Python人工智能实战之以图搜图怎么实现
短信预约 -IT技能 免费直播动态提醒
本篇内容介绍了“Python人工智能实战之以图搜图怎么实现”的有关知识,在实际案例的操作过程中,不少人都会遇到这样的困境,接下来就让小编带领大家学习一下如何处理这些情况吧!希望大家仔细阅读,能够学有所成!
一、实验要求
给出一张图像后,在整个数据集中(至少100个样本)找到与这张图像相似的图像(至少5张),并把图像有顺序的展示。
二、环境配置
解释器:python3.10
编译器:Pycharm
必用配置包:
numpy、h6py、matplotlib、keras、pillow
三、代码文件
1、vgg.py
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-import numpy as npfrom numpy import linalg as LA from keras.applications.vgg16 import VGG16from keras.preprocessing import imagefrom keras.applications.vgg16 import preprocess_input as preprocess_input_vggclass VGGNet: def __init__(self): self.input_shape = (224, 224, 3) self.weight = 'imagenet' self.pooling = 'max' self.model_vgg = VGG16(weights = self.weight, input_shape = (self.input_shape[0], self.input_shape[1], self.input_shape[2]), pooling = self.pooling, include_top = False) self.model_vgg.predict(np.zeros((1, 224, 224 , 3))) #提取vgg16最后一层卷积特征 def vgg_extract_feat(self, img_path): img = image.load_img(img_path, target_size=(self.input_shape[0], self.input_shape[1])) img = image.img_to_array(img) img = np.expand_dims(img, axis=0) img = preprocess_input_vgg(img) feat = self.model_vgg.predict(img) # print(feat.shape) norm_feat = feat[0]/LA.norm(feat[0]) return norm_feat2、index.py
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-import osimport h6pyimport numpy as npimport argparsefrom vgg import VGGNet def get_imlist(path): return [os.path.join(path, f) for f in os.listdir(path) if f.endswith('.jpg')] if __name__ == "__main__": database = r'D:\pythonProject5\flower_roses' index = 'vgg_featureCNN.h6' img_list = get_imlist(database) print(" feature extraction starts") feats = [] names = [] model = VGGNet() for i, img_path in enumerate(img_list): norm_feat = model.vgg_extract_feat(img_path) # 修改此处改变提取特征的网络 img_name = os.path.split(img_path)[1] feats.append(norm_feat) names.append(img_name) print("extracting feature from image No. %d , %d images in total" % ((i + 1), len(img_list))) feats = np.array(feats) output = index print(" writing feature extraction results ...") h6f = h6py.File(output, 'w') h6f.create_dataset('dataset_1', data=feats) # h6f.create_dataset('dataset_2', data = names) h6f.create_dataset('dataset_2', data=np.string_(names)) h6f.close()3、test.py
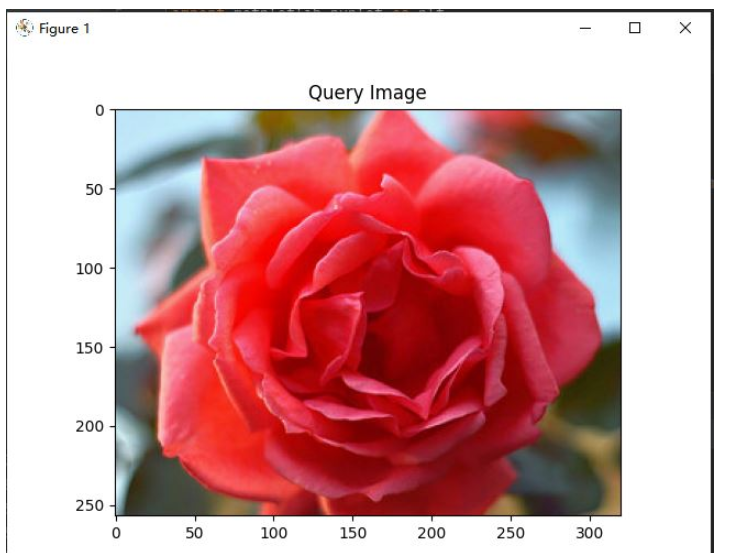
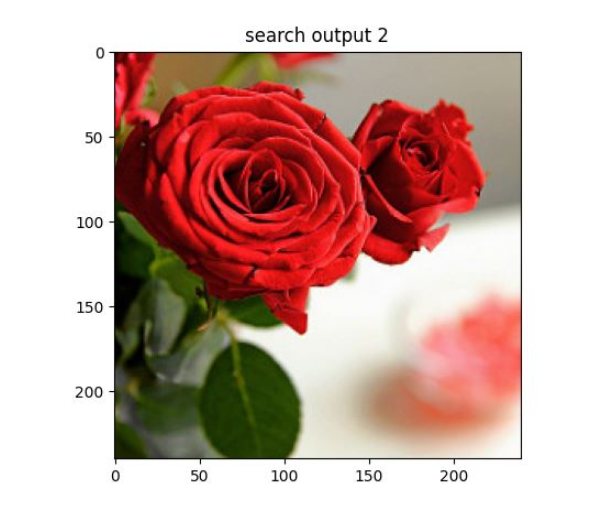
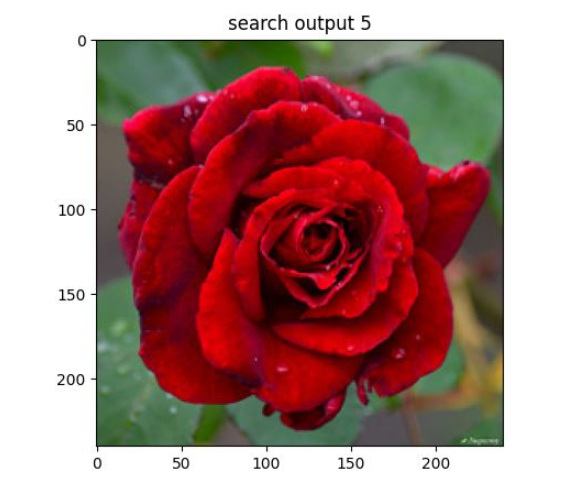
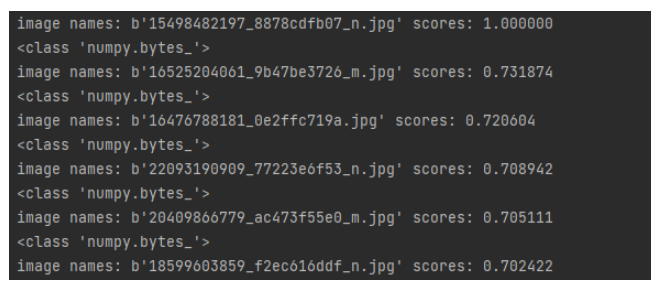
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-from vgg import VGGNetimport numpy as npimport h6pyimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltimport matplotlib.image as mpimgimport argparse query = r'D:\pythonProject5\rose\red_rose.jpg'index = 'vgg_featureCNN.h6'result = r'D:\pythonProject5\flower_roses'# read in indexed images' feature vectors and corresponding image namesh6f = h6py.File(index, 'r')# feats = h6f['dataset_1'][:]feats = h6f['dataset_1'][:]print(feats)imgNames = h6f['dataset_2'][:]print(imgNames)h6f.close()print(" searching starts")queryImg = mpimg.imread(query)plt.title("Query Image")plt.imshow(queryImg)plt.show() # init VGGNet16 modelmodel = VGGNet()# extract query image's feature, compute simlarity score and sortqueryVec = model.vgg_extract_feat(query) # 修改此处改变提取特征的网络print(queryVec.shape)print(feats.shape)scores = np.dot(queryVec, feats.T)rank_ID = np.argsort(scores)[::-1]rank_score = scores[rank_ID]# print (rank_ID)print(rank_score)# number of top retrieved images to showmaxres = 6 # 检索出6张相似度最高的图片imlist = []for i, index in enumerate(rank_ID[0:maxres]): imlist.append(imgNames[index]) print(type(imgNames[index])) print("image names: " + str(imgNames[index]) + " scores: %f" % rank_score[i])print("top %d images in order are: " % maxres, imlist)# show top #maxres retrieved result one by onefor i, im in enumerate(imlist): image = mpimg.imread(result + "/" + str(im, 'utf-8')) plt.title("search output %d" % (i + 1)) plt.imshow(np.uint8(image)) f = plt.gcf() # 获取当前图像 f.savefig(r'D:\pythonProject5\result\{}.jpg'.format(i),dpi=100) #f.clear() # 释放内存 plt.show()四、演示
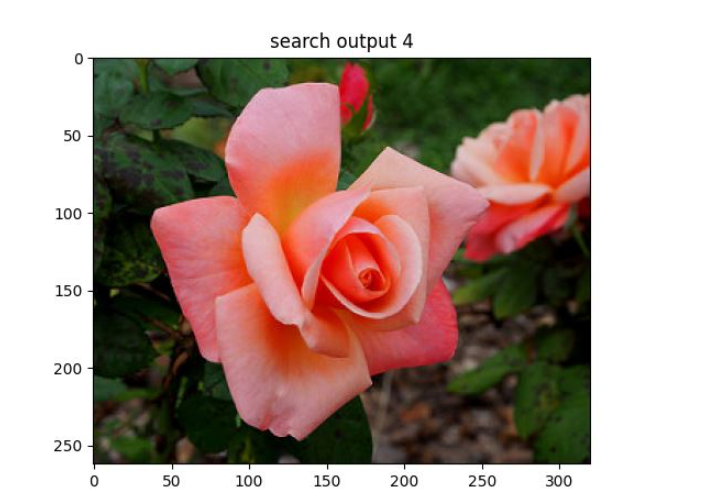

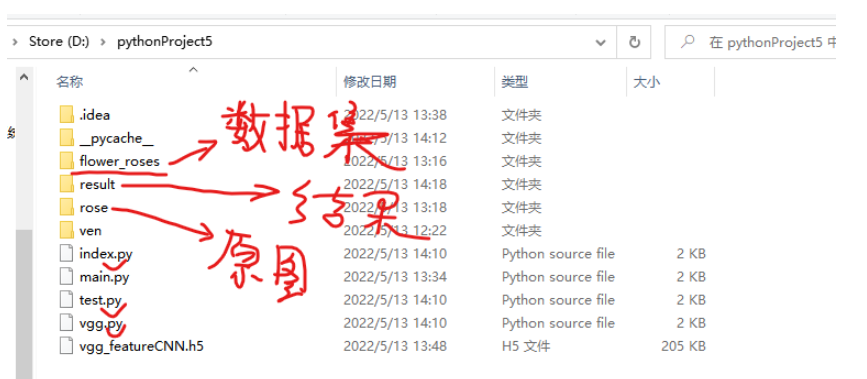
1、项目文件夹
数据集
结果(运行前)
原图
2、相似度排序输出
3、保存结果
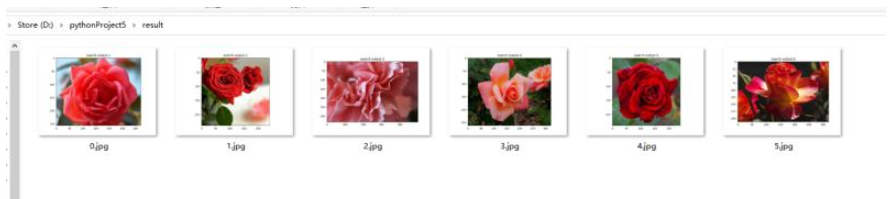
五、尾声
分享一个实用又简单的爬虫代码,搜图顶呱呱!
import osimport timeimport requestsimport redef imgdata_set(save_path,word,epoch): q=0 #停止爬取图片条件 a=0 #图片名称 while(True): time.sleep(1) url="https://image.baidu.com/search/flip?tn=baiduimage&ie=utf-8&word={}&pn={}&ct=&ic=0&lm=-1&width=0&height=0".format(word,q) #word=需要搜索的名字 headers={ 'User-Agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/88.0.4324.96 Safari/537.36 Edg/88.0.705.56' } response=requests.get(url,headers=headers) # print(response.request.headers) html=response.text # print(html) urls=re.findall('"objURL":"(.*?)"',html) # print(urls) for url in urls: print(a) #图片的名字 response = requests.get(url, headers=headers) image=response.content with open(os.path.join(save_path,"{}.jpg".format(a)),'wb') as f: f.write(image) a=a+1 q=q+20 if (q/20)>=int(epoch): breakif __name__=="__main__": save_path = input('你想保存的路径:') word = input('你想要下载什么图片?请输入:') epoch = input('你想要下载几轮图片?请输入(一轮为60张左右图片):') # 需要迭代几次图片 imgdata_set(save_path, word, epoch)“Python人工智能实战之以图搜图怎么实现”的内容就介绍到这里了,感谢大家的阅读。如果想了解更多行业相关的知识可以关注编程网网站,小编将为大家输出更多高质量的实用文章!
免责声明:
① 本站未注明“稿件来源”的信息均来自网络整理。其文字、图片和音视频稿件的所属权归原作者所有。本站收集整理出于非商业性的教育和科研之目的,并不意味着本站赞同其观点或证实其内容的真实性。仅作为临时的测试数据,供内部测试之用。本站并未授权任何人以任何方式主动获取本站任何信息。
② 本站未注明“稿件来源”的临时测试数据将在测试完成后最终做删除处理。有问题或投稿请发送至: 邮箱/279061341@qq.com QQ/279061341
















