怎么在tomcat中调用Servlet实现初始化
怎么在tomcat中调用Servlet实现初始化?相信很多没有经验的人对此束手无策,为此本文总结了问题出现的原因和解决方法,通过这篇文章希望你能解决这个问题。
一、代码启动tomcat
平常我们不论是Windows还是linux,我们都是通过脚本来启动tomcat,这对于我们分析源码不是很友好,所以我们 需要通过代码启动,启动代码如下:
Tomcat tomcat = new Tomcat(); tomcat.setPort(8080); //new 出各层容器,并且维护各层容器的关系 tomcat.addWebapp("/","/"); tomcat.start(); //阻塞监听端口 tomcat.getServer().await();启动代码还是非常非常简单,从代码中我们就可以看出,我们本篇博客主要分析的就是 addWebapp()方法和start()方法,通过这两个方法我们就可以找到servlet容器是在什么时候被初始化的。
二、tomcat框架
在我们进行分析上面两个方法之前,我们先总结一下tomcat的基础框架,其实从我们非常熟悉的 server.xml配置文件中就可以知道,tomcat就是一系列父子容器组成:
Server ---> Service --> Connector Engine addChild---> context(servlet容器) ,这就是我们从配置文件中分析出来的几个容器,tomcat启动时候就是逐层启动容器。
三、创建容器(addWebapp())
3.1 方法 调用流程图
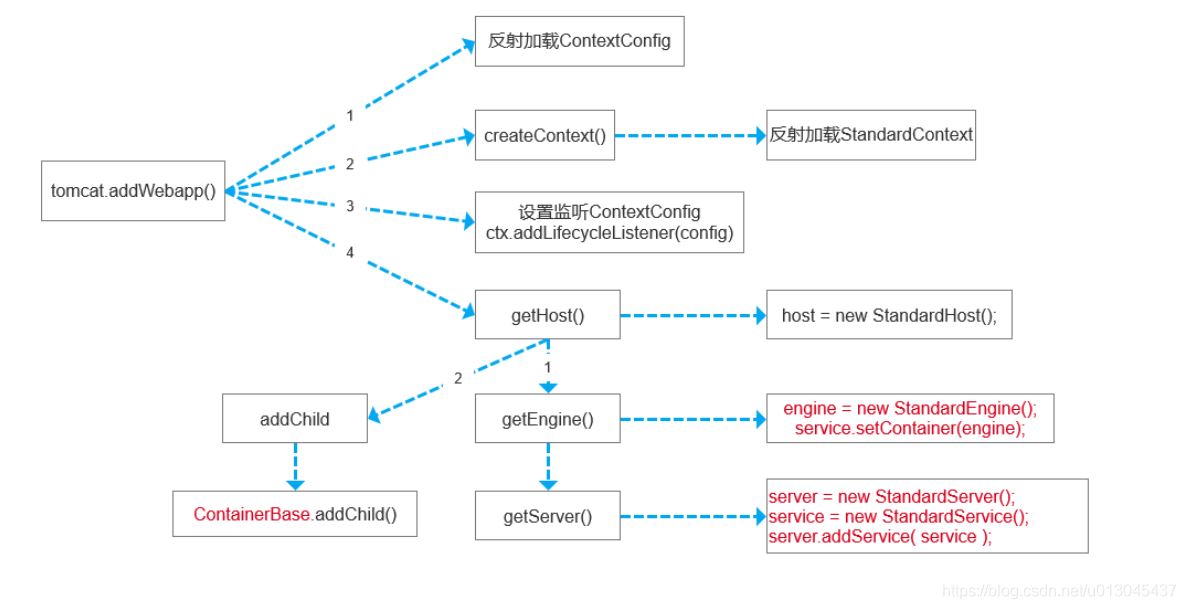
上面的流程图就是,从源码中逐步分析出来的几个重要的方法,这对于我们分析源码非常有帮助。
3.2 源码分析
1)通过反射获得configContext监听器
方法路径:package org.apache.catalina.startup.Tomcat.addWebapp(Host host, String contextPath, String docBase);
public Context addWebapp(Host host, String contextPath, String docBase) { //通过反射获得一个监听器 ContextConfig, //通过反射得到的一定是LifecycleListener的一个实现类,进入getConfigClass得到实现类(org.apache.catalina.startup.ContextConfig) LifecycleListener listener = null; try { Class<?> clazz = Class.forName(getHost().getConfigClass()); listener = (LifecycleListener) clazz.getConstructor().newInstance(); } catch (ReflectiveOperationException e) { // Wrap in IAE since we can't easily change the method signature to // to throw the specific checked exceptions throw new IllegalArgumentException(e); } return addWebapp(host, contextPath, docBase, listener); }2) 获得一个context容器(StandardContext)
