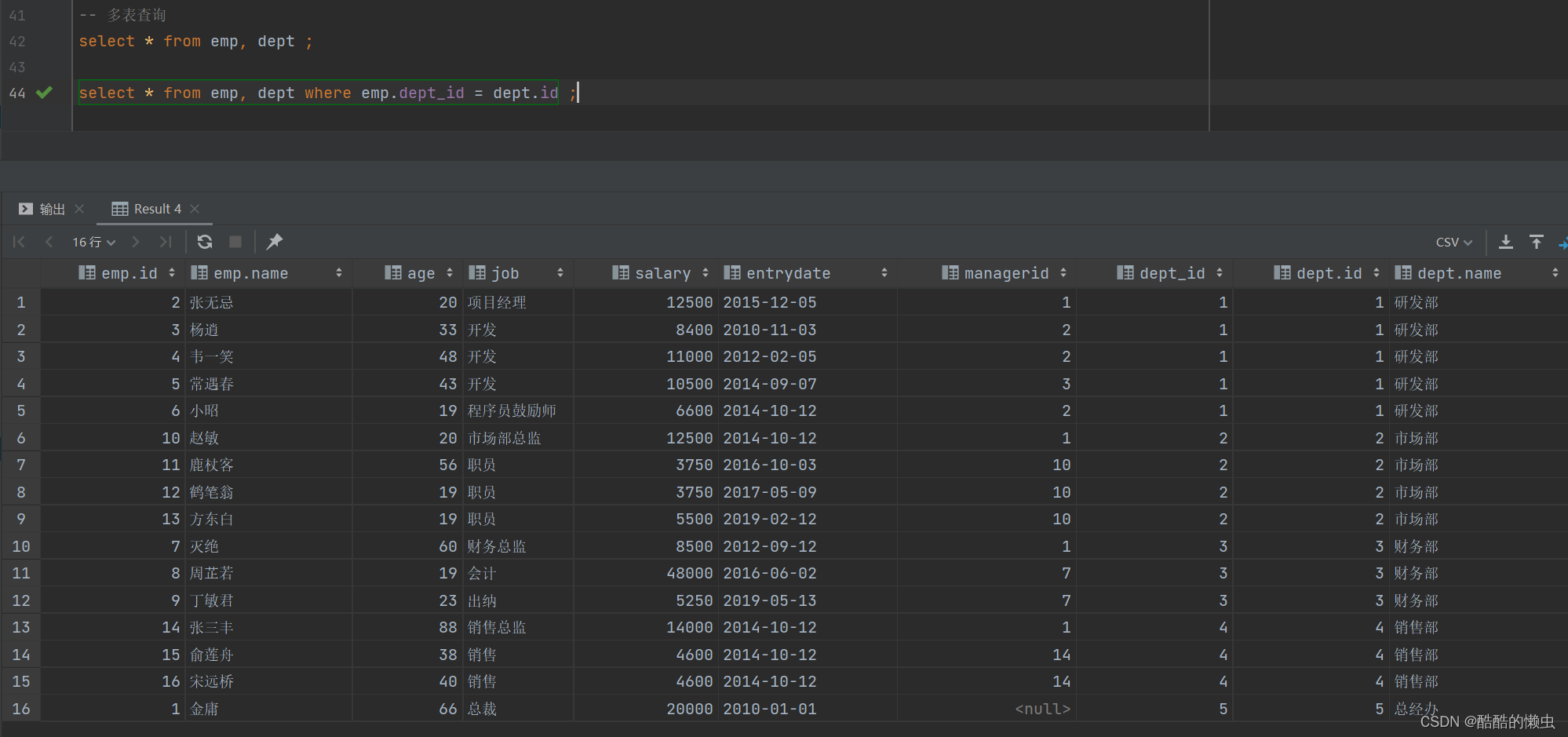
而由于 id 为17的员工,没有 dept_id 字段值,所以在多表查询时,根据连接查询的条件并没有查询到。
5.2.3 分类
⭐️ 连接查询
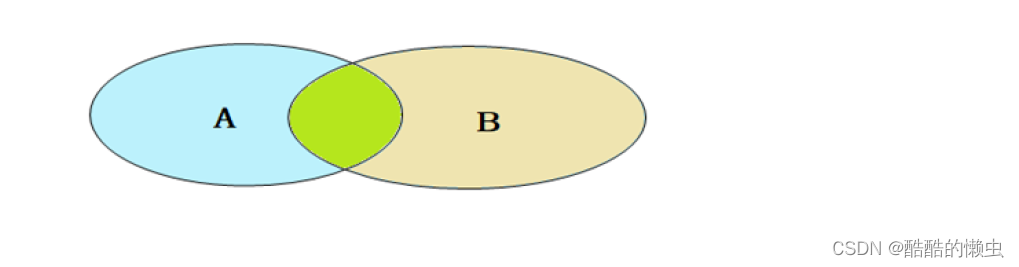
- 内连接:相当于查询
A、B交集部分数据 - 外连接:
- 左外连接:查询左表所有数据,以及两张表交集部分数据;
- 右外连接:查询右表所有数据,以及两张表交集部分数据。
- 自连接:当前表与自身的连接查询,自连接必须使用表别名。
⭐️ 子查询
5.3 内连接
内连接查询的是两张表交集部分的数据。(也就是 绿色 部分的数据).

内连接的语法分为两种: 隐式内连接、显式内连接。先来学习一下具体的语法结构。
⭐️ 1). 隐式内连接
select 字段列表 from 表1 , 表2 where 条件 ... ;⭐️ 2). 显式内连接
select 字段列表 from 表1 [ inner ] join 表2 on 连接条件 ... ;案例:
A. 查询每一个员工的姓名 , 及关联的部门的名称 (隐式内连接实现)
- 表结构:
emp,dept - 连接条件:
emp.dept_id = dept.id
select emp.name, dept.name from emp, dept where emp.dept_id = dept.id ;-- 为每一张表起别名,简化SQL编写select e.name, d.name from emp e, dept d where e.dept_id = d.id;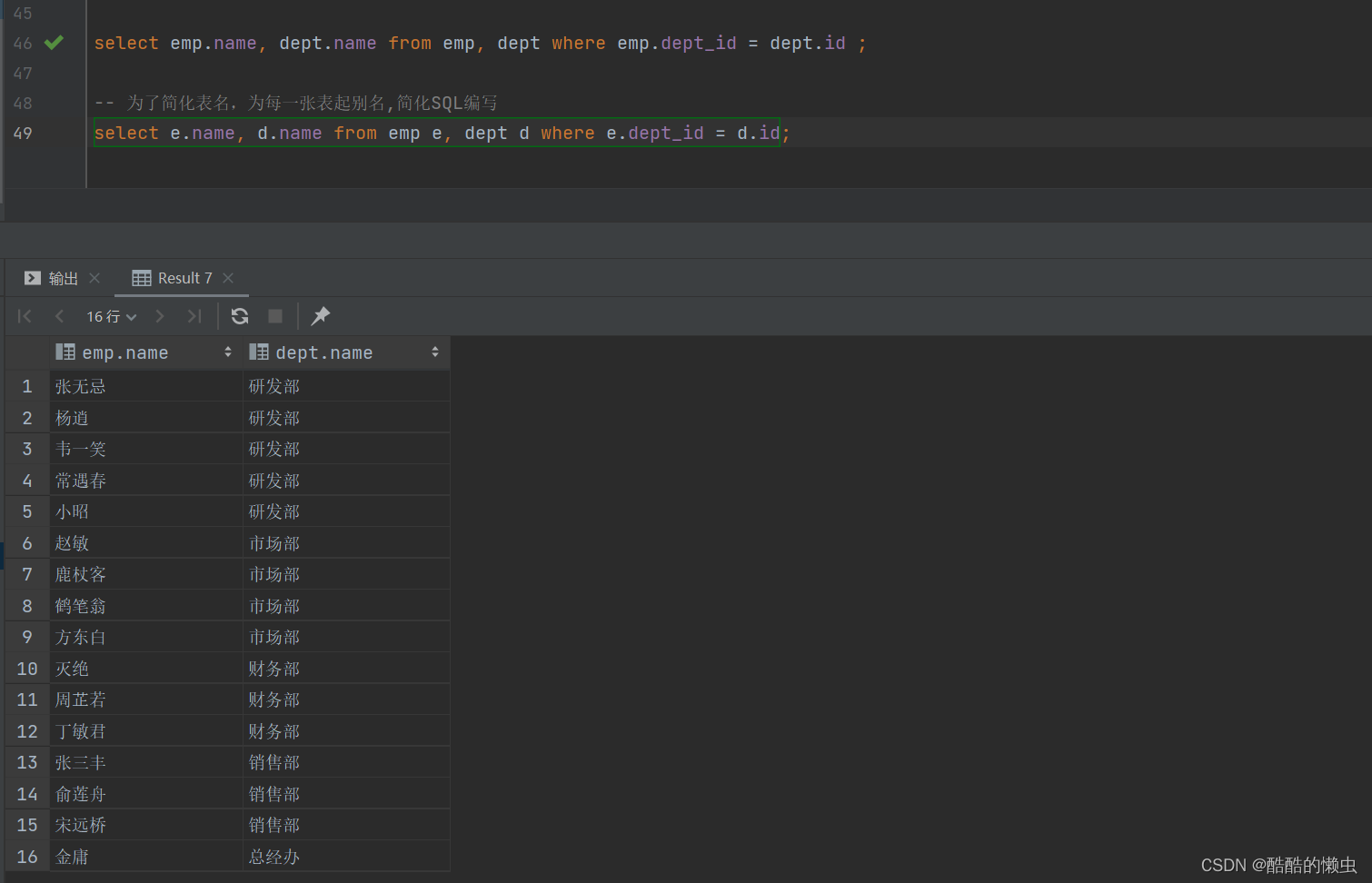
B. 查询每一个员工的姓名 , 及关联的部门的名称 (显式内连接实现) — INNER JOIN … ON …
- 表结构:
emp,dept - 连接条件:
emp.dept_id = dept.id
select e.name, d.name from emp e inner join dept d on e.dept_id = d.id;-- 为每一张表起别名,简化SQL编写select e.name, d.name from emp e join dept d on e.dept_id = d.id;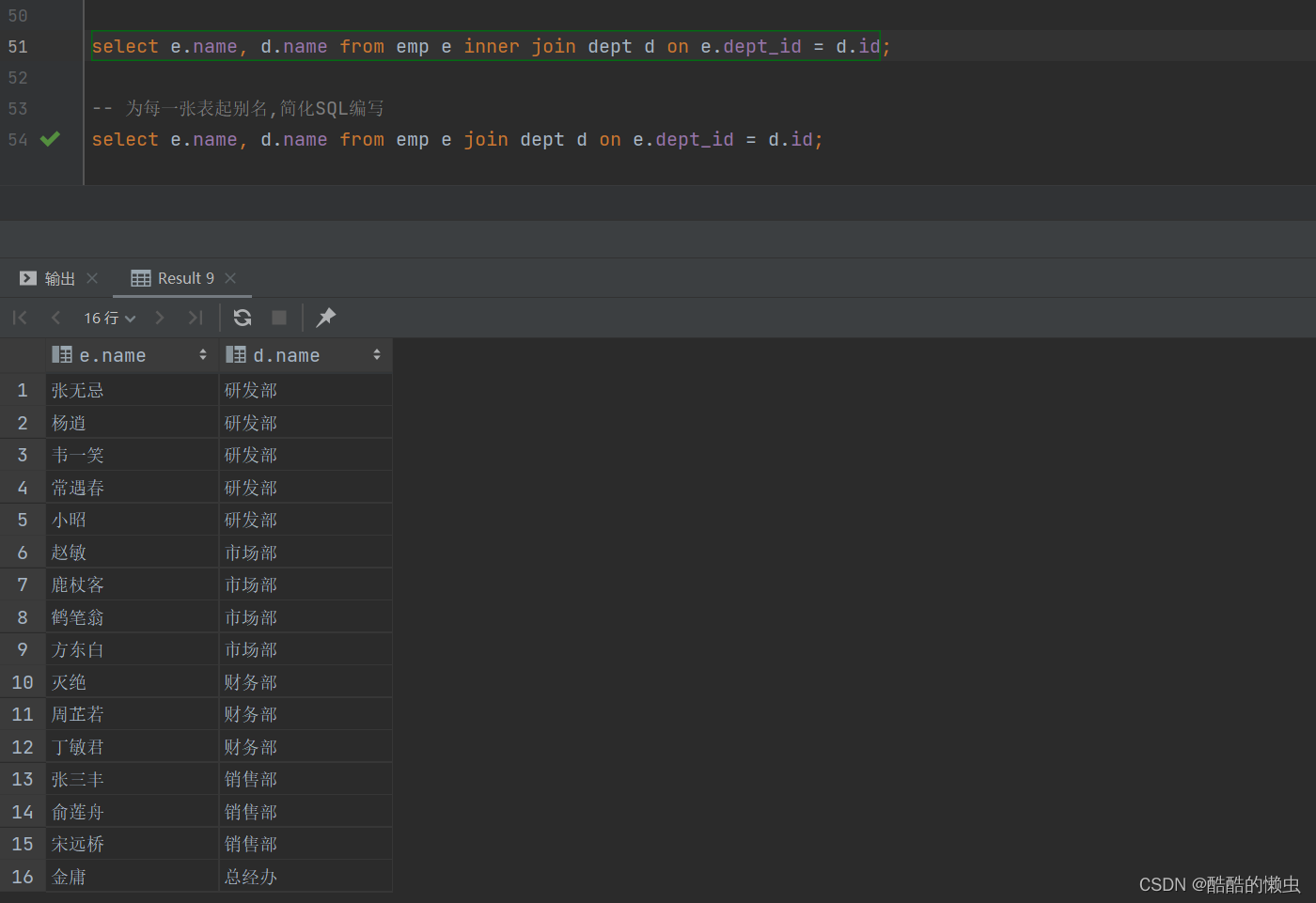
