python-图片之乐-ASCII 文本图形
ASCII:一个简单的字符编码方案
pillow模块:读取图像,访问底层数据
numpy模块:计算平均值
import sys, random, argparseimport numpy as npimport mathfrom PIL import Image定义两种灰度等级作为全局值,用于将亮度值转换为ASCII 字符
从最黑暗变到最亮
# 70 levels of graygscale1 = "$@B%8&WM#*oahkbdpqwmZO0QLCJUYXzcvunxrjft/\|()1{}[]?-_+~<>i!lI;:,\"^`'. "# 10 levels of graygscale2 = '@%#*+=-:. 'http://paulbourke.net/dataformats/asciiart/
准备图像,并分割成网格
cols = 80scale = 0.43# open the image and convert to grayscaleimage = Image.open('youling.png').convert("L")# store the image dimensions # image.sizeW, H = image.size[0], image.size[1]# compute the tile width 根据用户给定列数(cols)计算每个网格的宽度w = W/cols# compute the tile height based on the aspect ratio and scale of the fonth = w/scale# compute the number of rows to use in the final gridrows = int(H/h)w网格的宽 = W图片的宽 / cols列数
h网格的高度 = w网格的宽 / 垂直比例系数scale
rows行 总共有多少行
Pillow模块里的convert()函数可以将图像从一种模式转换为另一种模式
convert(‘L’)将原始图像转换为灰度图像 L is luminance:是图像亮度的单位
convert(‘1’)将原始图像转换为黑白模式
convert(‘P’, palette=Image.ADAPTIVE, colors=1)将原始图像转换为使用颜色调色板的单色模式,colors=2,图片只有2种颜色
还有RGB、RGBA,CMYK,LAB,HSV,YCbCr、XYZ等等模式
CMYK代表青、洋红、黄和黑色,是一种用于印刷的颜色模式。它是印刷过程中使用的四种油墨颜色的缩写,包括青色(Cyan)、洋红色(Magenta)、黄色(Yellow)和黑色(Key),通过它们的不同组合可以得到各种颜色和色调。相对于RGB颜色模式(红、绿、蓝),CMYK颜色模式更适合印刷。
计算灰度图像中每一小块的平均亮度
def getAverageL(image): # get the image as a numpy array im = np.array(image) # get the dimensions w,h = im.shape # get the average return np.average(im.reshape(w*h))将 image 转换成一个 numpy数组,此时 im 成为一个二维数组,包含每个像素的亮度
保存该图像的尺寸
numpy.average()计算该图像中的亮度平均值,做法是用 numpy.reshape()先将维度为宽和高(w,h)的二维数组转换成扁平的一维,其长度是宽度乘以高度(w*h)。然后 numpy.average()调用对这些数组值求和并计算平均值

# an ASCII image is a list of character stringsaimg = []# generate the list of tile dimensionsfor j in range(rows): # 计算每个图像小块的起始和结束 y 坐标 y1 = int(j*h) y2 = int((j+1)*h) # correct the last tile if j == rows-1: y2 = H # append an empty string aimg.append("") for i in range(cols): # crop the image to fit the tile x1 = int(i*w) x2 = int((i+1)*w) # correct the last tile if i == cols-1: x2 = W # crop the image to extract the tile into another Image object img = image.crop((x1, y1, x2, y2)) # get the average luminance # 获取网格的平均亮度值 avg = int(getAverageL(img)) # look up the ASCII character for grayscale value (avg) if moreLevels: # 将平均亮度值[0,255]对用到70级灰度[0,69] gsval = gscale1[int((avg*69)/255)] else: # 将平均亮度值[0,255]对用到10级灰度[0,9] gsval = gscale2[int((avg*9)/255)] # append the ASCII character to the string aimg[j] += gsvalint((avg69)/255)
if avg = 255,可得int((avg69)/255)=69,在该字符串中最后一个索引是69