在下面代码中,createContext()方法通过反射加载StandardContext容器,并且将设置监听ContextConfig, ctx.addLifecycleListener(config);
public Context addWebapp(Host host, String contextPath, String docBase, LifecycleListener config) { silence(host, contextPath); //获得一个context容器(StandardContext) Context ctx = createContext(host, contextPath); ctx.setPath(contextPath); ctx.setDocBase(docBase); if (addDefaultWebXmlToWebapp) { ctx.addLifecycleListener(getDefaultWebXmlListener()); } ctx.setConfigFile(getWebappConfigFile(docBase, contextPath)); //把监听器添加到context中去 ctx.addLifecycleListener(config); if (addDefaultWebXmlToWebapp && (config instanceof ContextConfig)) { // prevent it from looking ( if it finds one - it'll have dup error ) ((ContextConfig) config).setDefaultWebXml(noDefaultWebXmlPath()); } if (host == null) { //getHost会逐层创建容器,并维护容器父子关系 getHost().addChild(ctx); } else { host.addChild(ctx); } return ctx; }3)维护各层容器
getHost()方法中得到各层容器,并且维护父亲容器关系,其中包括,server容器、Engine容器。并且将StandardContext容器通过getHost().addChild(ctx); 调用containerBase中的addChild()方法维护在 children 这个map中。
public Host getHost() { //将每一层的容器都new 出来 Engine engine = getEngine(); if (engine.findChildren().length > 0) { return (Host) engine.findChildren()[0]; } Host host = new StandardHost(); host.setName(hostname); //维护tomcat中的父子容器 getEngine().addChild(host); return host; }getEngine().addChild(host); 方法选择调用父类containerBase中的addChild方法