表的别名:
- ①.
tablea as 别名1 , tableb as 别名2 ;- ②.
tablea 别名1 , tableb 别名2 ;注意事项:
一旦为表起了别名,就不能再使用表名来指定对应的字段了,此时只能够使用别名来指定字段。
5.4 外连接

外连接分为两种,分别是:左外连接 和 右外连接。具体的语法结构为:
⭐️ 1). 左外连接
select 字段列表 from 表1 left [ outer ] join 表2 on 条件 ... ;- 左外连接相当于查询 表1(左表)的所有数据,当然也包含表1和表2交集部分的数据。
⭐️ 2). 右外连接
select 字段列表 from 表1 right [ outer ] join 表2 on 条件 ... ;- 右外连接相当于查询 表2(右表)的所有数据,当然也包含表1和表2交集部分的数据。
案例:
A. 查询 emp 表的所有数据, 和对应的部门信息
由于需求中提到,要查询 emp 的所有数据,所以是不能内连接查询的,需要考虑使用外连接查询。
- 表结构:
emp,dept - 连接条件:
emp.dept_id = dept.id
select e.*, d.name from emp e left outer join dept d on e.dept_id = d.id;select e.*, d.name from emp e left join dept d on e.dept_id = d.id;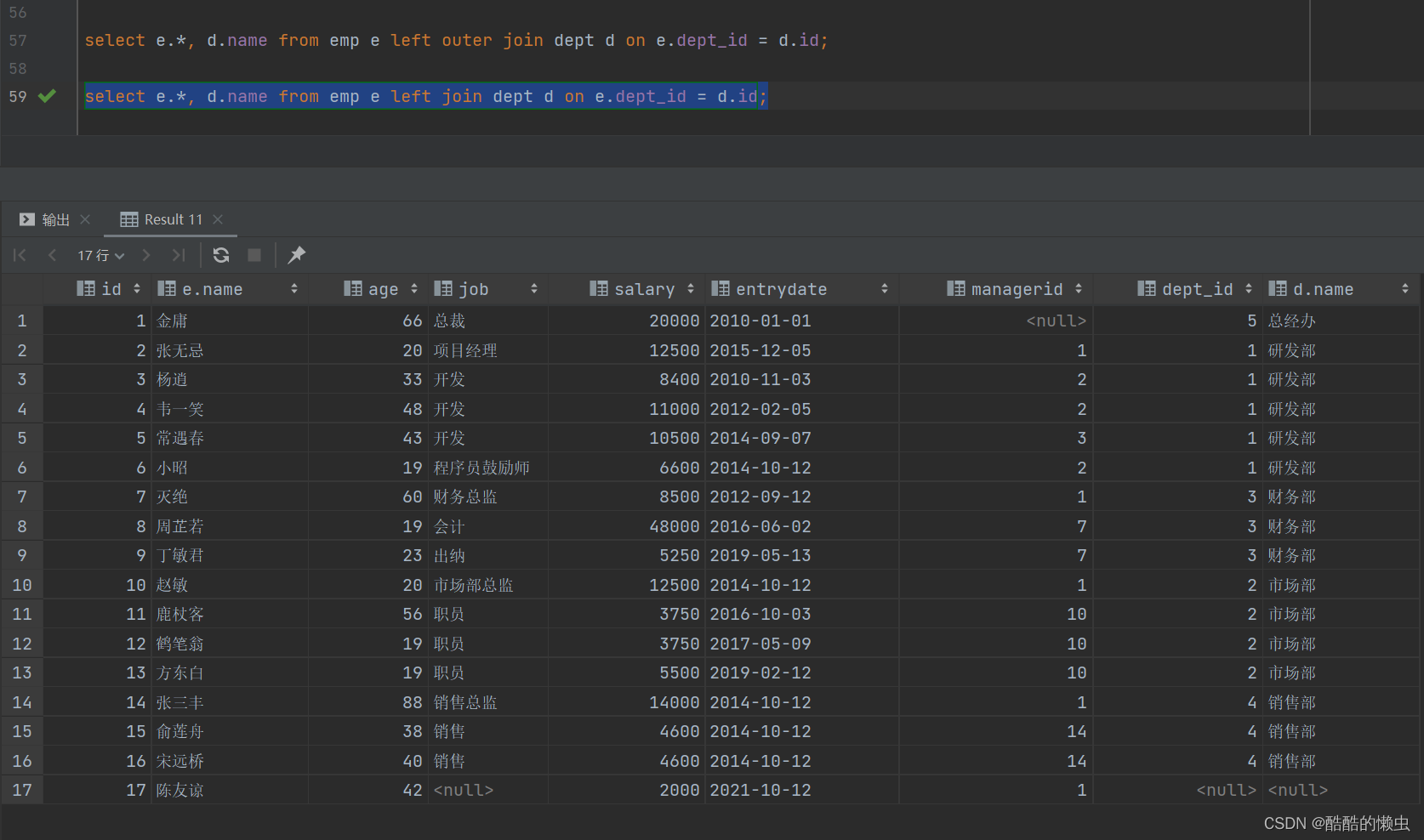
B. 查询 dept 表的所有数据, 和对应的 员工信息(右外连接)
由于需求中提到,要查询dept表的所有数据,所以是不能内连接查询的,需要考虑使用外连接查询。
- 表结构:
emp,dept - 连接条件:
emp.dept_id = dept.id
