Python中Pip的安装操作
Python有两个著名的包管理工具easy_install和pip。在Python2.7的安装包中,easy_install是默认安装的,而pip需要我们手动安装。随着Python版本的提高,easy_install已经逐渐被淘汰,但是一些比较老的第三方库,在现在仍然只能通过easy_install进行安装。目前,pip已经成为主流的安装工具,自Python2 >=2.7.9或者Python3.4以后默认都安装有pip。
如果很不巧,你的Python版本下恰好没有pip这个工具,怎么办呢?解决办法很多!
- 使用easy_install安装: 各种进入到
easy_install脚本的目录下,然后运行easy_inatall pip - 使用
get-pip.py安装: 在下面的url下载get-pip.py脚本curl https://bootstrap.pypa.io/get-pip.py -o get-pip.py然后运行:python get-pip.py这个脚本会同时安装setuptools和wheel工具。 - 在linux下使用包管理工具安装pip: 例如,ubuntu下:
sudo apt-get install python-pip。Fedora系下:sudo yum install python-pip - 在windows下安装pip: 在C:\python27\scirpts下运行
easy_install pip进行安装。
刚安装完毕的pip可能需要先升级一下自身: 在Linux或masOS中:pip install -U pip 在windows中:python -m pip install -U pip
get-pip.py安装
以方法2. 使用get-pip.py安装,为例
新建一个文本文档,起名为get-pip,后缀名该为.py
打开网址https://bootstrap.pypa.io/get-pip.py,复制所有文字到我们新建的文件get-pip.py中
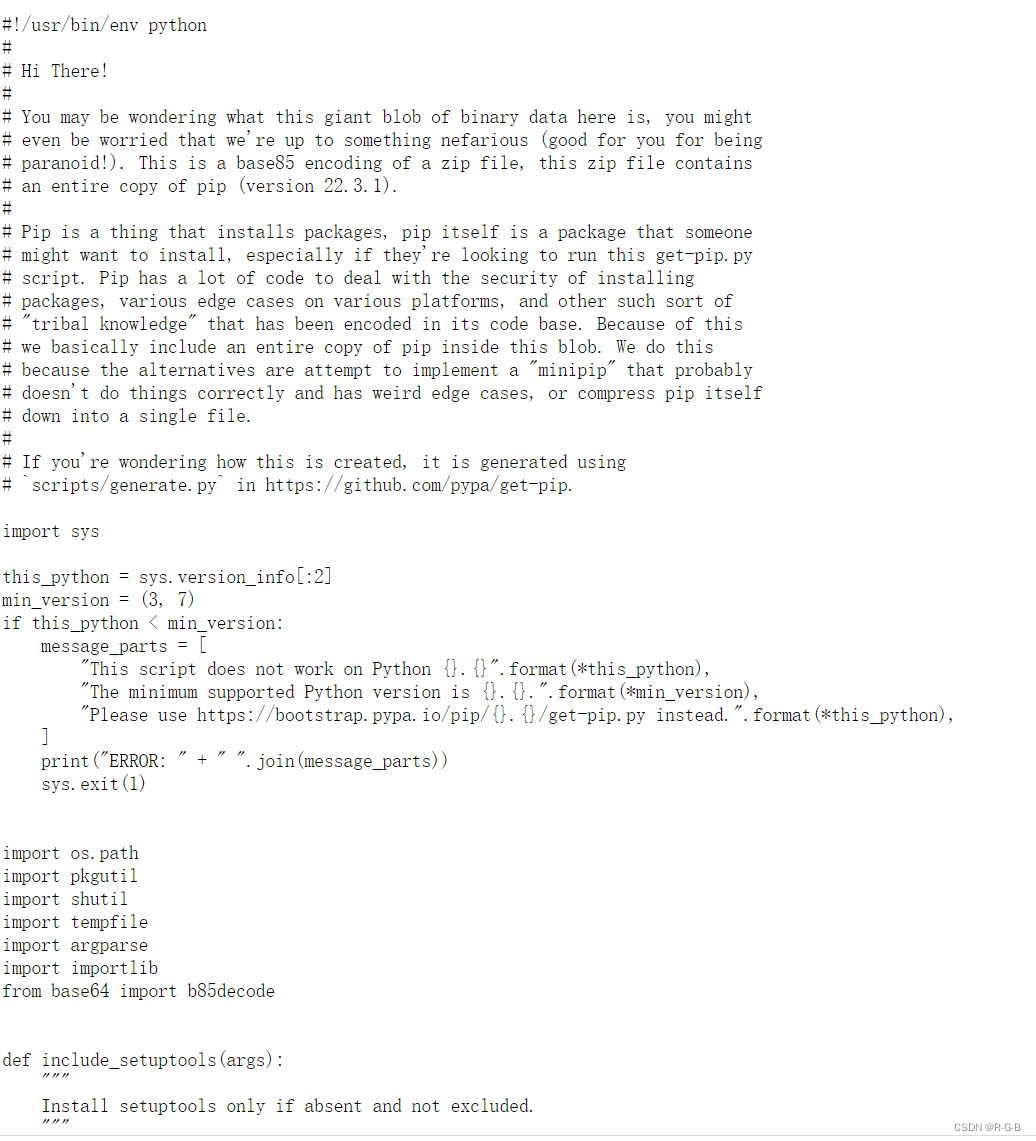
源代码中 DATA = b"“” 乱码 “”",,,DATA 后面注释的乱码有3万多行,我直接给删了,不影响
下面是我实际可运行的代码
#!/usr/bin/env python## Hi There!## You may be wondering what this giant blob of binary data here is, you might# even be worried that we're up to something nefarious (good for you for being# paranoid!). This is a base85 encoding of a zip file, this zip file contains# an entire copy of pip (version 22.3.1).## Pip is a thing that installs packages, pip itself is a package that someone# might want to install, especially if they're looking to run this get-pip.py# script. Pip has a lot of code to deal with the security of installing# packages, various edge cases on various platforms, and other such sort of# "tribal knowledge" that has been encoded in its code base. Because of this# we basically include an entire copy of pip inside this blob. We do this# because the alternatives are attempt to implement a "minipip" that probably# doesn't do things correctly and has weird edge cases, or compress pip itself# down into a single file.## If you're wondering how this is created, it is generated using# `scripts/generate.py` in https://github.com/pypa/get-pip.import systhis_python = sys.version_info[:2]min_version = (3, 7)if this_python < min_version: message_parts = [ "This script does not work on Python {}.