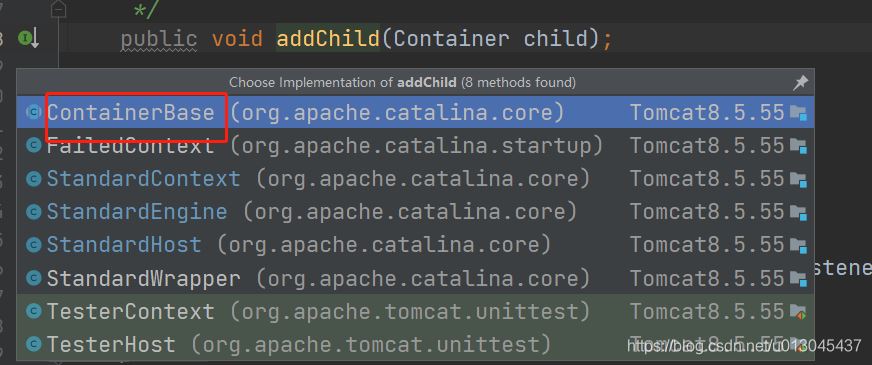
@Override public void addChild(Container child) { if (Globals.IS_SECURITY_ENABLED) { PrivilegedAction<Void> dp = new PrivilegedAddChild(child); AccessController.doPrivileged(dp); } else { //这里的child 参数是 context 容器 addChildInternal(child); } }addChildInternal()方法的 核心代码
private void addChildInternal(Container child) { if( log.isDebugEnabled() ) log.debug("Add child " + child + " " + this); synchronized(children) { if (children.get(child.getName()) != null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("addChild: Child name '" + child.getName() + "' is not unique"); child.setParent(this); // May throw IAE children.put(child.getName(), child); }四、启动容器(tomcat.start())
4.1、方法调用流程图
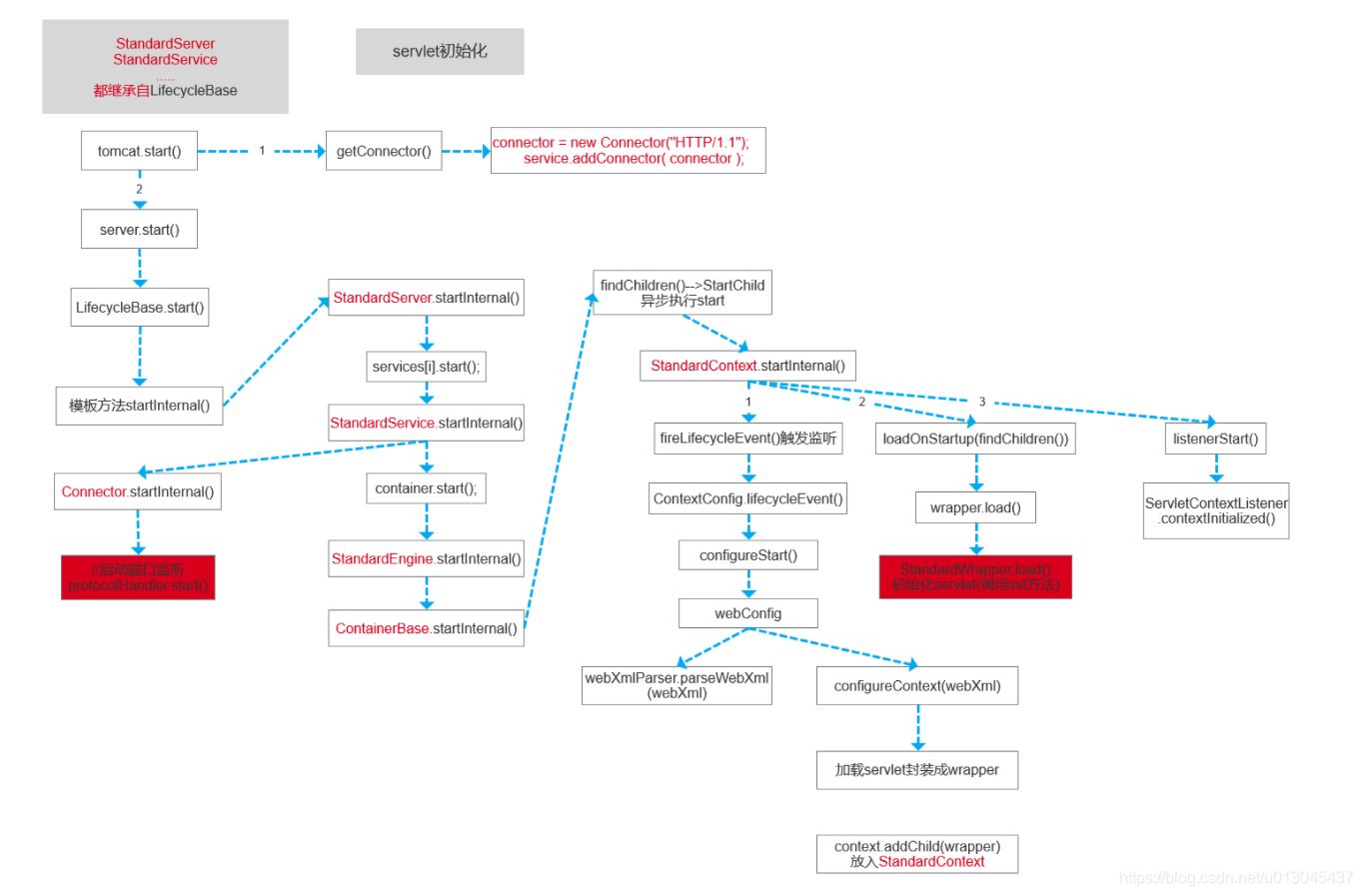
4.2、源码分析
说明:StandardServer 、StandardService、StandardEngine等容器都是继承LifecycleBase
所以这里是模板模式的经典应用
1)逐层启动容器
此时的server对应的是我们前面创建的StandardServer
public void start() throws LifecycleException { //防止server容器没有创建 getServer(); //获得connector容器,并且将得到的connector容器设置到service容器中 getConnector(); //这里的start的实现是在 LifecycleBase类中实现 //LifecycleBase方法是一个模板方法,在tomcat启动流程中非常关键 server.start(); }2) 进入start方法
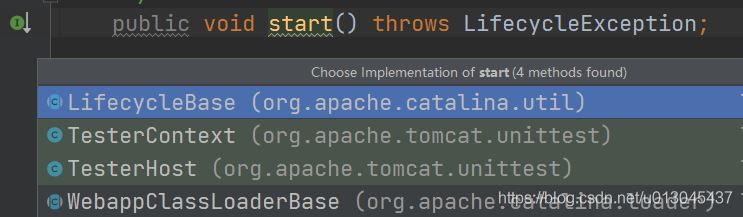
进入LifecycelBase中的start方法,其中核心方法是startInternal。
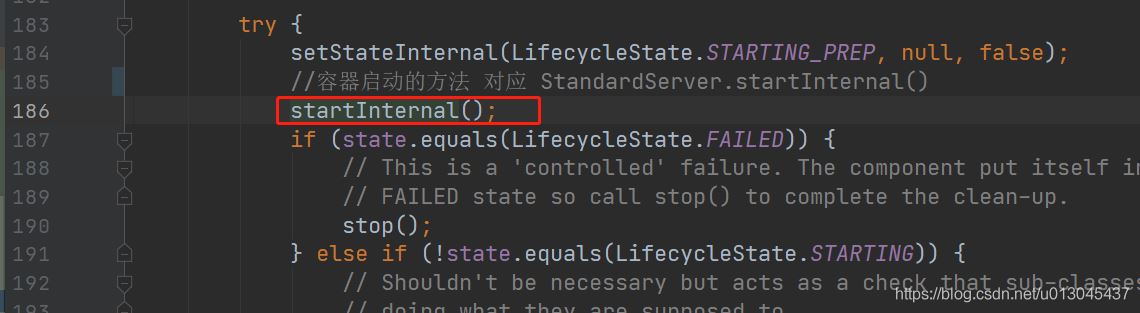
从上面我们知道现在我们调用的是StandardServer容器的startInternal()方法,所以我们这里选择的是StandardServer