select d.*, e.* from emp e right outer join dept d on e.dept_id = d.id;select d.*, e.* from dept d left outer join emp e on e.dept_id = d.id;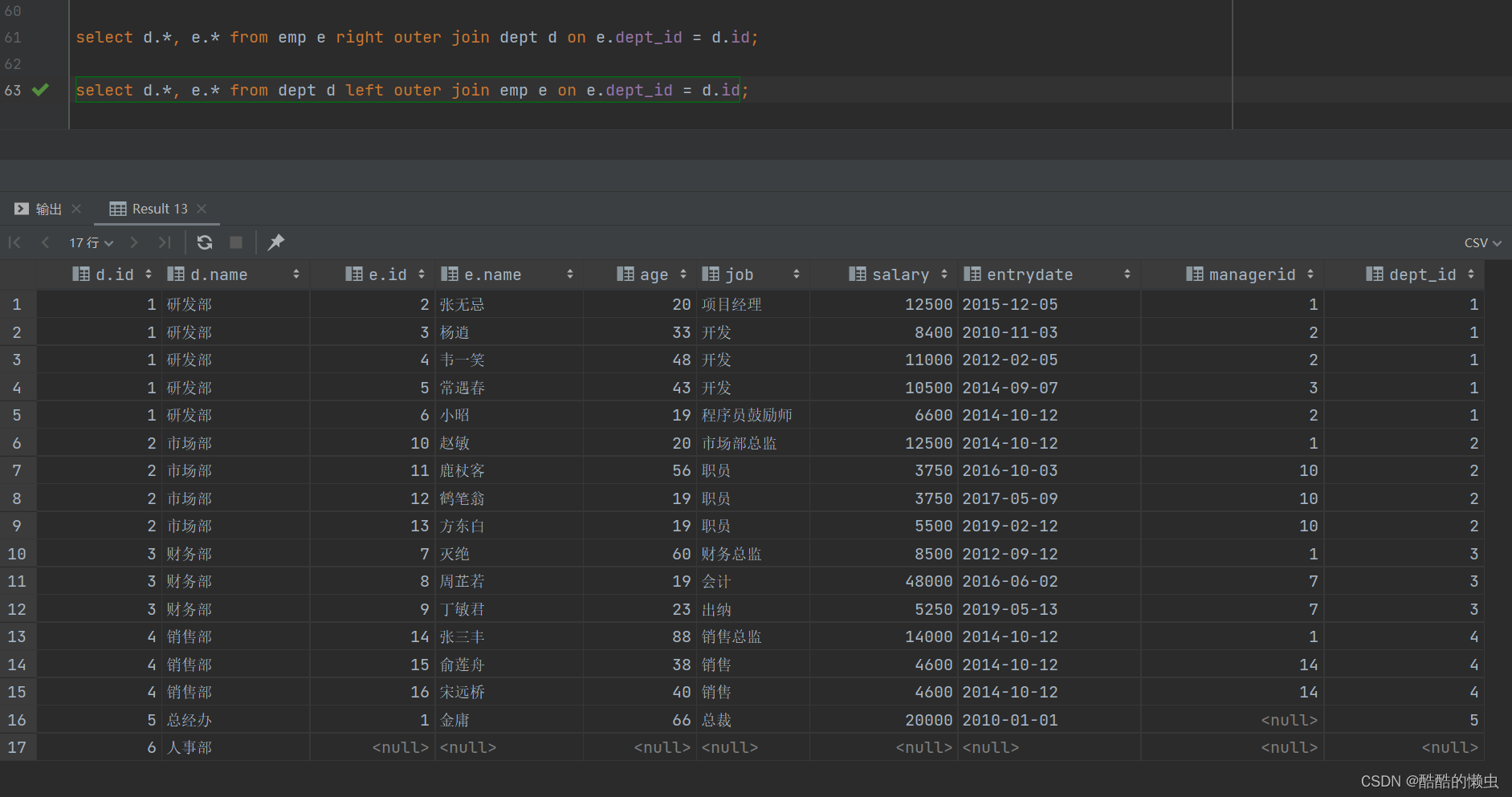
注意事项:
- 左外连接和右外连接是可以相互替换的,只需要调整在连接查询时SQL中,表结构的先后顺序就可以了。而我们在日常开发使用时,更偏向于 左外连接 。
5.5 自连接
5.5.1 自连接查询
自连接查询,顾名思义,就是自己连接自己,也就是把一张表连接查询多次。我们先来学习一下自连接的查询语法:
select 字段列表 from 表A 别名A join 表A 别名B on 条件 ... ;- 而对于自连接查询,可以是内连接查询,也可以是外连接查询。
案例:
A. 查询员工 及其 所属领导的名字
- 表结构:
emp
select a.name, b.name from emp a, emp b where a.managerid = b.id;
B. 查询所有员工 emp 及其领导的名字 emp , 如果员工没有领导, 也需要查询出来
- 表结构:
emp a , emp b
select a.name '员工', b.name '领导' from emp a left join emp b on a.managerid =b.id;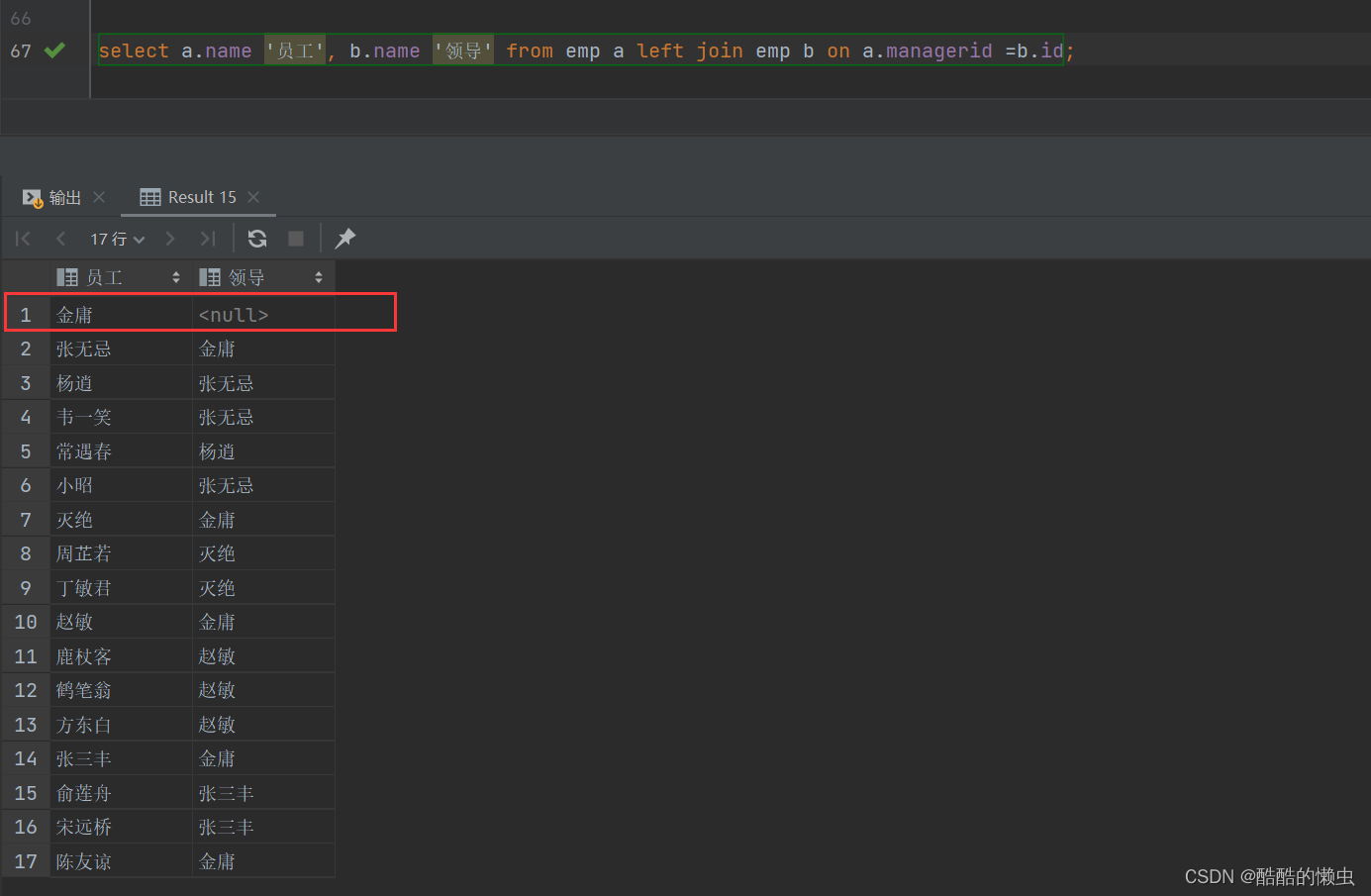
注意事项:
- 在自连接查询中,必须要为表起别名,要不然我们不清楚所指定的条件、返回的字段,到底是哪一张表的字段。
5.5.2 联合查询
对于 union 查询,就是把多次查询的结果合并起来,形成一个新的查询结果集。
select 字段列表 from 表A ...union [ all ]select 字段列表 from 表B ....;- 对于联合查询的多张表的 列数 必须保持一致,字段类型 也需要保持一致。
union all会将全部的数据直接合并在一起,union会对合并之后的数据去重。
案例:
A. 将薪资低于 5000 的员工 , 和 年龄大于 50 岁的员工全部查询出来.
- 当前对于这个需求,我们可以直接使用多条件查询,使用逻辑运算符
or连接即可。 那这里呢,我们
也可以通过union/union all来联合查询.