{}".format(*this_python), "The minimum supported Python version is {}.{}.".format(*min_version), "Please use https://bootstrap.pypa.io/pip/{}.{}/get-pip.py instead.".format(*this_python), ] print("ERROR: " + " ".join(message_parts)) sys.exit(1)import os.pathimport pkgutilimport shutilimport tempfileimport argparseimport importlibfrom base64 import b85decodedef include_setuptools(args): """ Install setuptools only if absent and not excluded. """ cli = not args.no_setuptools env = not os.environ.get("PIP_NO_SETUPTOOLS") absent = not importlib.util.find_spec("setuptools") return cli and env and absentdef include_wheel(args): """ Install wheel only if absent and not excluded. """ cli = not args.no_wheel env = not os.environ.get("PIP_NO_WHEEL") absent = not importlib.util.find_spec("wheel") return cli and env and absentdef determine_pip_install_arguments(): pre_parser = argparse.ArgumentParser() pre_parser.add_argument("--no-setuptools", action="store_true") pre_parser.add_argument("--no-wheel", action="store_true") pre, args = pre_parser.parse_known_args() args.append("pip") if include_setuptools(pre): args.append("setuptools") if include_wheel(pre): args.append("wheel") return ["install", "--upgrade", "--force-reinstall"] + argsdef monkeypatch_for_cert(tmpdir): """Patches `pip install` to provide default certificate with the lowest priority. This ensures that the bundled certificates are used unless the user specifies a custom cert via any of pip's option passing mechanisms (config, env-var, CLI). A monkeypatch is the easiest way to achieve this, without messing too much with the rest of pip's internals. """ from pip._internal.commands.install import InstallCommand # We want to be using the internal certificates. cert_path = os.path.join(tmpdir, "cacert.pem") with open(cert_path, "wb") as cert: cert.write(pkgutil.get_data("pip._vendor.certifi", "cacert.pem")) install_parse_args = InstallCommand.parse_args def cert_parse_args(self, args): if