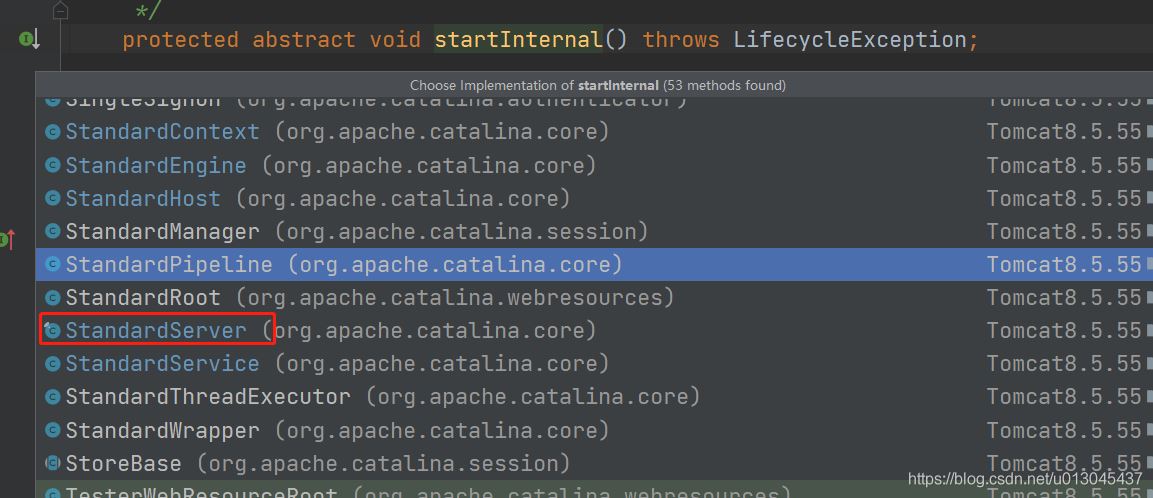
方法路径:org.apache.catalina.core.StandardServer.startInternal()
protected void startInternal() throws LifecycleException { fireLifecycleEvent(CONFIGURE_START_EVENT, null); setState(LifecycleState.STARTING); globalNamingResources.start(); // Start our defined Services synchronized (servicesLock) { //启动 service容器,一个tomcat中可以配置多个service容器,每个service容器都对应这我们的一个服务应用 for (Service service : services) { //对应 StandardService.startInternal() service.start(); } } }从上面代码中我们可以看出,启动server容器的时候需要启动子容器 service容器,从这里开始就是容器 逐层向向内引爆,所以接下来就是开始依次调用各层容器的star方法。在这里就不在赘述。
2)ContainerBase中的startInternal()方法 核心代码,从这开始启动StandardContext容器
// Start our child containers, if any //在addWwbapp的流程中 addChild方法中加入的,所以这里需要找出来 //这里找出来的就是 context 容器 Container children[] = findChildren(); List<Future<Void>> results = new ArrayList<>(); for (Container child : children) { //通过线程池 异步的方式启动线程池 开始启动 context容器,进入new StartChild results.add(startStopExecutor.submit(new StartChild(child))); }new StartChild(child)) 方法开始启动StandardContext容器
private static class StartChild implements Callable<Void> { private Container child; public StartChild(Container child) { this.child = child; } @Override public Void call() throws LifecycleException { //开始启动context,实际调用 StandardContext.startInternal() child.start(); return null; } }StandardContext.startInternal() 方法中的核心代码:
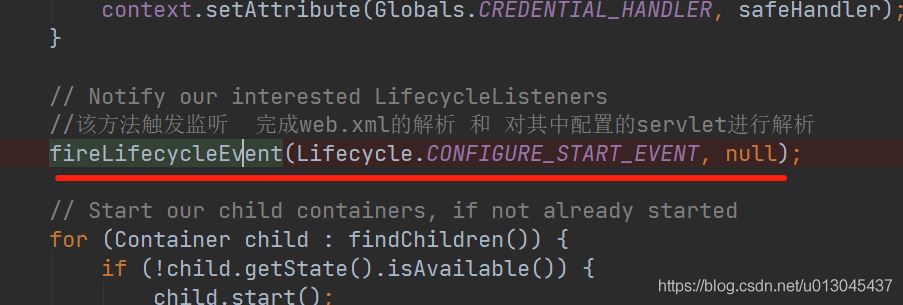
