Springboot项目如何快速实现Aop功能
这篇文章主要讲解了“Springboot项目如何快速实现Aop功能”,文中的讲解内容简单清晰,易于学习与理解,下面请大家跟着小编的思路慢慢深入,一起来研究和学习“Springboot项目如何快速实现Aop功能”吧!
依赖引入
Springboot引入AOP依赖包后,一般来说是不需要再做其他配置了,在比较低的版本或者有其他配置影响了AOP的相关功能,导致aop功能不生效,可以试试在启动类上增加@EnableAspectJAutoProxy来启用;
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-aop</artifactId></dependency>代码实现
自定义注解@TestAop
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)public @interface TestAop {}ExampleAop .java
@Component@Aspect@Slf4jpublic class ExampleAop { //切入点:增强标有@TestAop注解的方法 @Pointcut(value = "@annotation(TestAop)") //切入点签名 public void pointcut() { System.out.println("pointCut签名。。。"); } //前置通知 @Before("pointcut()") public void deBefore(JoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable { log.info("前置通知被执行"); //可以joinpoint中得到命中方法的相关信息,利用这些信息可以做一些额外的业务操作; } //返回通知 @AfterReturning(returning = "ret", pointcut = "pointcut()") public void doAfterReturning(Object ret) throws Throwable { log.info("返回通知被执行"); //可以joinpoint中得到命中方法的相关信息,利用这些信息可以做一些额外的业务操作; } //异常通知 @AfterThrowing(throwing = "ex", pointcut = "pointcut()") public void throwss(JoinPoint jp, Exception ex) { log.info("异常通知被执行"); //可以joinpoint中得到命中方法的相关信息,利用这些信息可以做一些额外的业务操作; //可以从ex中获取到具体的异常信息 } //后置通知 @After("pointcut()") public void after(JoinPoint jp) { log.info("后置通知被执行"); //可以joinpoint中得到命中方法的相关信息,利用这些信息可以做一些额外的业务操作; } @Around("pointcut()") public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint) throws Throwable { log.info("------环绕通知 start"); String methodName = proceedingJoinPoint.getSignature().getName(); String className = proceedingJoinPoint.getTarget().getClass().getName(); Object[] args = proceedingJoinPoint.getArgs(); String argsName = null; StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); if (args != null && args.length > 0) { for (int i = 0; i < args.length; i++) { if (args[i] != null) { sb.append(";").append(args[i].getClass().getName()); } } if (sb.toString().length() > 0) { argsName = sb.toString().substring(1); } } log.info("命中类:{},方法{},参数{};", className, methodName, argsName); Object proceed = proceedingJoinPoint.proceed(); log.info("------环绕通知 end"); return proceed; } }核心注解和类
Aspect,表示当前类是一个切面类,简单理解就是切入点和通知的抽象封装,表述的是切入点和通知方法之间的对应关系;
@Before,前置通知,用于方法上,被@Before注解标记的方法会在被切入方法执行之前执行;
@After,后置通知,用于方法上,被@After注解标记的方法会在被切入方法执行之后执行;
@AfterReturning,返回通知,用于方法上,被@AfterReturning注解标记的方法会在被切入方法返回结果之后执行;
@AfterThrowing:异常通知,用于方法上,被@AfterThrowing注解标记的方法会在被切入方法抛出异常之后执行,一般用于有目的的获取异常信息;
@Aroud:环绕通知,用于方法上,被@Around注解标记的方法会在被切入方法执行前后执行;
@Pointcut,切入点,标记在方法上,用于定义切入点,所谓的切入点是指对哪些连接点处进行切入增强的定义,在Spring中具体就是指对哪些方法进行切入增强的定义;被@Pointcut注解表示切入点的表达式有多种,最常用的是两种,execution表达式和注解;
Jointpoint,连接点,所谓的连接点是指被aop切面切入的位置点,在Spring中具体就是指被切入的方法;
PointCut,
Advice,通知,所谓的通知是指对定义好的切入点进行拦截后,要具体做哪些操作的定义;在Spring中就是指被@Before、@After、@AfterReturning、@AfterThrowing、@Around注解标记的方法;
标记切入点的常用方式
execution表达式
表达式请法:访问修饰符 返回值 包名.包名...类名.方法(参数列表)
示例1:表示匹配所有com.fanfu包以及子包下的所有类中以add开头的方法,返回值、参数不限;
@Pointcut("execution(* com.fanfu..*.*.add*(..))")示例2:表示匹配所有com.fanfu包以及子包下的所有类中以add开头,参数类型是String的方法,返回值不限;
@Pointcut("execution(* com.fanfu..*.*.add*(String))")示例3:表示匹配com.fanfu包下任意类、任意方法、任意参数;
@Pointcut("execution(* com.fanfu..*.*.*(String))")execution()为表达式的主体;
第一个*表示返回值类型为任意,即不限制返回值类型;
包后的*表示当前包,包后面连续两个..表示当前包以及子包;
(..)表示任意参数;
最后的*.*(..)表示匹配任意类、任意方法、任意参数;
注解
注解语法:@annotation(自定义的注解)
示例:表示匹配所有标记@TestAop注解的方法;
