如何用Python实时监控
这期内容当中小编将会给大家带来有关如何用Python实时监控,文章内容丰富且以专业的角度为大家分析和叙述,阅读完这篇文章希望大家可以有所收获。
最近突然有个奇妙的想法,就是当我对着电脑屏幕的时候,电脑会先识别屏幕上的人脸是否是本人,如果识别是本人的话需要回答电脑说的暗语,答对了才会解锁并且有三次机会。如果都没答对就会发送邮件给我,通知有人在动我的电脑并上传该人头像。
过程
环境是win10代码我使用的是python3所以在开始之前需要安装一些依赖包,请按顺序安装否者会报错
pip install cmake -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple
pip install dlib -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple
pip install face_recognition -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple
pip install opencv-python -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple接下来是构建识别人脸以及对比人脸的代码
import face_recognition
import cv2
import numpy as np
video_capture = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
my_image = face_recognition.load_image_file("my.jpg")
my_face_encoding = face_recognition.face_encodings(my_image)[0]
known_face_encodings = [
my_face_encoding
]
known_face_names = [
"Admin"
]
face_names = []
face_locations = []
face_encodings = []
process_this_frame = True
while True:
ret, frame = video_capture.read()
small_frame = cv2.resize(frame, (0, 0), fx=0.25, fy=0.25)
rgb_small_frame = small_frame[:, :, ::-1]
if process_this_frame:
face_locations = face_recognition.face_locations(rgb_small_frame)
face_encodings = face_recognition.face_encodings(rgb_small_frame, face_locations)
face_names = []
for face_encoding in face_encodings:
matches = face_recognition.compare_faces(known_face_encodings, face_encoding)
name = "Unknown"
face_distances = face_recognition.face_distance(known_face_encodings, face_encoding)
best_match_index = np.argmin(face_distances)
if matches[best_match_index]:
name = known_face_names[best_match_index]
face_names.append(name)
process_this_frame = not process_this_frame
for (top, right, bottom, left), name in zip(face_locations, face_names):
top *= 4
left *= 4
right *= 4
bottom *= 4
font = cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_DUPLEX
cv2.rectangle(frame, (left, top), (right, bottom), (0, 0, 255), 2)
cv2.rectangle(frame, (left, bottom - 35), (right, bottom), (0, 0, 255), cv2.FILLED)
cv2.putText(frame, name, (left + 6, bottom - 6), font, 1.0, (255, 255, 255), 1)
cv2.imshow('Video', frame)
if cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF == ord('q'):
break
video_capture.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()其中my.jpg需要你自己拍摄上传,运行可以发现在你脸上会出现Admin的框框,我去网上找了张图片类似这样子

识别功能已经完成了接下来就是语音识别和语音合成,这需要使用到百度AI来实现了,去登录百度AI的官网到控制台选择左边的语音技术,然后点击面板的创建应用按钮,来到创建应用界面
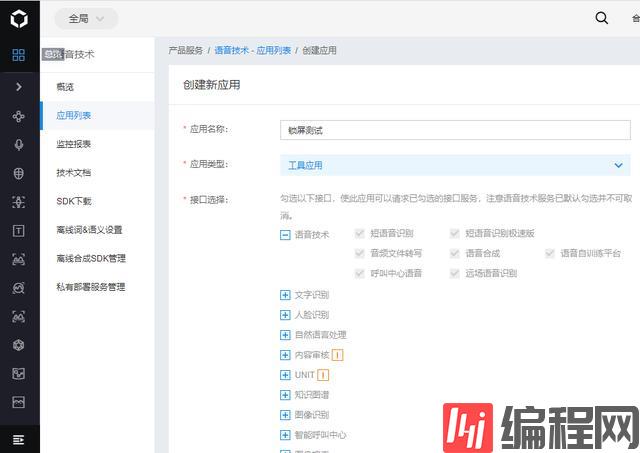
打造电脑版人脸屏幕解锁神器
创建后会得到AppID、API Key、Secret Key记下来,然后开始写语音合成的代码。安装百度AI提供的依赖包
pip install baidu-aip -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple
pip install playsound -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple然后是简单的语音播放代码,运行下面代码可以听到萌妹子的声音
import sys
from aip import AipSpeech
from playsound import playsound
APP_ID = ''
API_KEY = ''
SECRET_KEY = ''
client = AipSpeech(APP_ID, API_KEY, SECRET_KEY)
result = client.synthesis('你好吖', 'zh', 1, {'vol': 5, 'per': 4, 'spd': 5, })