protected void fireLifecycleEvent(String type, Object data) { LifecycleEvent event = new LifecycleEvent(this, type, data); //lifecycleListeners 在addwebapp方法的第一步中,设置的监听的 contextConfig对象 for (LifecycleListener listener : lifecycleListeners) { //这里调用的是 contextConfig的lifecycleEvent()方法 listener.lifecycleEvent(event); } }进入到 contextConfig中的lifecycleEvent()方法
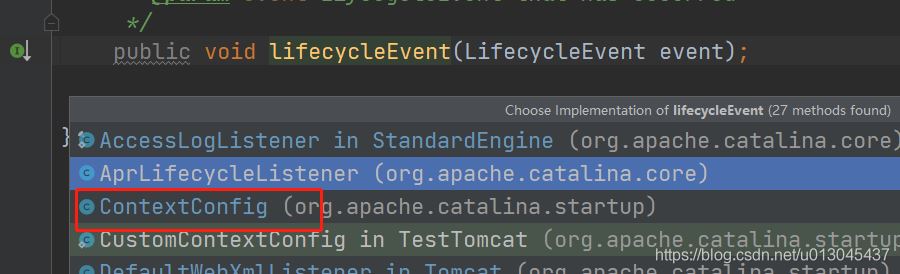
public void lifecycleEvent(LifecycleEvent event) { // Identify the context we are associated with try { context = (Context) event.getLifecycle(); } catch (ClassCastException e) { log.error(sm.getString("contextConfig.cce", event.getLifecycle()), e); return; } // Process the event that has occurred if (event.getType().equals(Lifecycle.CONFIGURE_START_EVENT)) { //完成web.xml的内容解析 configureStart(); } else if (event.getType().equals(Lifecycle.BEFORE_START_EVENT)) { beforeStart(); } else if (event.getType().equals(Lifecycle.AFTER_START_EVENT)) { // Restore docBase for management tools if (originalDocBase != null) { context.setDocBase(originalDocBase); } } else if (event.getType().equals(Lifecycle.CONFIGURE_STOP_EVENT)) { configureStop(); } else if (event.getType().equals(Lifecycle.AFTER_INIT_EVENT)) { init(); } else if (event.getType().equals(Lifecycle.AFTER_DESTROY_EVENT)) { destroy(); } }在上面方法中,完成对web.xml的加载和解析,同时加载xml中配置的servlet并且封装成wrapper对象。
3)、启动servlet容器,StandardContext.startInternal() 中的 loadOnStartup(findChildren())方法