select * from emp where salary < 5000union allselect * from emp where age > 50;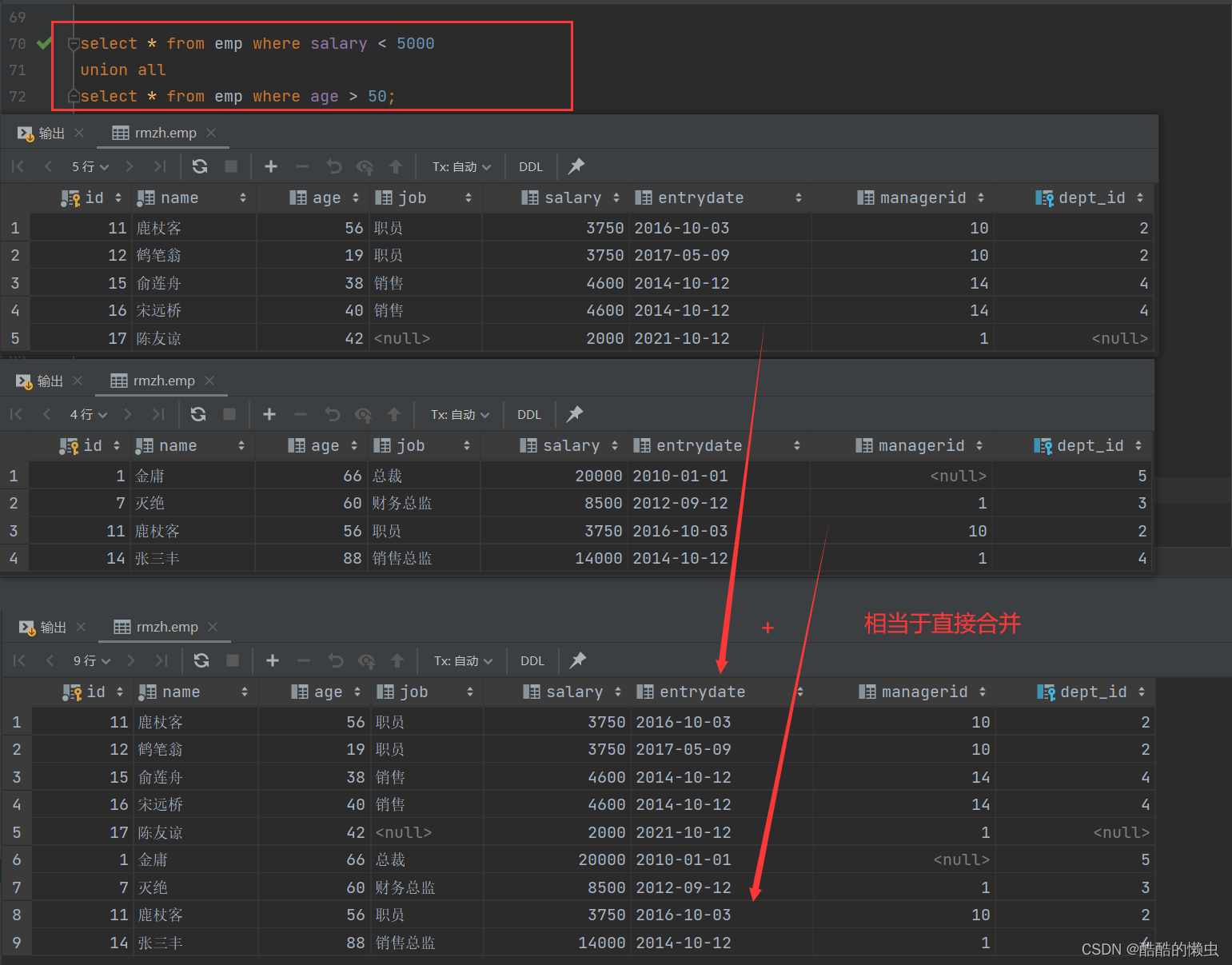
union all查询出来的结果,仅仅进行简单的合并,并未去重。
select * from emp where salary < 5000unionselect * from emp where age > 50;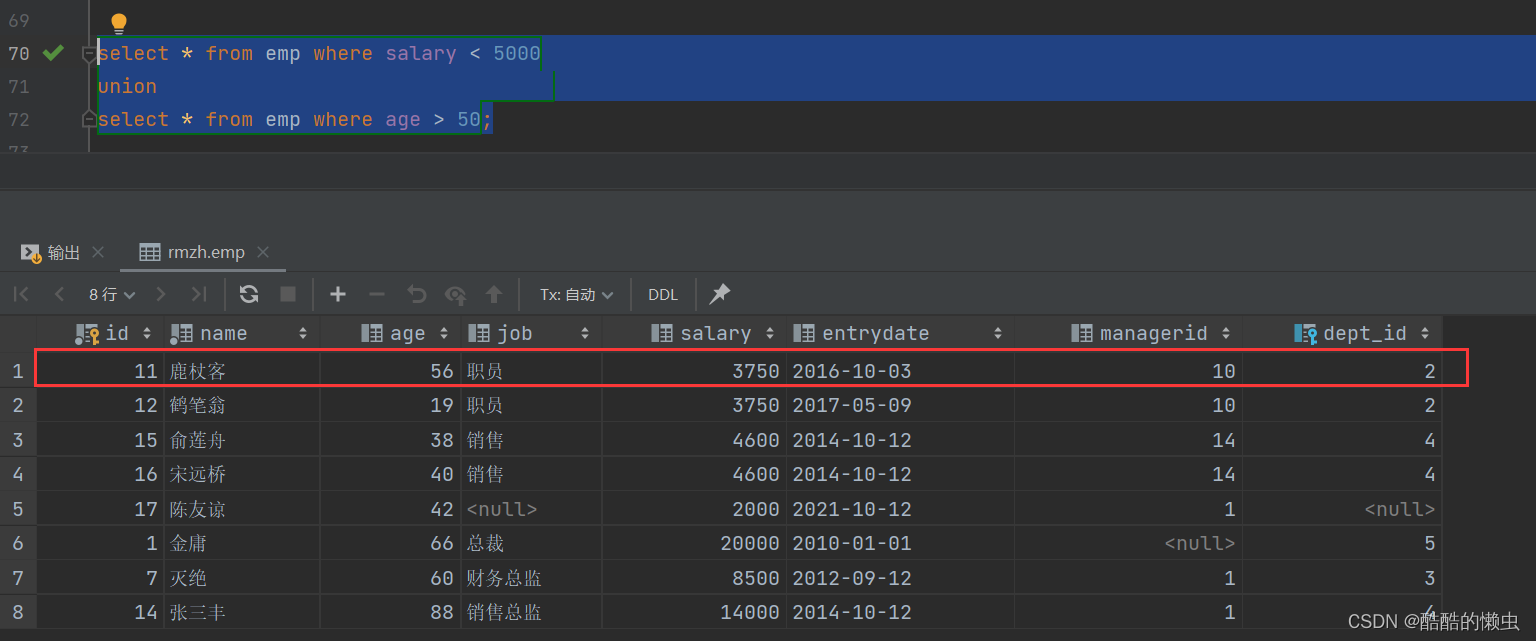
union联合查询,会对查询出来的结果进行去重处理。
注意:
- 如果多条查询语句查询出来的结果,字段数量 不一致,在进行
union/union all联合查询时,将会报错。
5.6 子查询
5.6.1 概述
⭐️ 1). 概念
SQL语句中 嵌套 SELECT 语句,称为 嵌套查询,又称 子查询。
select * from t1 where column1 = ( select column1 from t2 );- 子查询外部的语句可以是
insert / update / delete / select的任何一个。
⭐️ 2). 分类
根据子查询结果不同,分为:
- A. 标量子查询(子查询结果为单个值,只有一行一列)
- B. 列子查询 (子查询结果为一列)
- C. 行子查询 (子查询结果为一行)
- D. 表子查询 (子查询结果为多行多列)
根据子查询位置,分为:
- A.
where之后 - B.
from之后 - C.
select之后
5.6.2 标量子查询
子查询返回的结果是单个值(数字、字符串、日期等),最简单的形式,这种子查询称为 标量子查询。
- 常用的操作符:
=<>>>=<<=
案例:
A. 查询 “销售部” 的所有员工信息
- 完成这个需求时,我们可以将需求分解为两步:
-
- ①. 查询 “销售部” 部门ID
select id from dept where name = '销售部';-
- ②. 根据 “销售部” 部门ID, 查询员工信息
select * from emp where dept_id = (select id from dept where name = '销售部');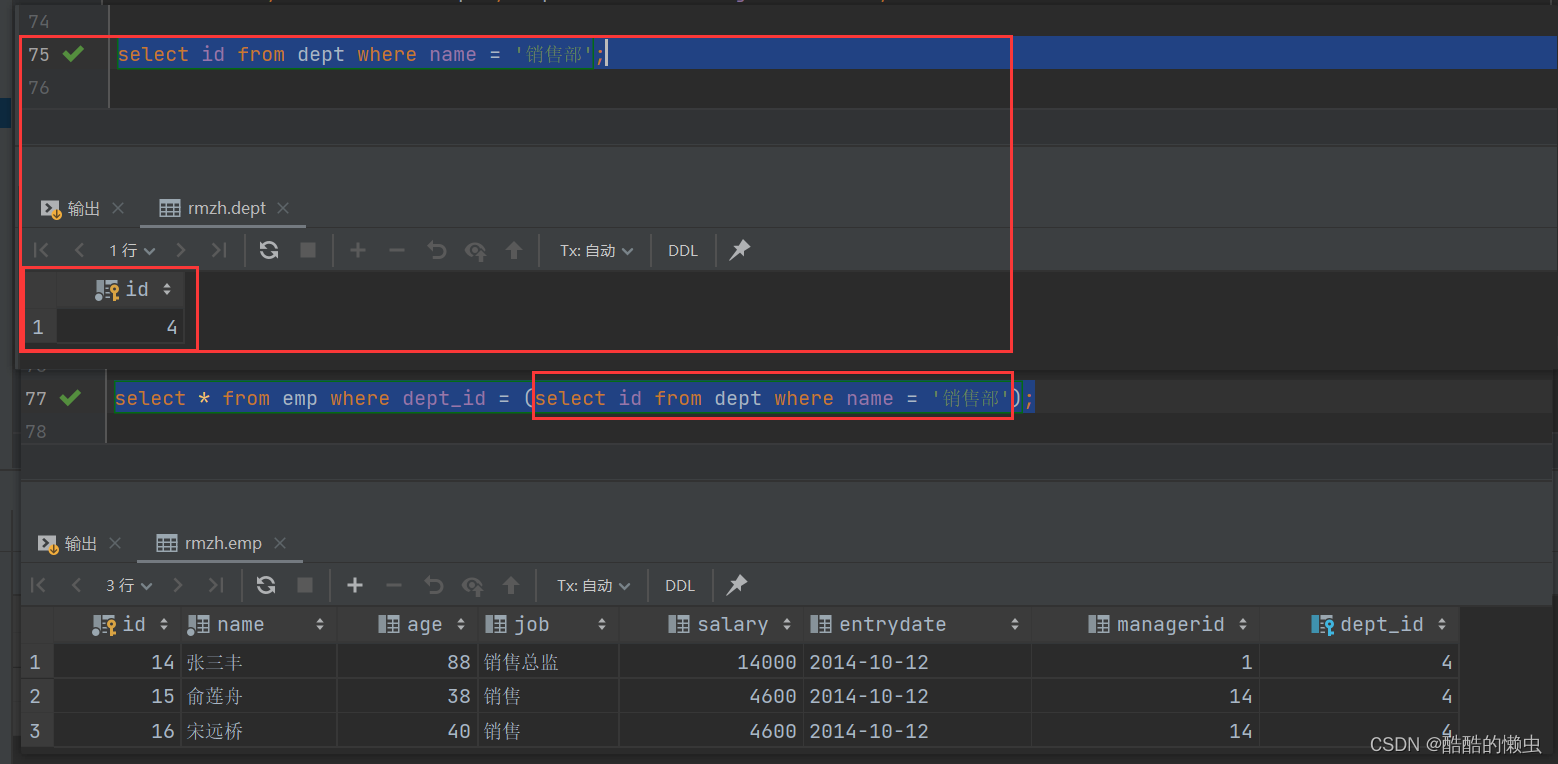