@Pointcut("@annotation(com.fanfu.config.TestAop)")Spring Aop的小技巧
每一个@Pointcut可以使用execution或注解来定义切入点,多个切点之间还可以使用逻辑运算符,如&&、||、!运算;
point1()&&point2()表示命中point1和point2的所有切入点的交集;如示例:com.fanfu包以及下属所有子包的所有类中,方法名是以add开头,参数类型是String的所有方法,与com.fanfu.service包以及下属所有子包的所有类中,不限方法名和参数类型的所有方法取交集,即com.fanfu.service包以及下属所有子包的所有类中,方法或是add1或add2的方法,在调用前后都会执行环绕通知around()方法内的逻辑;
@Component@Aspect@Slf4jpublic class ExampleAop { @Pointcut("execution(* com.fanfu..*.*.add*(String))") public void point1() { } @Pointcut("execution(* com.fanfu.service..*.*(..))") public void point2() { } @Pointcut("point1()&&point2()") public void point() { } @Around("point()") public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint) throws Throwable { log.info("------around start"); Object proceed = proceedingJoinPoint.proceed(); log.info("------around end"); return proceed; }}point1()&&point2()表示命中point1和point2的所有切入点的并集;如示例:com.fanfu.service包以及下属所有子包的所有类中,方法名是add1,参数类型是String的所有方法,与com.fanfu.controller包以及下属所有子包的所有类中,方法名是add2,参数类型是String的所有方法取并集,即com.fanfu.service或com.fanfu.controller的包以及下属所有子包的所有类中,方法或是add1或add2的方法,在调用前后都会执行环绕通知around()方法内的逻辑;
@Component@Aspect@Slf4jpublic class ExampleAop { @Pointcut("execution(* com.fanfu.service..*.add*(String))") public void point1() { } @Pointcut("execution(* com.fanfu.controller..*.*.add*(String))") public void point2() { } @Pointcut("point1()||point2()") public void point() { } @Around("point()") public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint) throws Throwable { log.info("------around start"); Object proceed = proceedingJoinPoint.proceed(); log.info("------around end"); return proceed; }}!point()表示命中point()的所有切入点取反,如示例:com.fanfu.service包及下属所有子包的所有类中,不是以add开头的方法,在调用前后都会执行环绕通知around()方法内的逻
@Component@Aspect@Slf4jpublic class ExampleAop { @Pointcut("execution(* com.fanfu.service..*.add*(String))") public void point() { } @Around("!point()") public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint) throws Throwable { log.info("------around start"); Object proceed = proceedingJoinPoint.proceed(); log.info("------around end"); return proceed; }}Spring Aop注意事项
与定义的切点匹配方法,如果在当前调用链中,方法在当前类是首次匹配则会命中,即执行相关的通知,如果当前的调用链没有结束,又在当前方法里调用了当前类的与其他切入点匹配方法,则不会再命中,即其他与切入点匹配的方法执行的时候不会再触发相关的通知;
如下示例:
当请求http://localhost:8080/example时,ExampleController中的example方法被触发,ExampleController#example()又调用了ExampleService#test(),在ExampleService#test()内部,又顺序调用了ExampleService#test1()和ExampleService#test2();在ExampleAop中,按照execution中的配置,是可以匹配到test()、test1()、test2(),实际是命中的方法只有test();
@Component@Aspect@Slf4jpublic class ExampleAop { @Pointcut("execution(* com.fanfu.service.impl.ExampleServiceImpl.test*(..))") public void point2() { log.info("切入点匹配"); } @Around("point()") public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint) throws Throwable { log.info("------around start"); String methodName = proceedingJoinPoint.getSignature().getName(); String className = proceedingJoinPoint.getTarget().getClass().getName(); Object[] args = proceedingJoinPoint.getArgs(); String argsName=null; StringBuilder sb=new StringBuilder(); if (args!