if not isinstance(result, dict):
with open('auido.mp3', 'wb') as file:
file.write(result)
filepath = eval(repr(sys.path[0]).replace('\\', '/')) + '//auido.mp3'
playsound(filepath)有了上面的代码就完成了检测是否在电脑前(人脸识别)以及电脑念出暗语(语音合成)然后我们还需要回答暗号给电脑,所以还需要完成语音识别。
import wave
import pyaudio
from aip import AipSpeech
APP_ID = ''
API_KEY = ''
SECRET_KEY = ''
client = AipSpeech(APP_ID, API_KEY, SECRET_KEY)
CHUNK = 1024
FORMAT = pyaudio.paInt16
CHANNELS = 1
RATE = 8000
RECORD_SECONDS = 3
WAVE_OUTPUT_FILENAME = "output.wav"
p = pyaudio.PyAudio()
stream = p.open(format=FORMAT, channels=CHANNELS, rate=RATE, input=True, frames_per_buffer=CHUNK)
print("* recording")
frames = []
for i in range(0, int(RATE / CHUNK * RECORD_SECONDS)):
data = stream.read(CHUNK)
frames.append(data)
print("* done recording")
stream.stop_stream()
stream.close()
p.terminate()
wf = wave.open(WAVE_OUTPUT_FILENAME, 'wb')
wf.setnchannels(CHANNELS)
wf.setsampwidth(p.get_sample_size(FORMAT))
wf.setframerate(RATE)
wf.writeframes(b''.join(frames))def get_file_content():
with open(WAVE_OUTPUT_FILENAME, 'rb') as fp:
return fp.read()result = client.asr(get_file_content(), 'wav', 8000, {'dev_pid': 1537, })
print(result)运行此代码之前需要安装pyaudio依赖包,由于在win10系统上安装会报错所以可以通过如下方式安装。到这个链接 https://www.lfd.uci.edu/~gohlke/pythonlibs/#pyaudio 去下载对应的安装包然后安装即可。
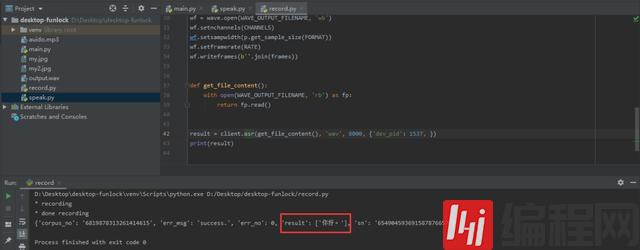
运行后我说了你好,可以看到识别出来了。那么我们的小模块功能就都做好了接下来就是如何去整合它们。可以发现在人脸识别代码中if matches[best_match_index]这句判断代码就是判断是否为电脑主人,所以我们把这个判断语句当作main函数的入口。
if matches[best_match_index]:
# 在这里写识别到之后的功能
name = known_face_names[best_match_index]那么识别到后我们应该让电脑发出询问暗号,也就是语音合成代码,然我们将它封装成一个函数,顺便重构下人脸识别的代码。
import cv2
import time
import numpy as np
import face_recognition
video_capture = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
my_image = face_recognition.load_image_file("my.jpg")
my_face_encoding = face_recognition.face_encodings(my_image)[0]
known_face_encodings = [
my_face_encoding
]
known_face_names = [
"Admin"
]
face_names = []
face_locations = []
face_encodings = []
process_this_frame = Truedef speak(content):
import sys
from aip import AipSpeech
from playsound import playsound
APP_ID = ''
API_KEY = ''
SECRET_KEY = ''
client = AipSpeech(APP_ID, API_KEY, SECRET_KEY)
result = client.synthesis(content, 'zh', 1, {'vol': 5, 'per': 0, 'spd': 5, })
if not isinstance(result, dict):
with open('auido.mp3', 'wb') as file:
file.write(result)
filepath = eval(repr(sys.path[0]).replace('\\', '/')) + '//auido.mp3'
playsound(filepath)try:
while True:
ret, frame = video_capture.read()
small_frame = cv2.resize(frame, (0, 0), fx=0.25, fy=0.25)
rgb_small_frame = small_frame[:, :, ::-1]
if process_this_frame:
face_locations = face_recognition.face_locations(rgb_small_frame)
face_encodings = face_recognition.face_encodings(rgb_small_frame, face_locations)
face_names = []
for face_encoding in face_encodings:
matches = face_recognition.compare_faces(known_face_encodings, face_encoding)
name = "Unknown"
face_distances = face_recognition.face_distance(known_face_encodings, face_encoding)