public boolean loadOnStartup(Container children[]) { // Collect "load on startup" servlets that need to be initialized TreeMap<Integer, ArrayList<Wrapper>> map = new TreeMap<>(); for (Container child : children) { //这里的 Wrapper就是 我们前面封装的 servlet Wrapper wrapper = (Wrapper) child; int loadOnStartup = wrapper.getLoadOnStartup(); if (loadOnStartup < 0) { continue; } Integer key = Integer.valueOf(loadOnStartup); ArrayList<Wrapper> list = map.get(key); if (list == null) { list = new ArrayList<>(); map.put(key, list); } list.add(wrapper); } // Load the collected "load on startup" servlets for (ArrayList<Wrapper> list : map.values()) { for (Wrapper wrapper : list) { try { //通过 load 方法 最终会调用 servlet的init方法 wrapper.load(); } catch (ServletException e) { getLogger().error(sm.getString("standardContext.loadOnStartup.loadException", getName(), wrapper.getName()), StandardWrapper.getRootCause(e)); // NOTE: load errors (including a servlet that throws // UnavailableException from the init() method) are NOT // fatal to application startup // unless failCtxIfServletStartFails="true" is specified if(getComputedFailCtxIfServletStartFails()) { return false; } } } } return true; }看完上述内容,你们掌握怎么在tomcat中调用Servlet实现初始化的方法了吗?如果还想学到更多技能或想了解更多相关内容,欢迎关注编程网行业资讯频道,感谢各位的阅读!
免责声明:
① 本站未注明“稿件来源”的信息均来自网络整理。其文字、图片和音视频稿件的所属权归原作者所有。本站收集整理出于非商业性的教育和科研之目的,并不意味着本站赞同其观点或证实其内容的真实性。仅作为临时的测试数据,供内部测试之用。本站并未授权任何人以任何方式主动获取本站任何信息。
② 本站未注明“稿件来源”的临时测试数据将在测试完成后最终做删除处理。有问题或投稿请发送至: 邮箱/279061341@qq.com QQ/279061341