B. 查询在 “方东白” 入职之后的员工信息
- 完成这个需求时,我们可以将需求分解为两步:
-
- ①. 查询 方东白 的入职日期
select entrydate from emp where name = '方东白';-
- ②. 查询指定入职日期之后入职的员工信息
select * from emp where entrydate > (select entrydate from emp where name = '方东白');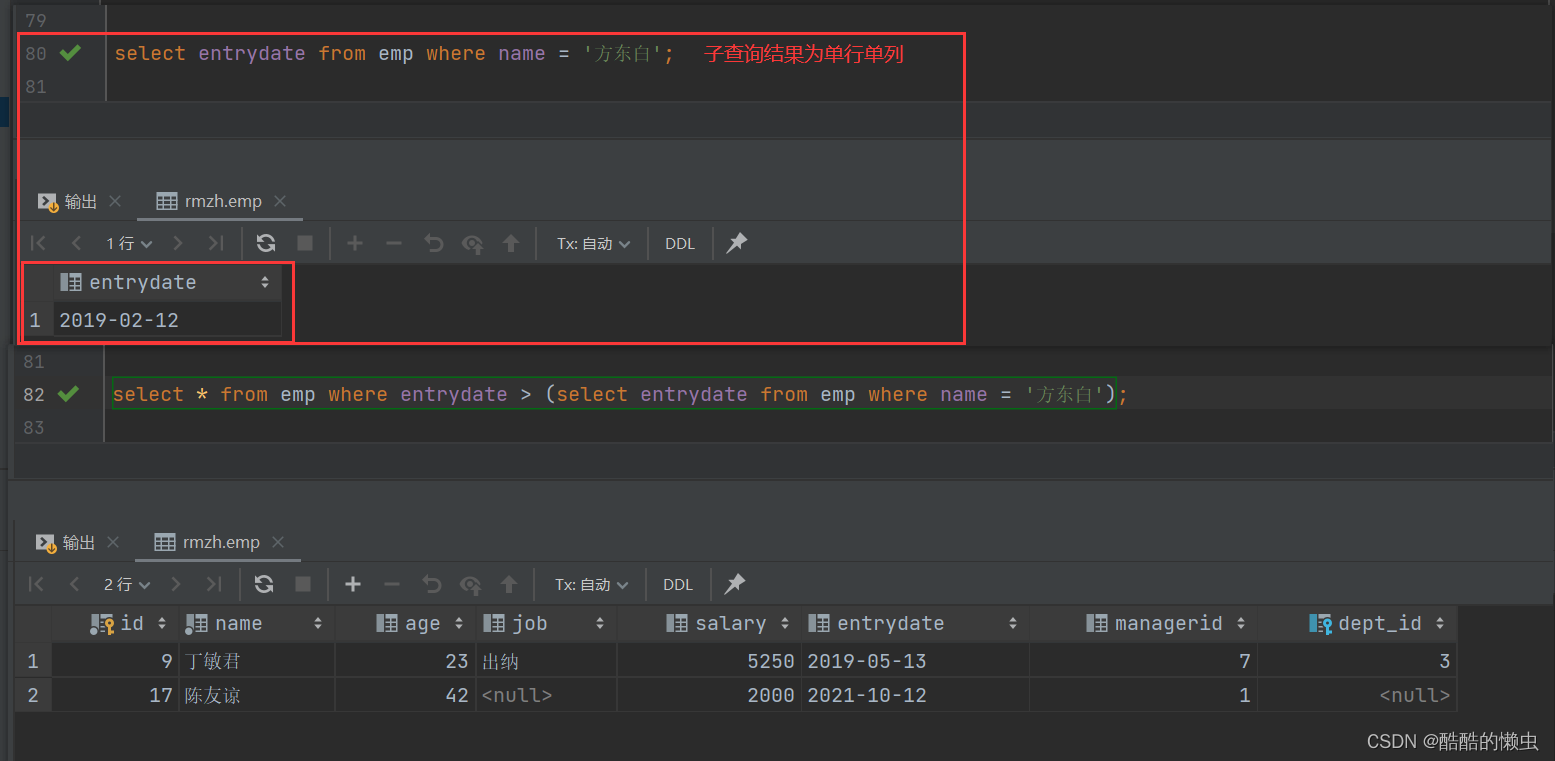
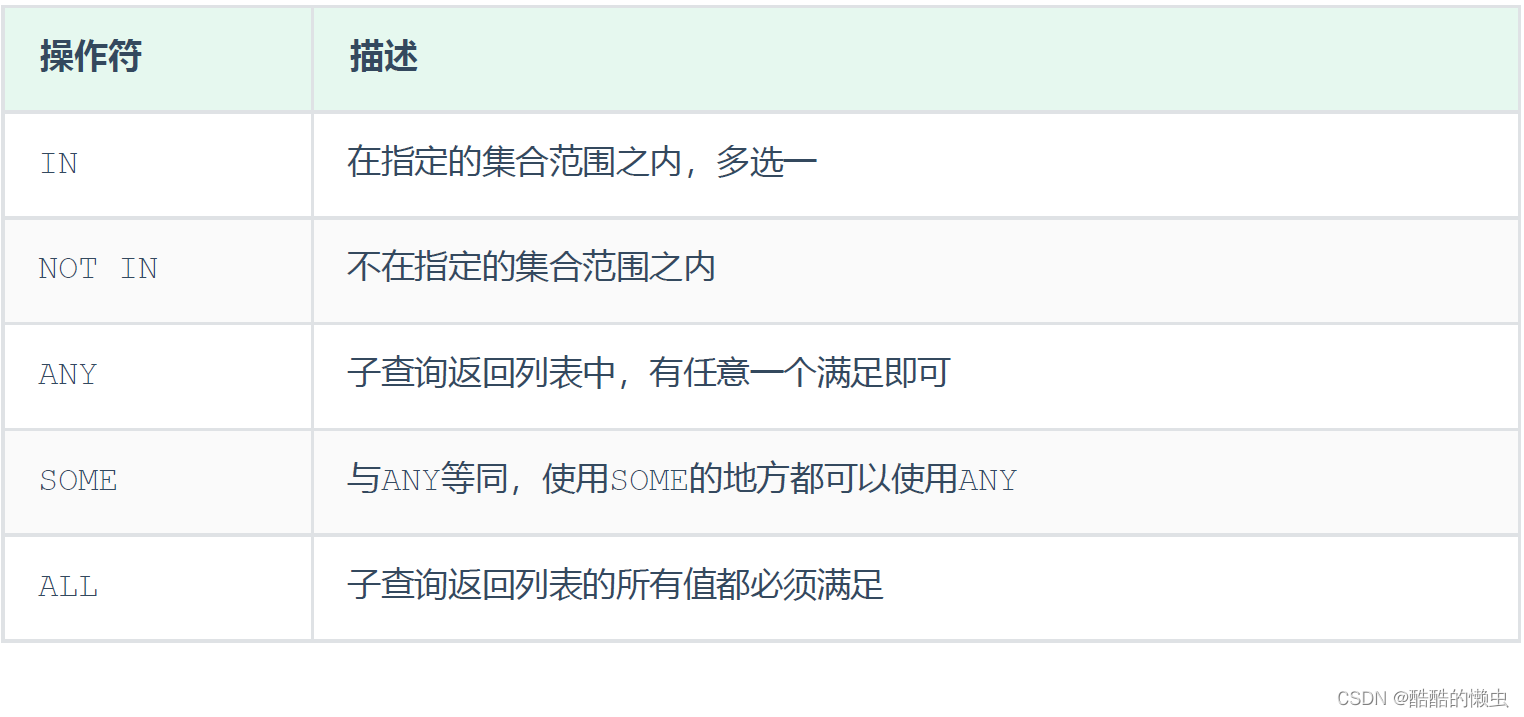
5.6.3 列子查询
子查询返回的结果是一列(可以是多行),这种子查询称为 列子查询。
- 常用的操作符:
in、not in、any、some、all
案例:
A. 查询 “销售部” 和 “市场部” 的所有员工信息
- 分解为以下两步:
-
- ①. 查询 “销售部” 和 “市场部” 的部门ID
select id from dept where name = '销售部' or name = '市场部';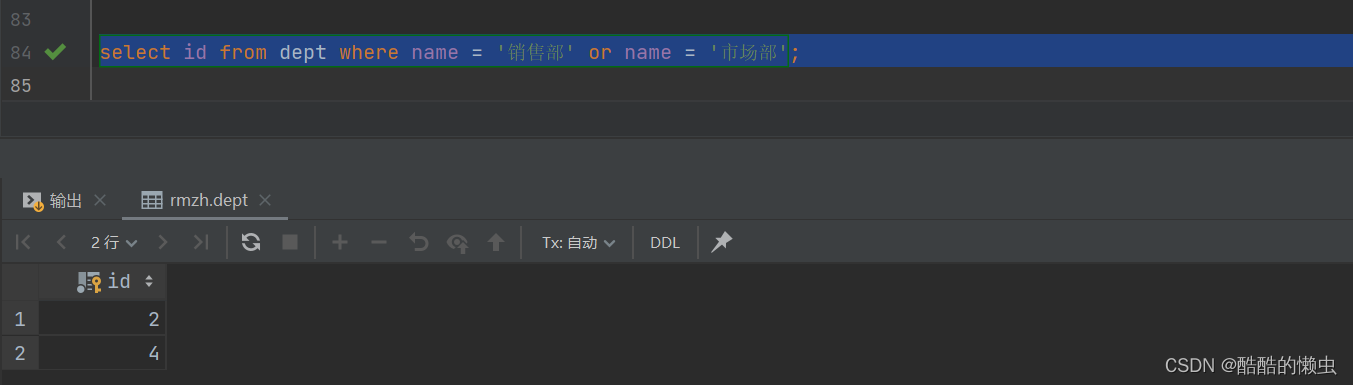
-
- ②. 根据部门ID, 查询员工信息
select * from emp where dept_id in (select id from dept where name = '销售部' or name = '市场部');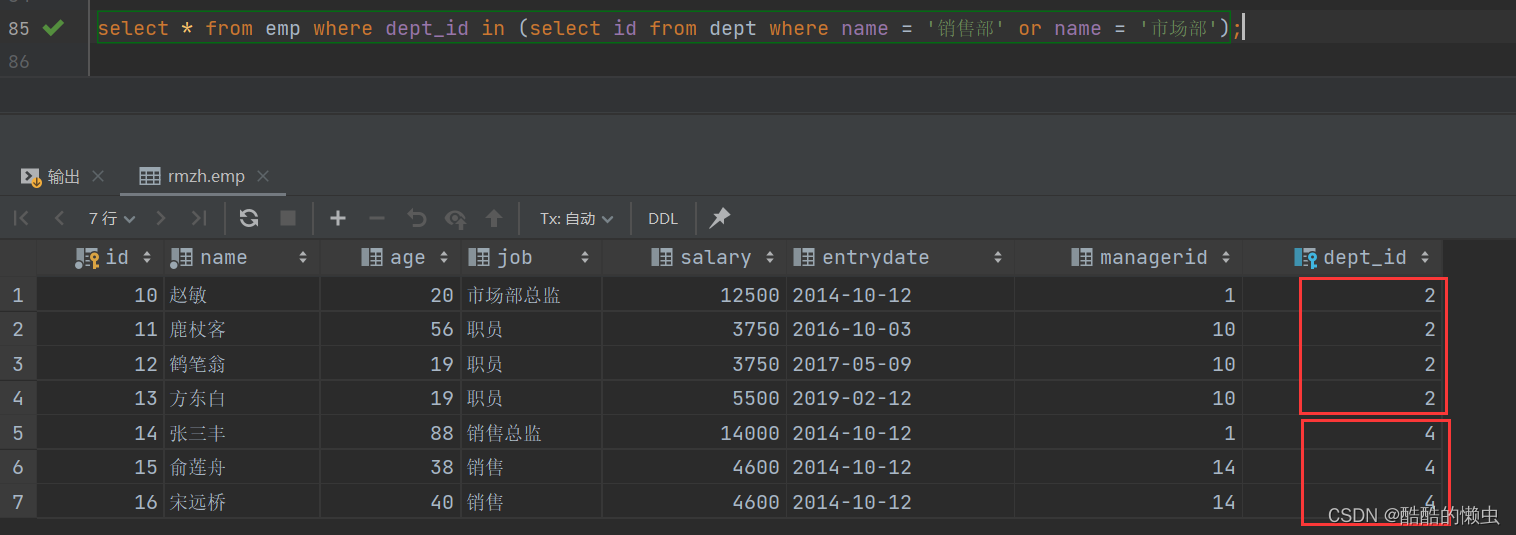
B. 查询比 财务部 所有人工资都高的员工信息
- 分解为以下两步:
-
- ①. 查询所有 财务部 人员工资
select id from dept where name = '财务部';select salary from emp where dept_id = (select id from dept where name = '财务部');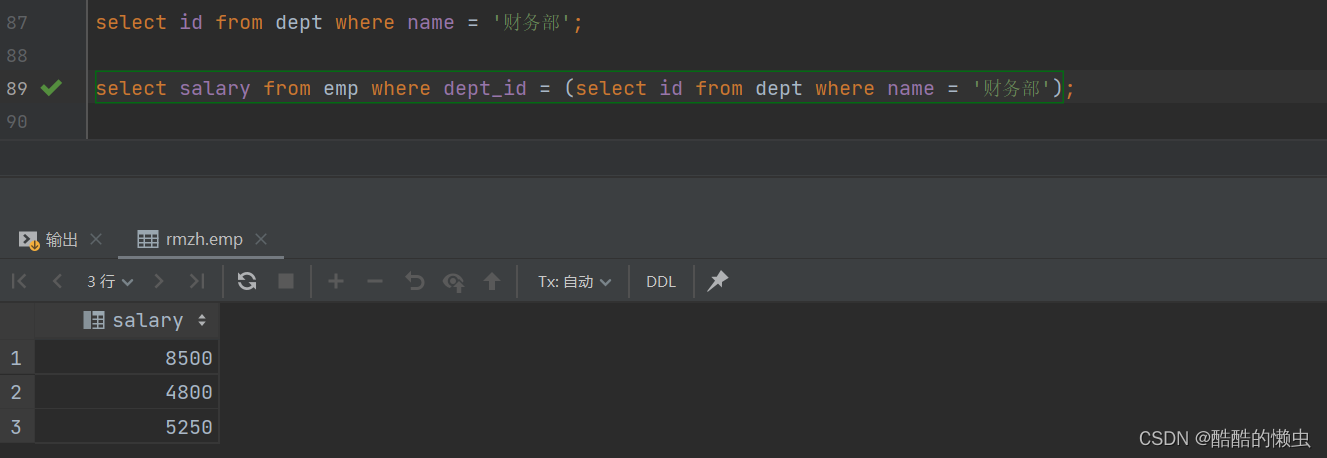
-