not self.parser.get_default_values().cert: # There are no user provided cert -- force use of bundled cert self.parser.defaults["cert"] = cert_path # calculated above return install_parse_args(self, args) InstallCommand.parse_args = cert_parse_argsdef bootstrap(tmpdir): monkeypatch_for_cert(tmpdir) # Execute the included pip and use it to install the latest pip and # setuptools from PyPI from pip._internal.cli.main import main as pip_entry_point args = determine_pip_install_arguments() sys.exit(pip_entry_point(args))def main(): tmpdir = None try: # Create a temporary working directory tmpdir = tempfile.mkdtemp() # Unpack the zipfile into the temporary directory pip_zip = os.path.join(tmpdir, "pip.zip") with open(pip_zip, "wb") as fp: fp.write(b85decode(DATA.replace(b"\n", b""))) # Add the zipfile to sys.path so that we can import it sys.path.insert(0, pip_zip) # Run the bootstrap bootstrap(tmpdir=tmpdir) finally: # Clean up our temporary working directory if tmpdir: shutil.rmtree(tmpdir, ignore_errors=True) DATA = b"""""" if __name__ == "__main__": main()代码开头的一段说明文字
你可能想知道这一大块二进制数据是什么甚至担心我们在做一些邪恶的事情(对你来说是件好事偏执!)这是一个base85编码的zip文件,这个zip文件包含pip的完整副本(版本22.3.1)。pip是一个安装包的东西,pip本身就是一个包可能想要安装,特别是如果他们想要运行这个get-pip.py脚本。Pip有很多代码来处理安装的安全性包,各种平台上的各种边缘情况,等等“部落知识”已被编码在其代码库中。正因为如此我们基本上在这个blob中包含了PIP的完整副本。我们这样做因为替代方案是试图实现一个“小程序”,可能不能正确地做事情,并且有奇怪的边缘情况,或者压缩pip本身分解成一个文件。如果你想知道这是如何创建的,它是使用https://github.com/pypa/get-pip中的' scripts/generate.py '打开cmd,找到get-pip.py文件的路径 ,然后输入python get-pip.py,敲回车就开始安装
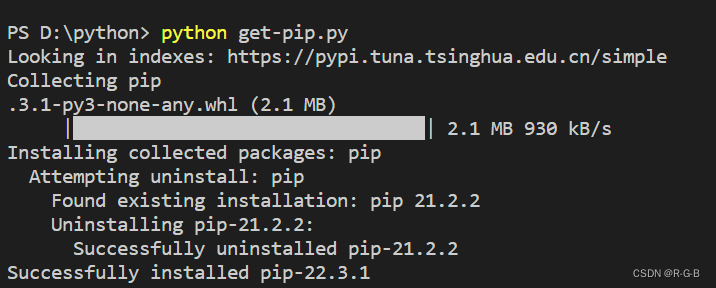
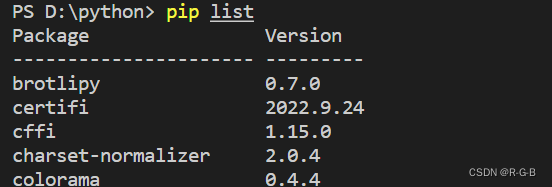
4、安装完成后,可以在cmd中输入pip list测试一下,显示如下信息就是安装成功了。
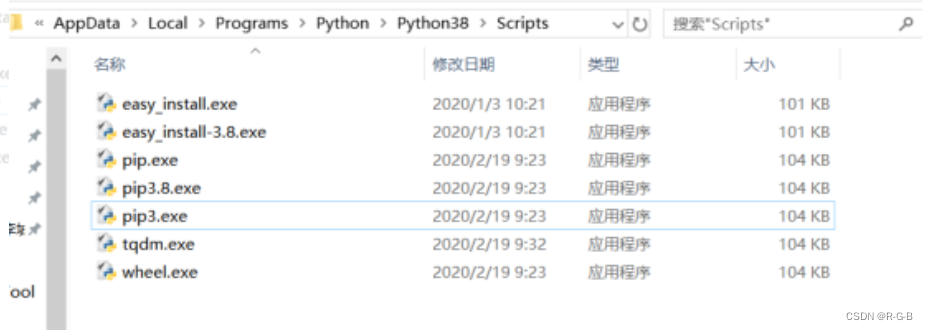
5、如果没有显示,则需要回到python的安装目录,将scripts目录加到path环境变量中,然后重启cmd
来源地址:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_51233386/article/details/128465906
免责声明:
① 本站未注明“稿件来源”的信息均来自网络整理。其文字、图片和音视频稿件的所属权归原作者所有。本站收集整理出于非商业性的教育和科研之目的,并不意味着本站赞同其观点或证实其内容的真实性。仅作为临时的测试数据,供内部测试之用。本站并未授权任何人以任何方式主动获取本站任何信息。
② 本站未注明“稿件来源”的临时测试数据将在测试完成后最终做删除处理。有问题或投稿请发送至: 邮箱/279061341@qq.com QQ/279061341

