=null&&args.length>0) { for (int i = 0; i < args.length; i++) { if (args[i] != null) { sb.append(";").append(args[i].getClass().getName()); } } if (sb.toString().length()>0) { argsName=sb.toString().substring(1); } } log.info("命中类:{},方法{},参数{};",className,methodName,argsName); Object proceed = proceedingJoinPoint.proceed(); log.info("------around end"); return proceed; }}@Service@Slf4jpublic class ExampleServiceImpl implements IExampleService { @Override public String test(String msg) { log.info("test方法被执行"); this.test1(msg); this.test2(msg); return msg; } public String test1(String msg) { log.info("test1方法被执行"); return "msg1"; } public String test2(String msg) { log.info("test2方法被执行"); return "msg2"; }}public interface IExampleService { public String test(String msg); public String test1(String msg); public String test2(String msg);}@RestController@Slf4jpublic class ExampleController { @Autowired private IExampleService exampleService; @GetMapping("/example") public String example() { log.info("example start"); exampleService.test(null); log.info("example end"); return String.valueOf(System.currentTimeMillis()); }}
对于上面的问题,如果把execution表达换成注解,会不会结果不一样?再把ExampleAop中的@Pointcut改成注解形式,再在ExampleService#test1()、ExampleService#test2()、ExampleService#test()添加注解@TestAop,验证结果依然是一样的,只有test()会命中,其他不会!所以要注意呀。
@Component@Aspect@Slf4jpublic class ExampleAop { @Pointcut("@annotation(TestAop)") public void point() { } @Around("point()") public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint) throws Throwable { log.info("------around start"); String methodName = proceedingJoinPoint.getSignature().getName(); String className = proceedingJoinPoint.getTarget().getClass().getName(); Object[] args = proceedingJoinPoint.getArgs(); String argsName = null; StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); if (args != null && args.length > 0) { for (int i = 0; i < args.length; i++) { if (args[i] != null) { sb.append(";").append(args[i].getClass().getName()); } } if (sb.toString().length() > 0) { argsName = sb.toString().substring(1); } } log.info("命中类:{},方法{},参数{};", className, methodName, argsName); Object proceed = proceedingJoinPoint.proceed(); log.info("------around end"); return proceed; }}@Service@Slf4jpublic class ExampleServiceImpl implements IExampleService { @Override @TestAop public String test(String msg) { log.info("test方法被执行"); this.test1(msg); this.test2(msg); return msg; } @Override @TestAop public String test1(String msg) { log.info("test1方法被执行"); return "msg1"; } @Override @TestAop public String test2(String msg) { log.info("test2方法被执行"); return "msg2"; } }那什么情况下,ExampleService#test1()、ExampleService#test2()、ExampleService#test()会同时命中呢?让从ExampleController#example()到ExampleService#test1()、ExampleService#test2()、ExampleService#test()分别在不同的调用链上,那么就可以同时命中了;
@RestController@Slf4jpublic class ExampleController { @Autowired private IExampleService exampleService; @GetMapping("/example") public String example() { log.info("example start"); exampleService.test(null); exampleService.test1(null); exampleService.test2(null); log.info("example end"); return String.valueOf(System.currentTimeMillis()); }}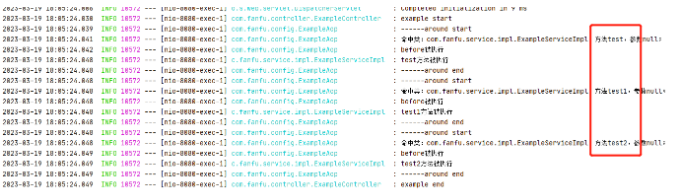
感谢各位的阅读,以上就是“Springboot项目如何快速实现Aop功能”的内容了,经过本文的学习后,相信大家对Springboot项目如何快速实现Aop功能这一问题有了更深刻的体会,具体使用情况还需要大家实践验证。这里是编程网,小编将为大家推送更多相关知识点的文章,欢迎关注!
免责声明:
① 本站未注明“稿件来源”的信息均来自网络整理。其文字、图片和音视频稿件的所属权归原作者所有。本站收集整理出于非商业性的教育和科研之目的,并不意味着本站赞同其观点或证实其内容的真实性。仅作为临时的测试数据,供内部测试之用。本站并未授权任何人以任何方式主动获取本站任何信息。
② 本站未注明“稿件来源”的临时测试数据将在测试完成后最终做删除处理。有问题或投稿请发送至: 邮箱/279061341@qq.com QQ/279061341