- ②. 比 财务部 所有人工资都高的员工信息
select * from emp where salary > all ( select salary from emp where dept_id = (select id from dept where name = '财务部') );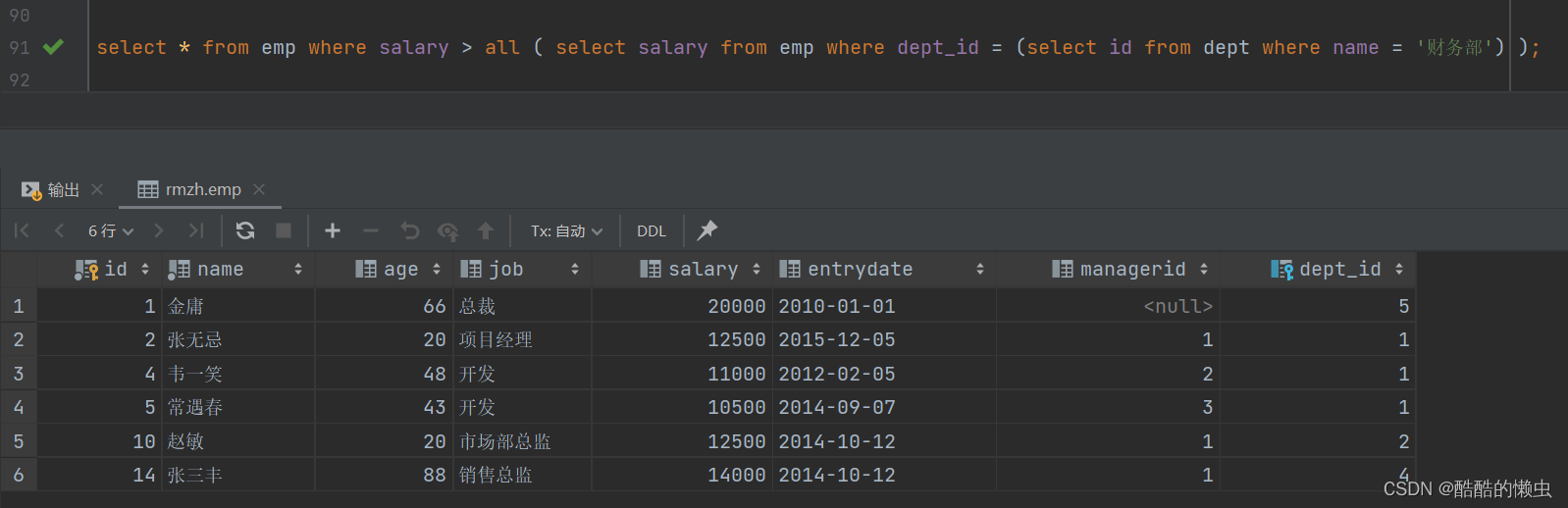
C. 查询比研发部其中任意一人工资高的员工信息
- 分解为以下两步:
-
- ①. 查询研发部所有人工资
select salary from emp where dept_id = (select id from dept where name = '研发部');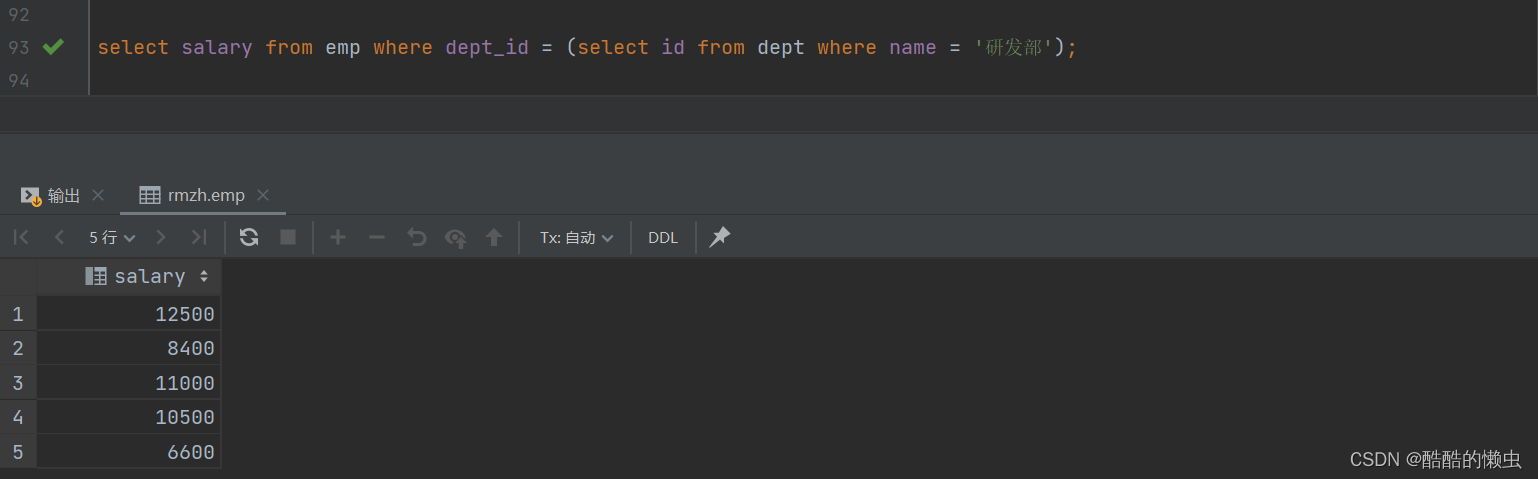
-
- ②. 比研发部其中任意一人工资高的员工信息
select * from emp where salary > any ( select salary from emp where dept_id = (select id from dept where name = '研发部') );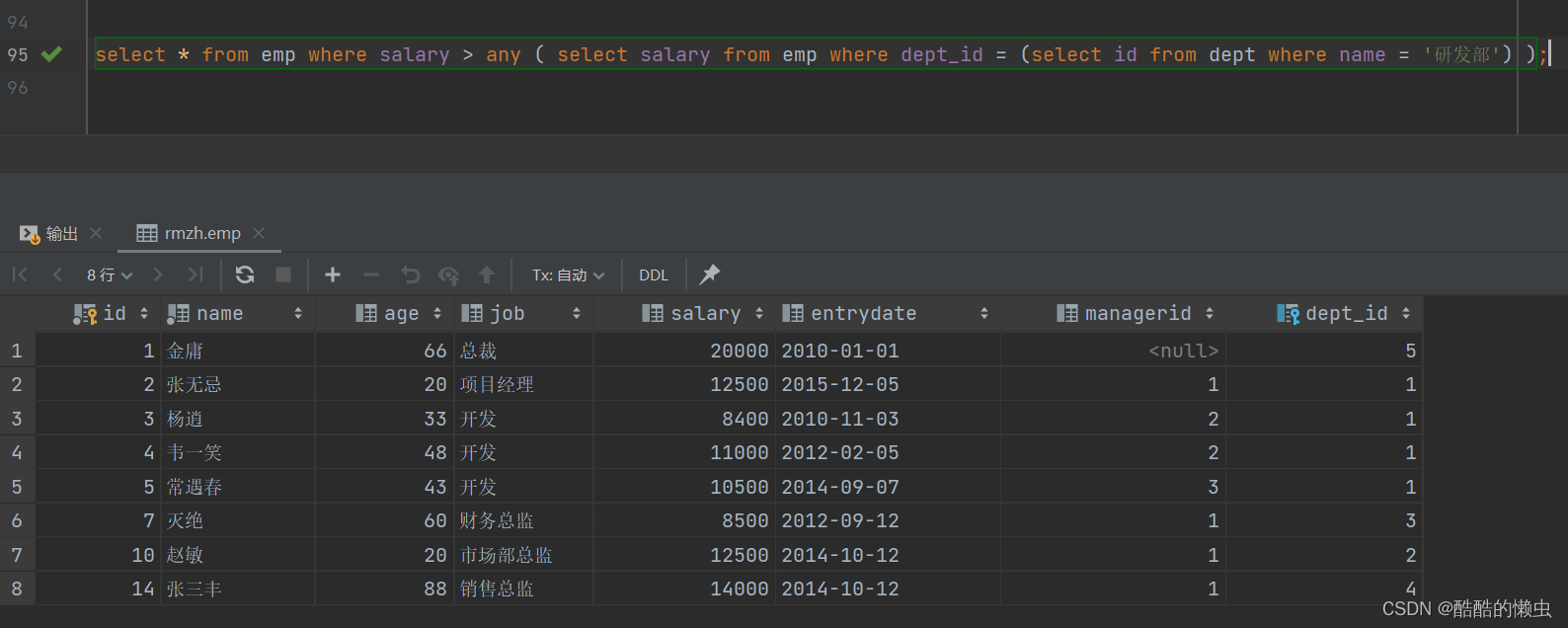
5.6.4 行子查询
子查询返回的结果是一行(可以是多列),这种子查询称为行子查询。
- 常用的操作符:
=、<>、in、not in
案例:
A. 查询与 “张无忌” 的薪资及直属领导相同的员工信息 ;
- 这个需求同样可以拆解为两步进行:
-
- ①. 查询 “张无忌” 的薪资及直属领导
select salary, managerid from emp where name = '张无忌';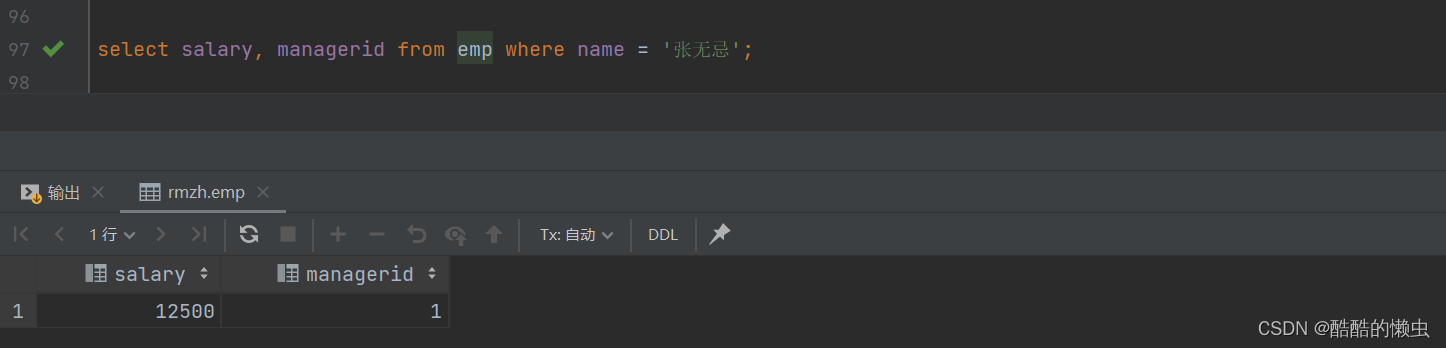
-
- ②. 查询与 “张无忌” 的薪资及直属领导相同的员工信息 ;
select * from emp where (salary,managerid) = (select salary, managerid from emp where name = '张无忌');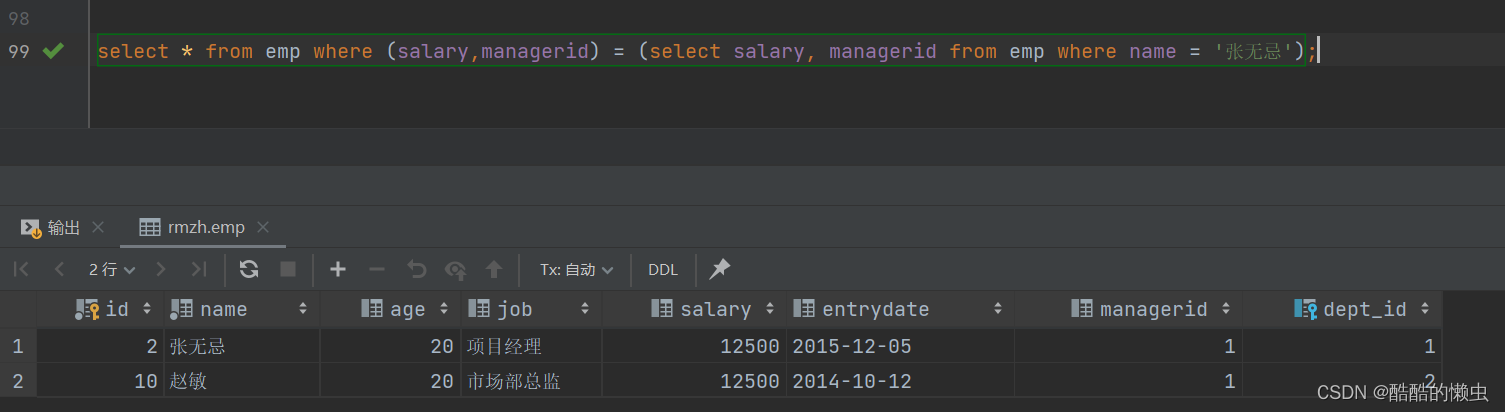
5.6.5 表子查询