best_match_index = np.argmin(face_distances)
if matches[best_match_index]:
speak("识别到人脸,开始询问暗号,请回答接下来我说的问题")
time.sleep(1)
speak("天王盖地虎")
error = 1 / 0
name = known_face_names[best_match_index]
face_names.append(name)
process_this_frame = not process_this_frame
for (top, right, bottom, left), name in zip(face_locations, face_names):
top *= 4
left *= 4
right *= 4
bottom *= 4
font = cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_DUPLEX
cv2.rectangle(frame, (left, top), (right, bottom), (0, 0, 255), 2)
cv2.rectangle(frame, (left, bottom - 35), (right, bottom), (0, 0, 255), cv2.FILLED)
cv2.putText(frame, name, (left + 6, bottom - 6), font, 1.0, (255, 255, 255), 1)
cv2.imshow('Video', frame)
if cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF == ord('q'):
break
except Exception as e:
print(e)
finally:
video_capture.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()这里有一点需要注意,由于playsound播放音乐的时候会一直占用这个资源,所以播放下一段音乐的时候会报错,解决方法是修改~\Python37\Lib\site-packages下的playsound.py文件,找到如下代码
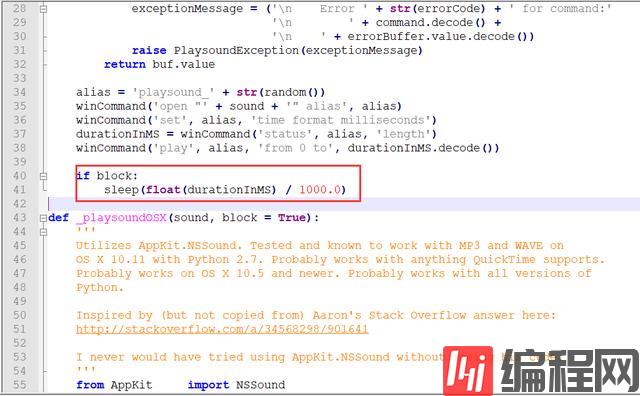
在sleep函数下面添加winCommand('close', alias)这句代码,保存下就可以了。运行发现可以正常将两句话都说出来。那么说出来之后就要去监听了,我们还要打包一个函数。
def record():
import wave
import json
import pyaudio
from aip import AipSpeech
APP_ID = ''
API_KEY = ''
SECRET_KEY = ''
client = AipSpeech(APP_ID, API_KEY, SECRET_KEY)
CHUNK = 1024
FORMAT = pyaudio.paInt16
CHANNELS = 1
RATE = 8000
RECORD_SECONDS = 3
WAVE_OUTPUT_FILENAME = "output.wav"
p = pyaudio.PyAudio()
stream = p.open(format=FORMAT, channels=CHANNELS, rate=RATE, input=True, frames_per_buffer=CHUNK)
print("* recording")
frames = []
for i in range(0, int(RATE / CHUNK * RECORD_SECONDS)):
data = stream.read(CHUNK)
frames.append(data)
print("* done recording")
stream.stop_stream()
stream.close()
p.terminate()
wf = wave.open(WAVE_OUTPUT_FILENAME, 'wb')
wf.setnchannels(CHANNELS)
wf.setsampwidth(p.get_sample_size(FORMAT))
wf.setframerate(RATE)
wf.writeframes(b''.join(frames))
def get_file_content():
with open(WAVE_OUTPUT_FILENAME, 'rb') as fp:
return fp.read()
result = client.asr(get_file_content(), 'wav', 8000, {'dev_pid': 1537, })
result = json.loads(str(result).replace("'", '"'))
return result["result"][0]将识别到人脸后的代码修改成如下
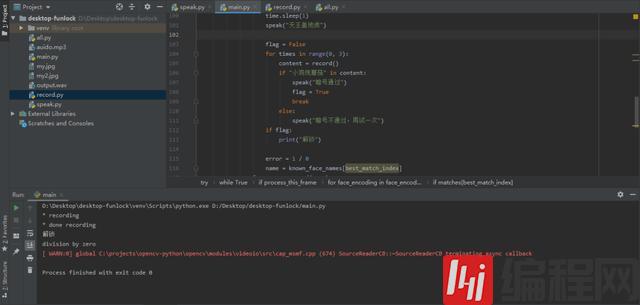
if matches[best_match_index]:
speak("识别到人脸,开始询问暗号,请回答接下来我说的问题")
time.sleep(1)
speak("天王盖地虎")
flag = False
for times in range(0, 3):
content = record()
if "小鸡炖蘑菇" in content:
speak("暗号通过")
flag = True
break
else:
speak("暗号不通过,再试一次")
if flag:
print("解锁")
else:
print("发送邮件并将坏人人脸图片上传!")
error = 1 / 0
name = known_face_names[best_match_index]运行看看效果,回答电脑小鸡炖蘑菇,电脑回答暗号通过。这样功能就基本上完成了。
结语
至于发送邮件的功能和锁屏解锁的功能我就不一一去实现了,我想这应该难不倒大家的。锁屏功能可以HOOK让键盘时间无效化,然后用窗口再覆盖整个桌面即可,至于邮箱发送网上文章很多的。
上述就是小编为大家分享的如何用Python实时监控了,如果刚好有类似的疑惑,不妨参照上述分析进行理解。如果想知道更多相关知识,欢迎关注编程网行业资讯频道。
免责声明:
① 本站未注明“稿件来源”的信息均来自网络整理。其文字、图片和音视频稿件的所属权归原作者所有。本站收集整理出于非商业性的教育和科研之目的,并不意味着本站赞同其观点或证实其内容的真实性。仅作为临时的测试数据,供内部测试之用。本站并未授权任何人以任何方式主动获取本站任何信息。
② 本站未注明“稿件来源”的临时测试数据将在测试完成后最终做删除处理。有问题或投稿请发送至: 邮箱/279061341@qq.com QQ/279061341