接下来,为程序定义一些命令行选项。这段代码使用内置的 argparse 类:
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description="descStr")# add expected argumentsparser.add_argument('--file', dest='imgFile', required=True)parser.add_argument('--scale', dest='scale', required=False)parser.add_argument('--out', dest='outFile', required=False)parser.add_argument('--cols', dest='cols', required=False)parser.add_argument('--morelevels', dest='moreLevels', action='store_true')包含指定图像文件输入的选项(唯一必须的参数)
设置垂直比例因子
设置输出文件名
设置 ASCII 输出中的文本列数
添加–morelevels 选项,让用户选择更多层次的灰度梯度
最后,将生成的 ASCII 字符串列表,写入一个文本文件:
# open a new text filef = open(outFile, 'w')# write each string in the list to the new filefor row in aimg:f.write(row + '\n')# clean upf.close()import sys, random, argparseimport numpy as npimport mathfrom PIL import Image# 70 levels of graygscale1 = "$@B%8&WM#*oahkbdpqwmZO0QLCJUYXzcvunxrjft/\|()1{}[]?-_+~<>i!lI;:,\"^`'. "# 10 levels of graygscale2 = '@%#*+=-:. 'def getAverageL(image): # get the image as a numpy array im = np.array(image) # get the dimensions w,h = im.shape # get the average return np.average(im.reshape(w*h))def covertImageToAscii(fileName, cols, scale, moreLevels): """ Given Image and dimensions (rows, cols), returns an m*n list of Images """ # declare globals global gscale1, gscale2 # open image and convert to grayscale image = Image.open(fileName).convert('L') # store the image dimensions W, H = image.size[0], image.size[1] print("input image dims: %d x %d" % (W, H)) # compute tile width w = W/cols # compute tile height based on the aspect ratio and scale of the font h = w/scale # compute number of rows to use in the final grid rows = int(H/h) print("cols: %d, rows: %d" % (cols, rows)) print("tile dims: %d x %d" % (w, h)) # check if image size is too small if cols > W or rows > H: print("Image too small for specified cols!") exit(0) # an ASCII image is a list of character strings aimg = [] # generate the list of tile dimensions for j in range(rows): # 计算每个图像小块的起始和结束 y 坐标 y1 = int(j*h) y2 = int((j+1)*h) # correct the last tile if j == rows-1: y2 = H # append an empty string aimg.append("") for i in range(cols): # crop the image to fit the tile x1 = int(i*w) x2 = int((i+1)*w) # correct the last tile if i == cols-1: x2 = W # crop the image to extract the tile into another Image object img = image.crop((x1, y1, x2, y2)) # get the average luminance # 获取网格的平均亮度值 avg = int(getAverageL(img)) # look up the ASCII character for grayscale value (avg) if moreLevels: # 将平均亮度值[0,255]对用到70级灰度[0,69] gsval = gscale1[int((avg*69)/255)] else: # 将平均亮度值[0,255]对用到10级灰度[0,9] gsval = gscale2[int((avg*9)/255)] # append the ASCII character to the string aimg[j] += gsval # return text image return aimg# main() functiondef main(): # create parser descStr = "This program converts an image into ASCII art." parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description=descStr) # add expected arguments parser.add_argument('--file', dest='imgFile', required=True) parser.add_argument('--scale', dest='scale', required=False) parser.add_argument('--out', dest='outFile', required=False) parser.add_argument('--cols', dest='cols', required=False) parser.add_argument('--morelevels', dest='moreLevels', action='store_true') # parse arguments args = parser.parse_args() imgFile = args.imgFile # set output file outFile = 'out.txt' if args.outFile: outFile = args.outFile # set scale default as 0.43, which suits a Courier font scale = 0.43 if args.scale: scale = float(args.scale) # set cols cols = 80 if args.cols: cols = int(args.cols) print('generating ASCII art...') # convert image to ASCII text aimg = covertImageToAscii(imgFile, cols, scale, args.moreLevels) # open a new text file f = open(outFile, 'w') # write each string in the list to the new file for row in aimg: f.write(row + '\n') # clean up f.close() print("ASCII art written to %s" % outFile) # call mainif __name__ == '__main__': main()https://github.com/electronut/pp/blob/master/ascii/ascii.py
将完整代码保存到py文件中
打开终端,切换到ascii.py目录
输入下面代码
$ python ascii.py --file data/robot.jpg --cols 100
将 data/robot.jpg 替换为你想使用的图像文件的相对路径
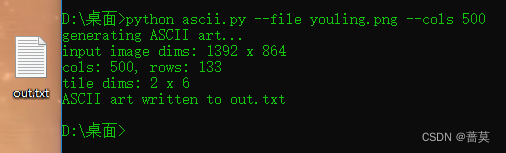
使用vscode打开out.txt文件,使用Ctrl±可以缩小,可以看到全屏,只能看10灰度等级
还可使用notepad查看out.txt文件

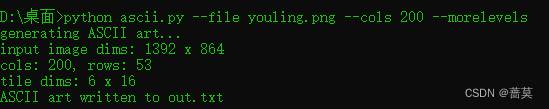
–morelevels就是70灰度等级

来源地址:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_64729620/article/details/132559047
免责声明:
① 本站未注明“稿件来源”的信息均来自网络整理。其文字、图片和音视频稿件的所属权归原作者所有。本站收集整理出于非商业性的教育和科研之目的,并不意味着本站赞同其观点或证实其内容的真实性。仅作为临时的测试数据,供内部测试之用。本站并未授权任何人以任何方式主动获取本站任何信息。
② 本站未注明“稿件来源”的临时测试数据将在测试完成后最终做删除处理。有问题或投稿请发送至: 邮箱/279061341@qq.com QQ/279061341