子查询返回的结果是 多行多列,这种子查询称为 表子查询。
- 常用的操作符:
in - 经常出现在
from之后,把表子查询返回的结果作为临时表,再和其他表进行联查操作。
案例:
A. 查询与 “鹿杖客” , “宋远桥” 的职位和薪资相同的员工信息
- 分解为两步执行:
-
- ①. 查询 “鹿杖客” , “宋远桥” 的职位和薪资
select job, salary from emp where name = '鹿杖客' or name = '宋远桥';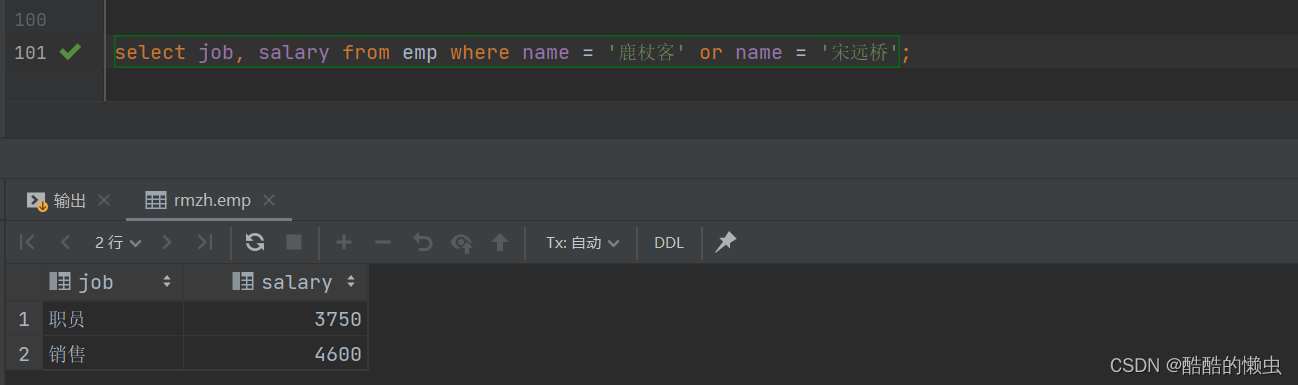
-
- ②. 查询与 “鹿杖客” , “宋远桥” 的职位和薪资相同的员工信息
select * from emp where (job,salary) in ( select job, salary from emp where name = '鹿杖客' or name = '宋远桥' );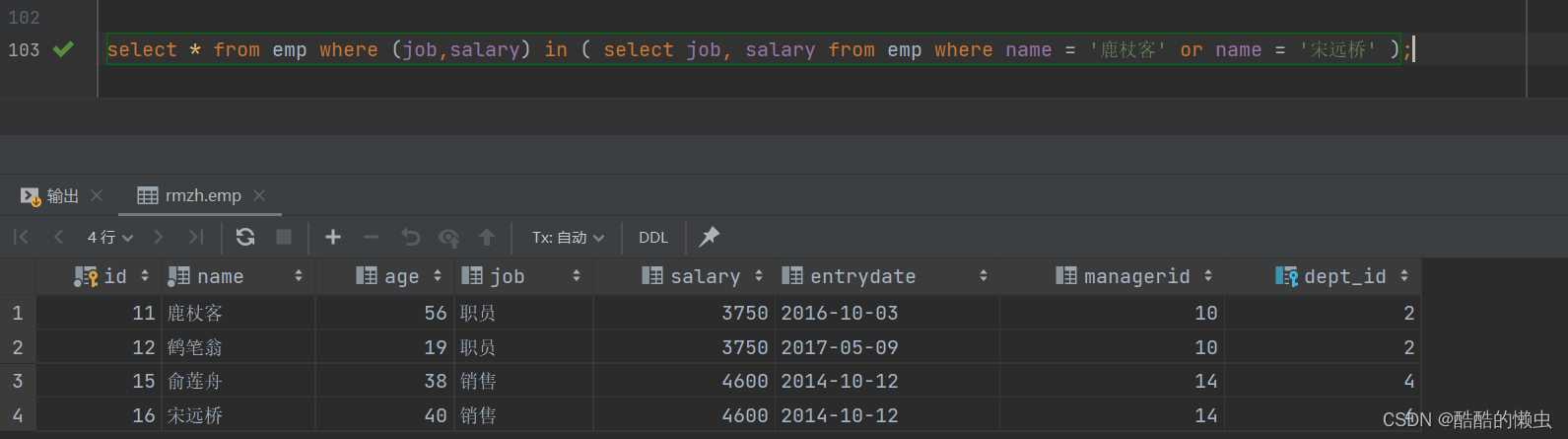
B. 查询入职日期是 “2016-01-01” 之后的员工信息 , 及其部门信息
- 分解为两步执行:
-
- ①. 入职日期是 “2016-01-01” 之后的员工信息
select * from emp where entrydate > '2016-01-01';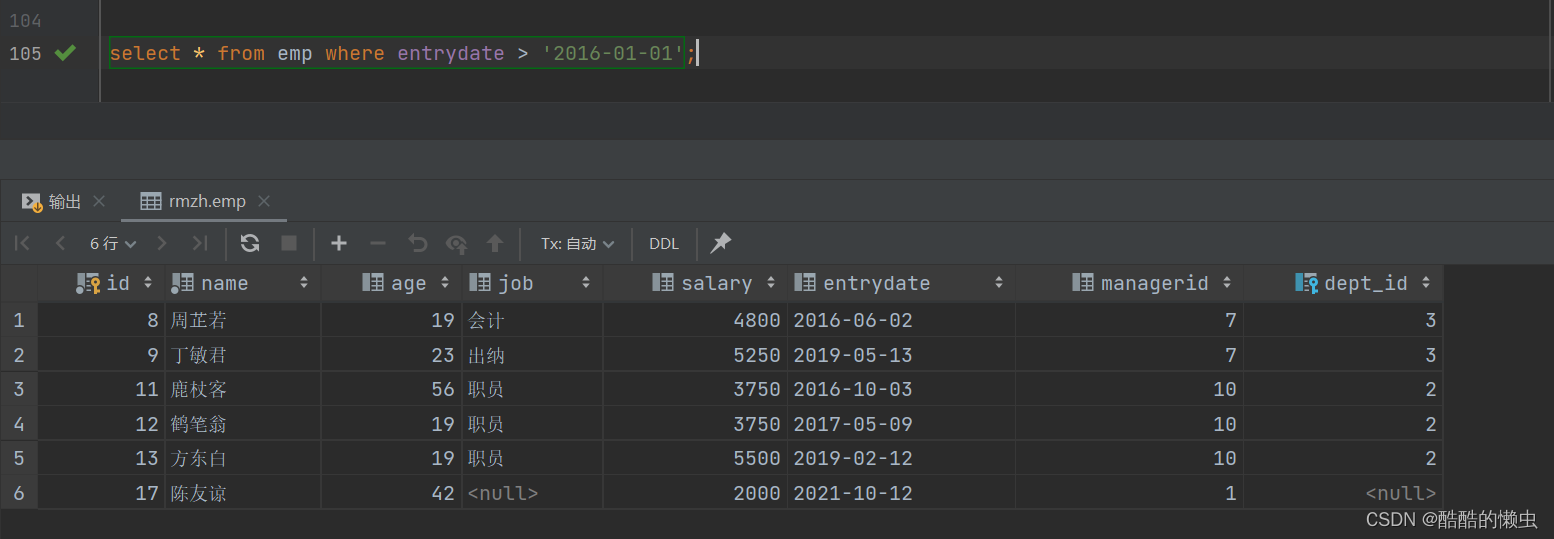
-
- ②. 查询这部分员工, 对应的部门信息;
select e.*, d.* from (select * from emp where entrydate > '2016-01-01') e left join dept d on e.dept_id = d.id ;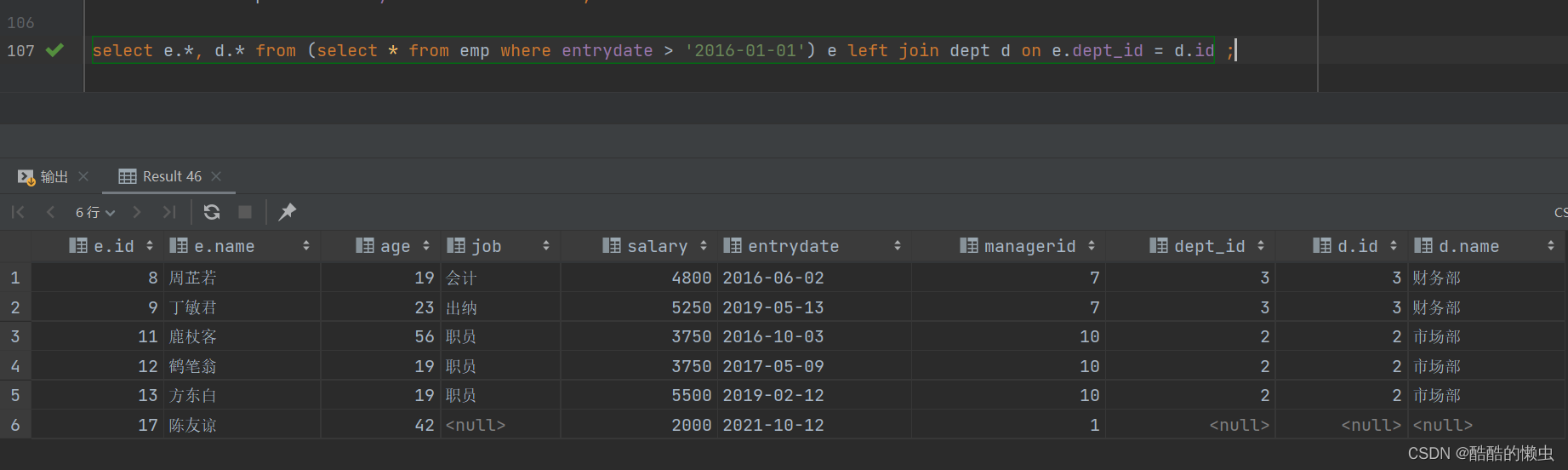
🚀🚀🚀 多表查询 快速食用:---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------->
# 1、内连接## 1.1). 隐式内连接select 字段列表 from 表1 , 表2 where 条件 ... ;## 1.2). 显式内连接select 字段列表 from 表1 [ inner ] join 表2 on 连接条件 ... ;# 2、外连接## 2.1). 左外连接select 字段列表 from 表1 left [ outer ] join 表2 on 条件 ... ;## 2.2). 右外连接select 字段列表 from 表1 right [ outer ] join 表2 on 条件 ... ;# 3、自连接select 字段列表 from 表A 别名A join 表A 别名B on 条件 ... ;# 4、联合查询select 字段列表 from 表A ...union [ all ] # 注意是否需要去重select 字段列表 from 表B ....;# 5、子查询/嵌套查询select * from t1 where column1 = ( select column1 from t2 );## 5.1). 标量子查询常用的操作符:= <> > >= < <=## 5.2). 列子查询常用的操作符:in 、not in 、 any 、some 、 all## 5.3). 行子查询常用的操作符:= 、<> 、in 、not in## 5.4). 表子查询常用的操作符:in注:仅供学习参考!如有不足,欢迎指正!!!
来源地址:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_43412762/article/details/132548235
免责声明:
① 本站未注明“稿件来源”的信息均来自网络整理。其文字、图片和音视频稿件的所属权归原作者所有。本站收集整理出于非商业性的教育和科研之目的,并不意味着本站赞同其观点或证实其内容的真实性。仅作为临时的测试数据,供内部测试之用。本站并未授权任何人以任何方式主动获取本站任何信息。
② 本站未注明“稿件来源”的临时测试数据将在测试完成后最终做删除处理。有问题或投稿请发送至: 邮箱/279061341@qq.com QQ/279061341





![[mysql]mysql8修改root密码](https://static.528045.com/imgs/21.jpg?imageMogr2/format/webp/blur/1x0/quality/35)









